Last Updated on 6 months by Francis
Bees, those tiny buzzing creatures that play a crucial role in pollination, have a fascinating ability that sets them apart from humans – their vision. While humans see the world in a range of colors from red to violet, bees see the world in a whole different way. They can perceive colors that are invisible to us, including ultraviolet light and even infrared light. But can bees see infrared light? Let’s delve into the incredible world of bees’ vision and find out.
Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Bees have a unique visual perception that allows them to see colors, including ultraviolet light and possibly even infrared light.
- Unlike humans, bees can’t see the color red, but they can see ultraviolet colors that are invisible to us.
- Bees’ vision is optimized for finding flowers, detecting nectar and pollen, and ensuring successful pollination.
- Understanding bees’ vision helps us appreciate their important role as pollinators and the significance of conserving their habitats.
- Bees’ ability to see ultraviolet light and distinguish visual cues is crucial for the reproduction of flowering plants and agricultural productivity.
The Science Behind Bee Vision

Bee vision is a fascinating subject that has intrigued researchers for years. Through behavior experiments, scientists have gained valuable insights into the visual capabilities of bees. These experiments involve training bees to respond to specific colors by associating them with food sources. By studying the photoreceptors in bee eyes, researchers have determined the specific wavelengths of light that bees can see. This research has shed light on how bees perceive their colorful world.
Bees have photoreceptors in their eyes that allow them to detect different colors, including ultraviolet (UV), blue, and green. These photoreceptors are specialized cells that respond to specific wavelengths of light. The range of color vision for bees extends from approximately 300 to 650 nanometers (nm), which includes UV, blue, and green light. In comparison, human color vision ranges from approximately 400 to 700 nm, missing out on the UV spectrum that bees can see.
The ability of bees to see in UV light has significant implications for their foraging behavior. Many flowers have evolved ultraviolet color patterns that are invisible to humans but are highly visible to bees. These patterns serve as landing zones, guiding bees to the nectar and pollen-rich parts of the flower. By being able to detect UV light, bees can efficiently locate and collect the resources they need to survive.
Understanding the science behind bee vision not only expands our knowledge of these remarkable creatures but also highlights the intricate relationship between bees and flowers. The ability of bees to perceive and respond to different wavelengths of light plays a vital role in their role as pollinators, ensuring the reproduction of flowering plants and the abundance of ecosystems.
The Wavelength Ranges of Human and Bee Vision:
| Humans | Bees |
|---|---|
| Visible Spectrum: Approximately 400-700 nm | Visible Spectrum: Approximately 300-650 nm |
| See Red, Green, Blue | See Ultraviolet, Blue, Green |
| Cannot See Ultraviolet | Can See Ultraviolet |
The Importance of Ultraviolet Light for Bees
Bees have the remarkable ability to detect ultraviolet light, which plays a crucial role in their foraging and pollination activities. Many flowers have evolved unique ultraviolet color patterns that are invisible to humans but stand out to bees. These patterns act as landing zones, guiding bees to the part of the flower that contains nectar and pollen. Without the ability to see ultraviolet light, bees would struggle to locate and access these essential food sources.
Ultraviolet vision is vital for bees as it enables them to efficiently locate and collect nectar. By detecting the specific ultraviolet patterns of flowers, bees can identify the presence of nectar guides, which are visual cues that lead them to the nectar-rich areas of the flower. This ability allows bees to navigate through complex floral landscapes and optimize their foraging efforts.
The importance of ultraviolet light for bees extends beyond their individual survival. Bees play a critical role in the pollination process, transferring pollen from one flower to another, which is essential for the reproduction of flowering plants. The ability to see ultraviolet light allows bees to accurately identify and recognize flowers, enabling them to make effective pollination visits. Without bees’ vision of ultraviolet patterns, the pollination process would be compromised, impacting the diversity and abundance of plant species.
| Benefits of Bees’ Ultraviolet Vision | Impact on Ecosystems and Agriculture |
|---|---|
| Efficient location of nectar and pollen sources | Key role in pollination of crops and wildflowers |
| Ability to navigate through complex floral landscapes | Contribution to food production and biodiversity |
| Precise identification of visual cues, such as nectar guides | Estimated economic value worth billions of dollars |
The ultraviolet vision of bees is a remarkable adaptation that allows them to thrive in their colorful world. Understanding and appreciating the importance of ultraviolet light for bees can help us recognize the significance of their role as pollinators and inspire efforts to protect and conserve these vital creatures.
