Near-infrared radiation, also known as NIR, is an invisible form of electromagnetic radiation that has a range of wavelengths just beyond what we can see with the naked eye. Although near-infrared radiation is not visible to us, it plays an important role in a wide range of applications from medical diagnostics to agriculture. In this article, we will explore what near-infrared radiation is and how it is used in the modern world.
Near Infrared Radiation (NIR) is a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength just larger than that of visible light. It is invisible to the human eye, but can be detected by specialized electronic equipment. NIR is used in many industries, including medical, agricultural and industrial applications. It can be used to detect changes in temperature, moisture content and other properties of materials.
Contents
What is Near Infrared Radiation (NIR)?
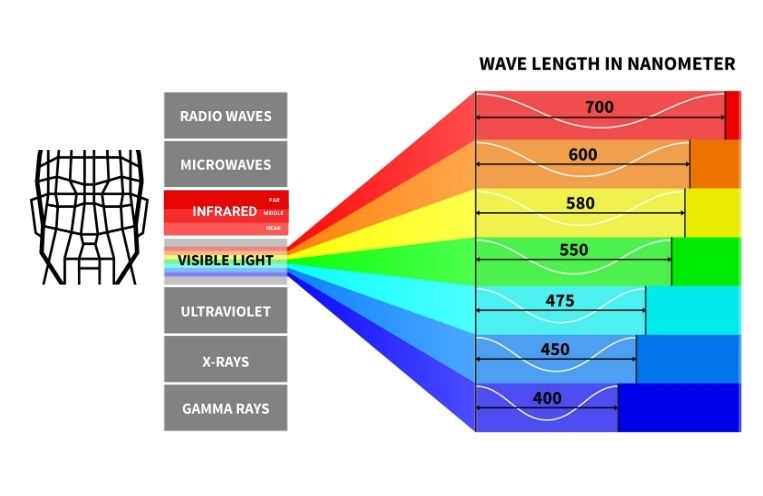
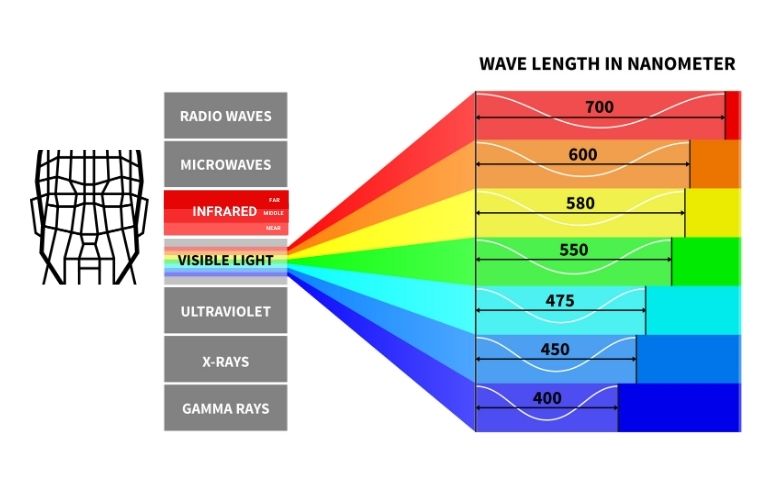
Near infrared radiation (NIR) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 700 and 1400 nanometers. NIR is invisible to the human eye, but can be detected by certain instruments. It is found in the spectrum just beyond the visible light region, making it a type of non-ionizing radiation. NIR is commonly used in industrial, commercial and medical applications due to its ability to penetrate materials, such as human tissue.
NIR is often used to measure the temperature of objects, such as in thermography, which can be used to detect heat loss in buildings. In medical applications, NIR can be used to detect tumors, measure blood flow and detect tissue damage. NIR is also used in spectroscopy and imaging, which can be used to analyze the chemical composition of compounds.
Benefits of NIR
NIR has many applications in industry and medical research, making it an important tool for scientists and engineers. NIR is non-ionizing radiation, meaning it is harmless to humans and animals, unlike X-rays and gamma rays. This makes it safer to use compared to other forms of radiation, and it is also less expensive.
