If you have ever been curious about the intensity of gamma radiation, then you have come to the right place. Gamma radiation is one of the most powerful types of radiation, but how hot is it exactly? In this article, we will explore the heat of gamma radiation and how it is measured. We will also discuss the potential risks associated with gamma radiation exposure and the ways it can be safely handled. Read on to find out more about this fascinating and potentially dangerous form of energy.
Gamma radiation is very hot and can cause burns, hair loss, and other tissue damage. Gamma rays are the most energetic and penetrating type of radiation, able to travel through most materials and even penetrate the human body. Gamma radiation has a range of effects, from mild to severe, depending on the dose and the time exposed. Gamma radiation is also known to cause cancer.

Contents
What Is Gamma Radiation?
Gamma radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is emitted from the nucleus of an atom when it undergoes radioactive decay. Gamma radiation is the most energetic form of radiation and has a very short wavelength, making it highly penetrating. Gamma radiation is one of the three primary types of radiation, along with alpha and beta radiation. Gamma radiation is emitted in a variety of different forms, including gamma rays, X-rays, and gamma particles. Gamma rays are the most commonly known form of gamma radiation and are the most energetic and penetrating form. Gamma particles are the least energetic form of gamma radiation and are composed of either a single gamma ray or a combination of gamma rays. Gamma radiation is used in a variety of applications, including medical imaging, radiation therapy, and food irradiation. Gamma radiation can also be used to detect leaks in nuclear facilities, as well as for the detection of gamma-emitting materials.
How Is Gamma Radiation Produced?
Gamma radiation is produced by the decay of certain radioactive elements and is emitted in the form of gamma rays. When a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay, it emits gamma radiation, as well as alpha and beta radiation. Gamma radiation is the most energetic form of radiation, with a very short wavelength and high penetrating power. Gamma radiation is also produced naturally in the atmosphere by cosmic rays. Cosmic rays are high energy particles, primarily protons and alpha particles, that originate outside the solar system. When these particles interact with the upper atmosphere, they produce gamma radiation, which can then reach the Earth’s surface.
What Are the Effects of Gamma Radiation?
Exposure to high levels of gamma radiation can be dangerous and can lead to a variety of health effects, such as skin burns, cataracts, and even death. Gamma radiation can also cause genetic mutation and damage to cells, which can lead to cancer. Gamma radiation is also associated with a number of other health effects, such as headaches, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Long-term exposure to gamma radiation can also lead to an increased risk of developing cancer, as well as other serious health problems.
How Hot Is Gamma Radiation?
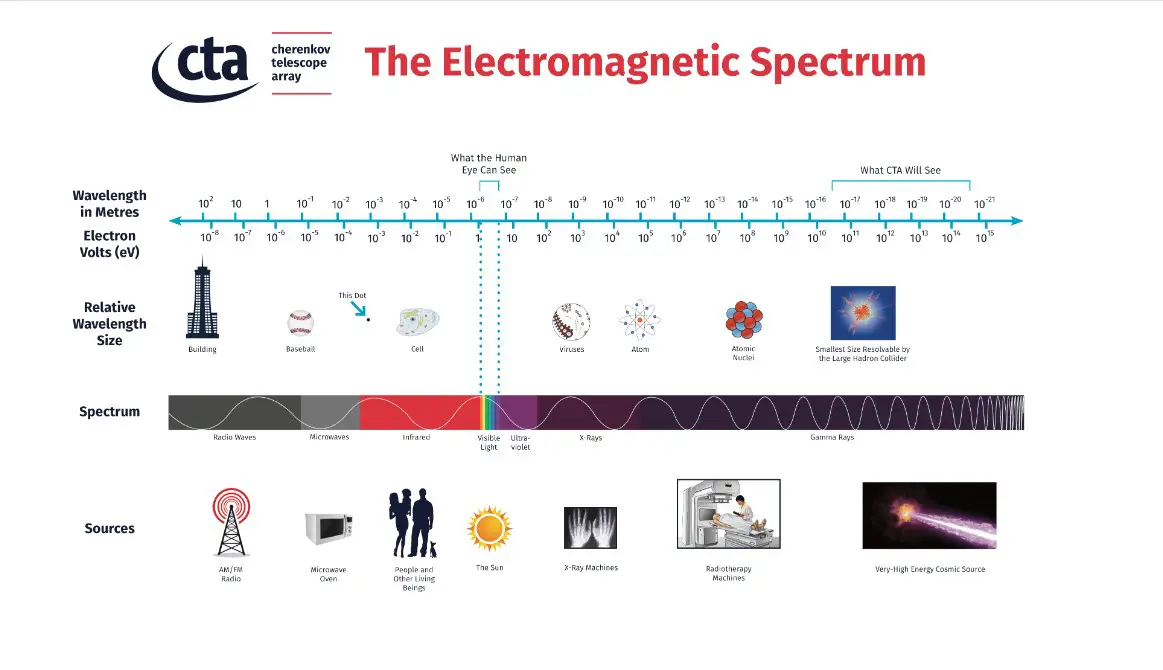
Gamma radiation is one of the most energetic forms of electromagnetic radiation, with a very short wavelength and high penetrating power. The energy of gamma radiation is measured in electron volts (eV), which is a unit of energy. Gamma radiation typically has an energy of between 10^-14 and 10^-6 eV, making it one of the hottest forms of radiation. Gamma radiation is also one of the most dangerous forms of radiation, as it is highly penetrating and can cause serious health effects, such as cancer and genetic mutation, when exposed to at high levels.