Comparing Human and Bee Vision

Humans and bees perceive the world in different colors due to the variations in their visual systems. While humans have a wide range of color vision from red to violet, bees’ color vision extends from orange to ultraviolet light. Bees have photoreceptors that are sensitive to ultraviolet, blue, and green light, whereas humans have photoreceptors for red, blue, and green light. The wavelength range of human vision is approximately 400 to 700 nm, while the range for bee vision is around 300 to 650 nm.
This difference in color perception means that bees can see ultraviolet patterns and colors that are invisible to humans. These ultraviolet patterns play a vital role in guiding bees to flowers and their nectar sources. For example, many flowers have ultraviolet color patterns called nectar guides, which are like landing zones for bees. These guides direct the bees to the part of the flower where the nectar is located. While these patterns are invisible to humans, bees can easily detect and follow them.
Bees’ ability to see ultraviolet light and perceive colors outside of the human visual spectrum gives them a unique advantage in their foraging and pollination activities. They can efficiently locate and collect nectar from flowers that have evolved to attract them with distinctive ultraviolet color patterns. This specialization in bee vision ensures that they can navigate their environment, find food sources, and carry out their vital role as pollinators in the ecosystem.
Visual Comparison: Human and Bee Vision
To further illustrate the differences between human and bee vision, we can compare the visible color ranges of both species. The table below shows the approximate color ranges for human and bee vision:
| Species | Color Range |
|---|---|
| Humans | Red to Violet (400 to 700 nm) |
| Bees | Orange to Ultraviolet (300 to 650 nm) |
As seen in the table, bees’ visual spectrum includes ultraviolet light, which is beyond human perception. This expanded color range gives bees a unique ability to detect and differentiate ultraviolet patterns, enabling them to navigate their environment and find essential resources such as nectar and pollen.
“Bees’ ability to see ultraviolet light allows them to perceive patterns and colors that are invisible to humans.”
The Advantages of Bee Vision

Bee vision provides several advantages for these incredible pollinators. Their ability to see ultraviolet light allows them to perceive unique patterns and colors that are invisible to humans. This specialized vision helps bees in various aspects of their lives, from finding flowers to navigating and judging distances while flying.
One of the key advantages of bee vision is their ability to see nectar guides. These patterns on flowers guide bees to the nectar source, acting as beacons to attract them. Nectar guides are often invisible to humans but are clearly visible to bees with their ultraviolet perception. This ability ensures that bees efficiently locate and collect nectar, supporting their energy needs and the pollination process.
Bee vision also plays a crucial role in their foraging behavior. Bees can see individual flowers even when moving at high speeds, thanks to their ability to detect moving objects. This allows them to quickly identify potential food sources and efficiently gather nectar and pollen. Their visual acuity and perception of edges and contrasts help them distinguish between flowers and select the ones that offer the best rewards.
| Advantages of Bee Vision | Examples |
|---|---|
| Bee ability to see ultraviolet light | Allows them to perceive nectar guides on flowers, guiding them to the nectar source |
| Detecting moving objects | Enables bees to locate individual flowers while moving at high speeds |
| Visual acuity and contrast perception | Helps bees distinguish between flowers and select the ones with the best rewards |
Overall, bee vision is optimized for their role as pollinators and contributes to the successful reproduction of flowering plants. Their ability to see ultraviolet light, detect nectar guides, and navigate their environment with precision ensures the efficient transfer of pollen and the diversity and abundance of plant species. Understanding the advantages of bee vision highlights the importance of protecting and conserving these incredible creatures and their unique visual abilities.
