Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
RNA is an essential component of genetic information, but it is a complex molecule that can be difficult to understand. In this article, we will explore the charge of RNA and how it affects its structure and function. We will also look at how it interacts with other molecules and how it is used in the process of gene expression. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of what charge is and why it is important to the world of genetics.
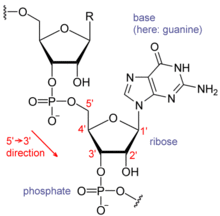
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. It is an essential molecule found in all living cells and plays a vital role in the production of proteins, which are the building blocks of life. RNA is composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone and four nitrogenous bases – adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil. RNA is single stranded, unlike its double-stranded counterpart, DNA. RNA is also more reactive and less stable than DNA, and is involved in many cellular processes, including gene expression, protein synthesis and regulation of the cell cycle.
Contents
What is the Charge of RNA?
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is an important molecule that plays a major role in the assembly of proteins and the transmission of genetic information from DNA. It is also a key component in many biological processes, including transcription, translation, and replication. RNA molecules are composed of several components, including a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous base and the sugar form a nucleotide, and the phosphates help to form the backbone of the molecule. In addition to these components, RNA molecules also have a charge associated with them. In this article, we will discuss what this charge is and how it affects the RNA molecule.
The Overall Charge of RNA
The overall charge of an RNA molecule depends on the type of nitrogenous base it contains. The four types of nitrogenous bases found in RNA molecules are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U). These bases have different charges associated with them. Adenine and guanine have a positive charge, while cytosine and uracil have a negative charge. The overall charge of the molecule is determined by the number of each type of base it contains and their respective charges. For example, if an RNA molecule contains equal amounts of adenine and guanine, the overall charge of the molecule would be neutral.
How the Charge of RNA Affects Its Structure
The charge of an RNA molecule can have an effect on its structure and function. The charge of an RNA molecule can affect its ability to bind to other molecules, and can also affect how it interacts with enzymes. For example, the positively charged adenine and guanine bases can bind to negatively charged molecules, such as tRNA or other RNA molecules. This binding can help stabilize the molecule and make it more resistant to degradation.
The Role of pH in RNA Charge
The charge of an RNA molecule can also be affected by the pH of its environment. At a lower pH, the positively charged adenine and guanine bases will be more positively charged, while the negatively charged cytosine and uracil bases will be more negatively charged. This can affect the structure of the molecule and its ability to bind to other molecules. At a higher pH, the charges of the nitrogenous bases will be more neutral, and the molecule will be more susceptible to binding.
How RNA Charge Affects Its Function
The charge of an RNA molecule can also affect its function. RNA molecules are involved in a variety of biological processes, such as transcription, translation, and replication. In order for these processes to occur, the charge of the molecule must be appropriate for the task. For example, the positively charged adenine and guanine bases are necessary for the transcription and translation of genetic information. The negatively charged cytosine and uracil bases are important for the replication of DNA.
The Role of Electrostatic Interactions in RNA Charge
The charge of an RNA molecule can also be affected by electrostatic interactions. Electrostatic interactions are the attractions and repulsions between charged particles. These interactions can affect the structure of the molecule and its ability to bind to other molecules. For example, positively charged adenine and guanine bases can bind to negatively charged molecules, such as tRNA or other RNA molecules. This binding can help stabilize the molecule and make it more resistant to degradation.
The Role of Hydrogen Bonds in RNA Charge
The charge of an RNA molecule can also be affected by hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are the attractions between molecules that contain hydrogen atoms. These bonds can affect the structure of the molecule and its ability to bind to other molecules. For example, the negatively charged cytosine and uracil bases can form hydrogen bonds with the positively charged adenine and guanine bases. This can help stabilize the molecule and make it more resistant to degradation.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is RNA?
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. It is a type of nucleic acid that assists in the process of gene expression and helps to produce proteins, and is essential for all known forms of life. RNA is composed of a single strand of nucleotides and is similar to DNA in structure and function.
What are the Different Types of RNA?
There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA is responsible for the transmission of genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, the site of protein synthesis. tRNA is responsible for carrying amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Finally, rRNA is responsible for the assembly of proteins on the ribosome.
What Charge is RNA?
RNA is a negatively charged molecule due to the presence of phosphate groups attached to the nucleotides. This negative charge is important for the interactions between the various components of the RNA molecule, such as the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides and base pairing between complementary nucleotides.
What is the Role of RNA in Gene Expression?
RNA plays a major role in gene expression, which is the process of turning genes into proteins. This process begins with the transcription of DNA into mRNA, which is then translated into proteins by the ribosome. This process is essential for all known forms of life, as it allows for the production of proteins to carry out cellular processes.
What are the Physical Properties of RNA?
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that is composed of nucleotides. The nucleotides are composed of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds, and the whole molecule is negatively charged due to the presence of the phosphate groups.
How is RNA Synthesized?
RNA is synthesized in the nucleus by the enzyme RNA polymerase. This enzyme binds to the DNA and transcribes it into an mRNA molecule. The mRNA then exits the nucleus and is translated into proteins by the ribosomes. The ribosomes use the mRNA as a template to assemble the amino acid sequence of the protein.
RNA is a powerful and complex molecule that is crucial for life and many other biological processes. Its charge is a negative one that is essential for the formation of a variety of different structures, such as mRNA and tRNA, which enable communication between cells and transfer of genetic information. Understanding the charge of RNA is integral for gaining a thorough understanding of the biochemistry of life and unlocking the potential of this molecule for countless applications.


.jpg)
.jpg)