How Is Gamma Radiation Measured?
Gamma radiation is typically measured in units of absorbed dose, which is a measure of the energy absorbed by a material when exposed to gamma radiation. The most commonly used unit of absorbed dose is the gray (Gy), which is equal to one joule of energy absorbed per kilogram of material. Gamma radiation can also be measured in units of exposure, which is a measure of the amount of gamma radiation that passes through a material. The most commonly used unit of exposure is the roentgen (R), which is equal to one coulomb of gamma radiation passing through one kilogram of material.
How Is Gamma Radiation Used?
Gamma radiation is used in a variety of applications, including medical imaging, radiation therapy, food irradiation, and the detection of gamma-emitting materials. Gamma radiation is also used in the nuclear industry for the detection of leaks and the monitoring of radiation levels. Gamma radiation is also used in the space industry for the detection of cosmic rays. Gamma radiation is highly penetrating and can be used to detect cosmic rays, which are high energy particles that originate outside the solar system.
What Are the Safety Precautions for Working with Gamma Radiation?
Working with gamma radiation requires special safety precautions, as gamma radiation can be dangerous when exposed to at high levels. Protective clothing, such as lead aprons, should always be worn when working with gamma radiation. In addition, the area should be monitored for radiation levels, and personnel should be regularly monitored for radiation exposure. Special shielding, such as lead or concrete, should also be used to reduce the risk of exposure to gamma radiation.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Gamma Radiation?
Gamma radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation, similar to x-rays and visible light. It is produced by the decay of atomic nuclei, and has a very short wavelength, ranging from about 0.1 to 10 nanometers. Gamma radiation is the highest energy form of electromagnetic radiation and has a high penetrating power, meaning it can pass through many materials.
What Are the Effects of Gamma Radiation?
Gamma radiation can be dangerous to living organisms, as it has the ability to damage cells and DNA. This can lead to the development of cancer, as well as other health problems, such as cataracts and skin burns. Long-term exposure to gamma radiation can also cause genetic mutations, which can be passed on to future generations.
How Hot Is Gamma Radiation?
Gamma radiation is not actually hot, but rather a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Gamma radiation has a high penetrating power, meaning it can pass through most materials, and its energy is measured in electron volts (eV). The energy of gamma radiation ranges from about 0.1 to 10 MeV, with the highest energies being around 10 MeV.
What Types of Sources Produce Gamma Radiation?
Gamma radiation is produced by the decay of unstable atomic nuclei, such as those in radioactive materials or nuclear reactors. It can also be produced by high-energy particle accelerators and other radioactive sources.
What Is Gamma Radiation Used For?
Gamma radiation is used for a variety of purposes, such as medical imaging and cancer treatment. It is also used in industrial processes, such as sterilization of food and medical equipment. Gamma radiation is used in research and development, for example in the study of atomic energy and nuclear physics.
What Are Some Safety Precautions for Handling Gamma Radiation?
When working with gamma radiation, it is important to take safety precautions to protect both people and the environment. The use of protective equipment such as lead aprons and gloves is recommended when handling gamma radiation sources. It is also important to keep gamma radiation sources away from populated areas and to properly dispose of any materials contaminated with gamma radiation.
NASA | What Are Gamma Rays?
In conclusion, gamma radiation is a powerful form of radiation that can be extremely dangerous. It is highly energetic, and can have devastating effects on biological systems. It is important to take the necessary precautions and safety measures when dealing with gamma radiation since the consequences can be severe. Despite the dangers, gamma radiation can be a useful tool when used properly and with the necessary safety precautions in place.


.jpg)