Bees’ Incredible Eye Structure
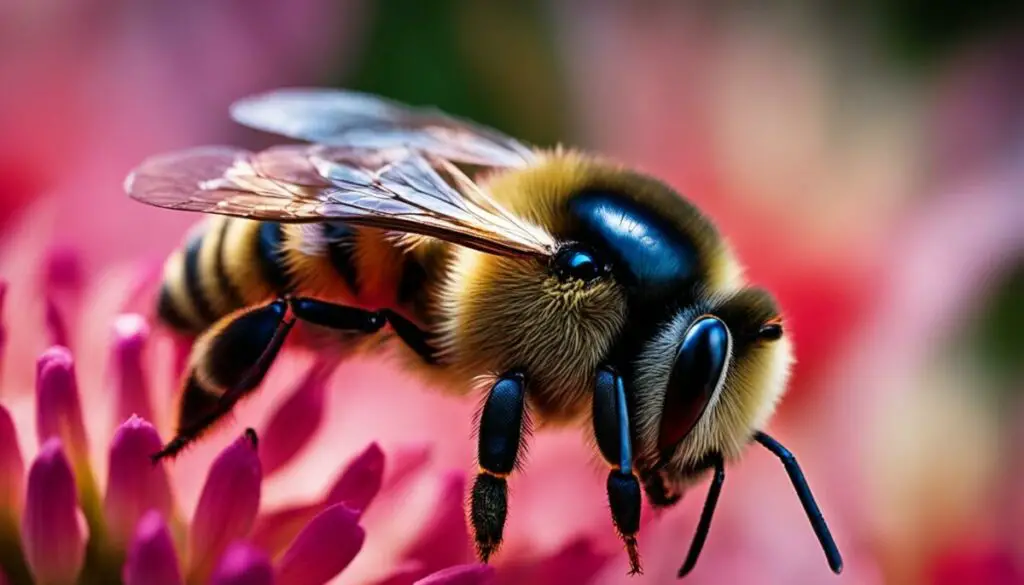

Bees have an amazing eye structure that contributes to their remarkable vision. They have two types of eyes: compound eyes and ocelli. Compound eyes are composed of thousands of tiny lenses called facets, each connected to a photoreceptor unit called an ommatidium. This unique structure provides bees with a wide field of vision and allows them to see in a mosaic-like manner, enabling them to detect movement and discern shapes effectively.
On the top of a bee’s head, they also have three smaller eyes called ocelli. These ocelli play a crucial role in helping bees maintain stability, navigate, and detect ultraviolet light. With their combined compound eyes and ocelli, bees possess the ability to perceive the world in a way that is vastly different from humans.
Understanding the intricate eye structure of bees helps us appreciate their visual capabilities, which play a significant role in their survival and their crucial role as pollinators. It is through their remarkable vision that bees are able to efficiently locate flowers, navigate their surroundings, and contribute to the pollination process.
The Structure of Bee Eyes
Compound Eyes:
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Lenses (Facets) | Thousands of tiny lenses that make up the compound eyes, each connected to an ommatidium |
| Ommatidium | Photoreceptor unit that detects light and transmits information to the bee’s brain |
| Wide Field of Vision | Compound eyes provide bees with a wide field of vision, allowing them to see in many directions simultaneously |
Ocelli:
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Three Smaller Eyes | Located on the top of a bee’s head |
| Stability and Navigation | Ocelli help bees maintain stability and navigate their surroundings |
| Ultraviolet Detection | Ocelli assist bees in detecting ultraviolet light, which is crucial for finding flowers and nectar sources |
Bees’ Vision and Pollination
Bees’ vision is a vital component of their role as pollinators. Their ability to see and distinguish specific visual cues allows them to locate flowers and navigate their environment with precision. Flowers have evolved to have distinct colors, patterns, and ultraviolet markers that attract bees and guide them to the nectar and pollen. This visual communication between flowers and bees ensures successful pollination, which is crucial for the reproduction of flowering plants.
Bees’ extraordinary vision also enables them to efficiently forage for nectar and pollen. They can detect and follow nectar guides, which are patterns on flowers that indicate the location of the nectar source. These guides are often invisible to the human eye but clearly visible to bees, thanks to their ability to see ultraviolet light. By following these guides, bees can quickly and accurately locate the precious resources they need for sustenance.
