Last Updated on 5 months by Francis
Welcome to our exploration of infrared camera technology and its ability to detect infrared light. Have you ever wondered if cameras can see what is invisible to the human eye? In this article, we will delve into the world of infrared light and how it can be detected and captured by specialized cameras. Whether you’re curious about the science behind it or interested in the practical applications, we’ve got you covered. So, let’s dive in and uncover the fascinating world of infrared camera technology!
Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Cameras can be modified to see infrared light by hacking the webcam or using infrared filters.
- Infrared light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is not visible to the human eye.
- Infrared cameras use different image sensors, such as CCD or CMOS, to detect infrared light.
- Infrared camera technology is used in various applications, including surveillance, night vision, and thermal imaging.
- Exploring infrared camera technology expands our understanding of the world around us.
Understanding Infrared Light

Infrared light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that exists beyond the range of visible light. While the human eye can detect wavelengths from 400 to 700 nanometers, infrared light has longer wavelengths ranging from 700 nanometers to 15,000 nanometers. This means that infrared light falls outside the range of what we can see, but it can be detected and utilized by specialized cameras and sensors.
Within the electromagnetic spectrum, infrared light sits between visible light and microwaves. It is commonly divided into three categories: near-infrared, mid-infrared, and far-infrared. Near-infrared has shorter wavelengths and is closest to the visible light spectrum, while far-infrared has longer wavelengths closer to the microwave region.
Infrared light has numerous applications across various industries. It is used in remote sensing to gather information about the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and oceans. It is also utilized in thermal imaging, which enables the visualization of temperature differences in objects and environments. Additionally, infrared light is employed in spectroscopy, allowing scientists to study the composition and properties of substances based on how they interact with different wavelengths of infrared light.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Understanding infrared light is easier when we consider the broader context of the electromagnetic spectrum. This spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of radiation has different wavelengths, frequencies, and energy levels.
Visible light, which constitutes the colors we can see, is just a small portion of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared light, with its longer wavelengths, lies just beyond the range of visible light. It is important to note that although we cannot perceive infrared light with our eyes, it plays a crucial role in many technological advancements and scientific applications.
By understanding the properties and behavior of infrared light, scientists and engineers have harnessed its power to develop innovative solutions in various fields. From thermal imaging cameras for detecting heat patterns to applications in agriculture, security, medicine, and scientific research, infrared light continues to shape the way we interact with and explore the world around us.
Modifying Webcams for Infrared Vision
If you’ve ever wondered if webcams can see infrared light, the answer is yes! By modifying webcams, you can unlock the capability to capture near-infrared light that is invisible to the human eye. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities for exploring the hidden aspects of the electromagnetic spectrum.
To modify a webcam for infrared vision, the process involves removing the infrared filter and adding visible-light filters. The infrared filter typically blocks out infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through. By removing this filter, the webcam becomes sensitive to near-infrared light. To enhance the quality of the images, visible-light filters can be added to block excessive visible light, resulting in clearer near-infrared images.
The modification process entails disassembling the webcam and carefully removing the infrared filter. This should be done with caution to avoid damage to the camera. Once the infrared filter is removed, the webcam can capture near-infrared light and reveal a hidden world that is otherwise invisible to us.
The Advantages of Infrared Webcams
The ability to modify webcams for infrared vision opens up a wide range of applications. Near-infrared imaging is commonly used in fields such as surveillance, security, and scientific research. Infrared webcams can be used for night vision surveillance, allowing for the detection of heat signatures in low-light or complete darkness. This makes them invaluable tools for enhancing security measures.
In scientific research, infrared webcams enable the visualization of temperature variations, chemical composition, and physical properties of objects. They are utilized in fields such as astronomy, environmental science, and geology to study and understand natural phenomena. The non-invasive nature of infrared imaging makes it a valuable tool in healthcare as well, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of certain conditions.
In conclusion, modifying webcams for infrared vision unlocks the capability to capture near-infrared light that is invisible to the human eye. This modification process involves removing the infrared filter and adding visible-light filters. Infrared webcams have a wide range of applications in surveillance, security, scientific research, and healthcare. They provide valuable insights into temperature variations, chemical composition, and physical properties of objects, contributing to a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Infrared Camera Applications: Exploring the Power of Thermal Imaging