NIR is also able to penetrate materials, making it ideal for imaging and analysis. It can be used to detect objects and measure their temperature, making it useful for thermal imaging. NIR is also used in spectroscopy, which can be used to analyze the chemical composition of compounds.
Uses of NIR
NIR is used in many industries, from medical research to industrial applications. In medical research, NIR can be used to detect tumors, measure blood flow and detect tissue damage. It can also be used for imaging and spectroscopy.
In industrial applications, NIR can be used to detect heat loss in buildings, as well as for imaging and spectroscopy. NIR is also used in agriculture, where it can be used to detect crop stress and assess soil quality.
Limitations of NIR
NIR has limitations, such as the fact that it cannot penetrate certain materials, such as metal and glass. It also has a limited range, meaning it cannot be used to measure objects that are too far away. Additionally, NIR is affected by water vapor and dust, which can interfere with its readings.
Safety Considerations
NIR is a form of non-ionizing radiation, meaning it is harmless to humans and animals. However, it is important to use proper safety precautions when using NIR, such as wearing protective clothing and using proper shielding. It is also important to use instruments that are designed to detect NIR, as some instruments are not designed for such purposes.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Near Infrared Radiation?
Answer: Near Infrared Radiation (NIR) is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 700 nanometers and 1 millimeter. It is invisible to the human eye, but can be detected by certain devices such as cameras and thermometers. NIR is commonly used in many applications such as medical imaging, industrial temperature measurement, and night vision.
How does Near Infrared Radiation Differ from Visible Light?
Answer: Visible light is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 380 to 700 nanometers, and is visible to the human eye. Near Infrared Radiation, on the other hand, is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 700 nanometers and 1 millimeter, and is invisible to the human eye. Due to its longer wavelength, NIR has a lower frequency and less energy than visible light.
What are the Applications of Near Infrared Radiation?
Answer: Near Infrared Radiation has a number of applications, including medical imaging, industrial temperature measurement, and night vision. NIR is used in medical imaging to detect tumors and other abnormalities, and to measure tissue thickness and other properties. In industrial temperature measurement, NIR is used to measure the temperature of objects and surfaces. Finally, NIR is also used in night vision applications, as it can be detected by certain devices such as cameras and thermometers.
What are the Benefits of Using Near Infrared Radiation?
Answer: Near Infrared Radiation has a number of benefits. One of the main benefits is its accuracy. NIR is able to detect very small changes in temperature and other properties, which is useful in applications such as medical imaging and industrial temperature measurement. NIR also has a lower frequency and less energy than visible light, meaning that it can be used in applications such as night vision, where visible light would be too bright or too dangerous.
Are there any Hazards Associated with Near Infrared Radiation?
Answer: While Near Infrared Radiation does not pose any immediate health risks, it is important to take safety precautions when using NIR in certain applications. For example, in medical imaging, it is important to ensure that the radiation levels used are not too high, as this could damage the patient’s tissue. Similarly, for industrial temperature measurement, it is important to ensure that the radiation levels are safe for workers.
What are the Limitations of Near Infrared Radiation?
Answer: One of the main limitations of NIR is its ineffectiveness at greater depths. As NIR has a lower frequency and less energy than visible light, it is not as effective at penetrating materials as visible light. This means that NIR is not suitable for applications such as night vision, where greater depths need to be penetrated. Additionally, NIR is not as effective at detecting small changes in temperature and other properties as other types of radiation, such as X-rays.
Near Infrared Light Mitigates Neuroinflammation in Mice
Near Infrared radiation is an essential and powerful tool for many industries. From medical diagnostics to environmental protection, this type of radiation has revolutionized the way we observe, analyze, and interact with the world around us. With its vast applications, the potential for further research and development is nearly limitless. By understanding the properties of Near Infrared radiation, we can continue to develop and expand its use in a multitude of ways to make our lives better.