The relationship between bees’ vision and pollination goes beyond individual flowers. Bees play a significant role in maintaining the diversity and abundance of plant species, which in turn supports entire ecosystems. The efficient and precise pollination performed by bees ensures the successful reproduction of various plants, including important agricultural crops. Without bees’ ability to see and interpret visual cues, the pollination process would be less effective, leading to decreased biodiversity and a negative impact on food production.
The Significance of Bee Vision for Ecology and Agriculture
Bee vision plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and sustaining agricultural productivity. As key pollinators for various crops and wildflowers, bees rely on their unique ability to see ultraviolet light to locate flowers and navigate their environment. This remarkable vision allows bees to efficiently collect nectar and pollen, contributing significantly to food production.
Without bees’ ability to detect nectar guides and perceive ultraviolet color patterns, the pollination process of many plant species would be compromised. These visual cues, invisible to humans but visible to bees, guide them towards the reproductive parts of flowers, promoting successful pollination. By facilitating the transfer of pollen, bees ensure the diversity and abundance of plant species.
Not only are bees essential for maintaining biodiversity, but they also have a significant economic impact. The role of bees in pollination is estimated to be worth billions of dollars in the United States alone. Their work translates into increased yield and quality of crops, benefiting farmers, consumers, and the agricultural industry as a whole.
Conserving and protecting bees and their incredible vision is of utmost importance. By preserving their habitats, reducing pesticide use, and promoting sustainable farming practices, we can ensure that bees continue to thrive and fulfill their vital ecological and agricultural role. Recognizing the significance of bee vision highlights the interconnectedness of all species and the importance of safeguarding our natural world.
| Benefit | Importance |
|---|---|
| Pollination | Ensures reproduction of flowering plants |
| Food Production | Contributes significantly to agricultural productivity |
| Economic Value | Estimated to be worth billions of dollars |
| Biodiversity | Maintains healthy ecosystems and supports plant diversity |
Quote:
“Bees’ ability to see ultraviolet light and navigate their environment is essential for successful pollination and the reproduction of flowering plants.” – Bee Conservation Society
Conclusion
Bees have an extraordinary ability to perceive the world around them through their unique vision. They can see colors that are invisible to humans, including ultraviolet light. This special vision allows bees to find flowers, detect nectar and pollen, and navigate their environment with precision. By understanding and appreciating the incredible sight of bees, we can better protect and conserve these vital creatures and the natural systems they contribute to.
Bees’ vision is crucial for their role as pollinators, ensuring the reproduction of flowering plants. Without bees’ ability to see ultraviolet light and perceive visual cues, the pollination process would be less efficient, impacting the diversity and abundance of plant species. Additionally, bees play a significant role in ecosystems and agriculture, contributing to food production and sustaining healthy environments. Preserving their vision is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of our natural world.
In conclusion, bees’ ability to see infrared light and their remarkable perception of colors are what make them such remarkable creatures. Their colorful world is a testament to their visual prowess, and understanding their unique vision can help us protect and conserve these important insects. So, the next time you encounter a bee buzzing around a flower, take a moment to marvel at their incredible sight and appreciate the vital role they play in our ecosystem.
FAQ
Can bees see colors that humans can’t?
Yes, bees can see ultraviolet colors that are invisible to humans.
What colors can bees see?
Bees can see a range of colors, including ultraviolet, blue, and green, but they cannot see red.
Why is ultraviolet light important for bees?
Ultraviolet light helps bees locate nectar sources on flowers and is crucial for the pollination process.
Bees use their vision to detect moving objects and can see individual flowers even when moving at high speeds.
What is the difference between human and bee vision?
Humans see a wider range of colors, while bees see ultraviolet, blue, and green light.
How do bees’ compound eyes and ocelli contribute to their vision?
Bees’ compound eyes provide them with a wide field of vision, and their ocelli help them detect ultraviolet light and maintain stability.
Why is bee vision important for pollination?
Bee vision allows them to locate and distinguish flowers, ensuring successful pollination and the reproduction of flowering plants.
What role do bees play in ecosystems and agriculture?
Bees are crucial pollinators for various crops and wildflowers, contributing significantly to food production and ecosystem health.
How can we protect and conserve bees and their vision?
Protecting and conserving bees’ habitats and promoting pesticide-free practices can help maintain the health of bee populations and their vision.