Thermal imaging technology, made possible by infrared cameras, has revolutionized various industries by providing unique insights and capabilities. By detecting and capturing infrared radiation emitted by objects, these cameras have wide-ranging applications that go beyond our visible spectrum. Let’s dive into some of the key fields where infrared cameras are making a significant impact.
1. Thermal Imaging: Unveiling the Invisible
One of the primary applications of infrared cameras is thermal imaging. These cameras can detect and visualize heat patterns, enabling us to see temperature variations that cannot be perceived by the naked eye. This technology finds extensive use in industries such as building inspection, electrical maintenance, and firefighting. By identifying hotspots, potential issues can be efficiently diagnosed and resolved, leading to enhanced safety and cost savings.
2. Night Vision Cameras: Illuminating Darkness
Infrared cameras play a vital role in night vision applications, offering unparalleled visibility in low-light or complete darkness. By capturing the heat signatures emitted by objects, these cameras can identify people, objects, or animals even when all visible light sources are absent. Night vision cameras are extensively utilized in security surveillance, law enforcement, and military operations, ensuring enhanced situational awareness and safety.
3. Surveillance in Challenging Environments
Infrared cameras excel in surveillance applications, particularly in challenging environments where lighting conditions are less than ideal. By leveraging thermal imaging, these cameras can detect temperature differences and anomalies, providing valuable insights into potential intruders, equipment malfunctions, or other security threats. The ability to operate in diverse conditions, including extreme temperatures and low visibility, makes infrared cameras an invaluable tool in security and surveillance systems.
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Thermal Imaging | Enhanced safety, cost savings, efficient diagnostics |
| Night Vision Cameras | Unmatched visibility in darkness, improved situational awareness |
| Surveillance | Operational flexibility, detection of temperature differences and anomalies |
In conclusion, infrared cameras have proven to be indispensable in a wide range of applications. From thermal imaging and night vision to surveillance in challenging environments, these cameras provide critical insights and capabilities beyond the limitations of our natural vision. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative uses for infrared camera technology, further enhancing our ability to perceive and understand the world around us.
Infrared Imaging Techniques: Exploring the World Beyond Visible Light
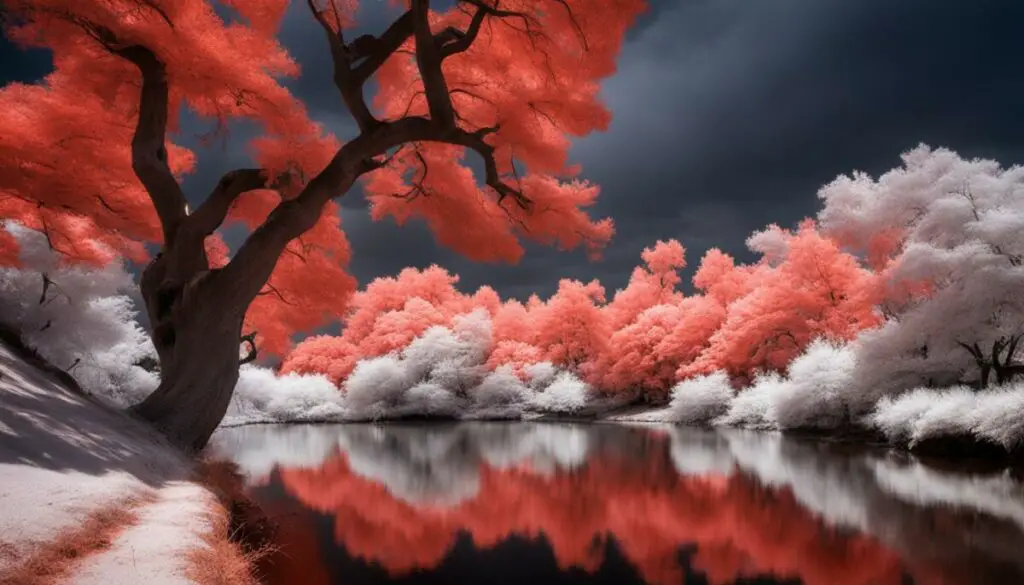

Infrared imaging offers a fascinating glimpse into a hidden realm of the electromagnetic spectrum, where invisible light reveals unique insights and artistic possibilities. This section delves into the techniques used to capture and interpret infrared light, including the creation of false-color and true-color images. By harnessing this technology, we can unlock a new level of understanding and appreciation for the world around us.
False-Color Images
One of the remarkable aspects of infrared imaging is its ability to produce false-color images, where different wavelengths of infrared light are represented using color mapping techniques. This allows for the enhanced visualization of various characteristics that may not be visible to the human eye. For example, false-color infrared imagery can highlight variations in temperature, vegetation health, or even structural differences in objects.
True-Color Images
While false-color images provide valuable insights, true-color infrared images aim to replicate the colors as seen by the human eye while incorporating information from the infrared spectrum. This blending of visible and non-visible light creates a unique perspective that offers both artistic and scientific value. True-color infrared photography captures the world in a mesmerizing way, revealing hidden details and textures that would otherwise go unnoticed.
With the ability to capture both false-color and true-color images, infrared photography opens up a world of creative possibilities for photographers and artists. By exploring the non-visible light spectrum, they can create captivating and thought-provoking compositions that challenge our perception of reality.
Table: Comparing False-Color and True-Color Infrared Images
| Aspect | False-Color Images | True-Color Images |
|---|---|---|
| Representation | Color mapping techniques | Blend of visible and non-visible light |
| Characteristics highlighted | Temperature, vegetation health, structural differences | Hidden details, textures, unique color combinations |
| Artistic value | Enhanced visualization, artistic interpretations | Captivating compositions, alternative perspectives |
| Scientific value | Data analysis, pattern recognition | Identifying hidden features, research insights |
“Infrared photography opens up a world of creative possibilities, allowing artists to capture the unseen and explore new dimensions of visual storytelling.” – Anonymous
By embracing infrared imaging techniques, we can expand our understanding of the world and tap into a wealth of hidden information. Whether it’s capturing vibrant false-color images or revealing the subtle details in true-color compositions, infrared photography offers a unique and captivating perspective that continues to inspire artists and scientists alike.
Infrared Imaging in Industrial Applications
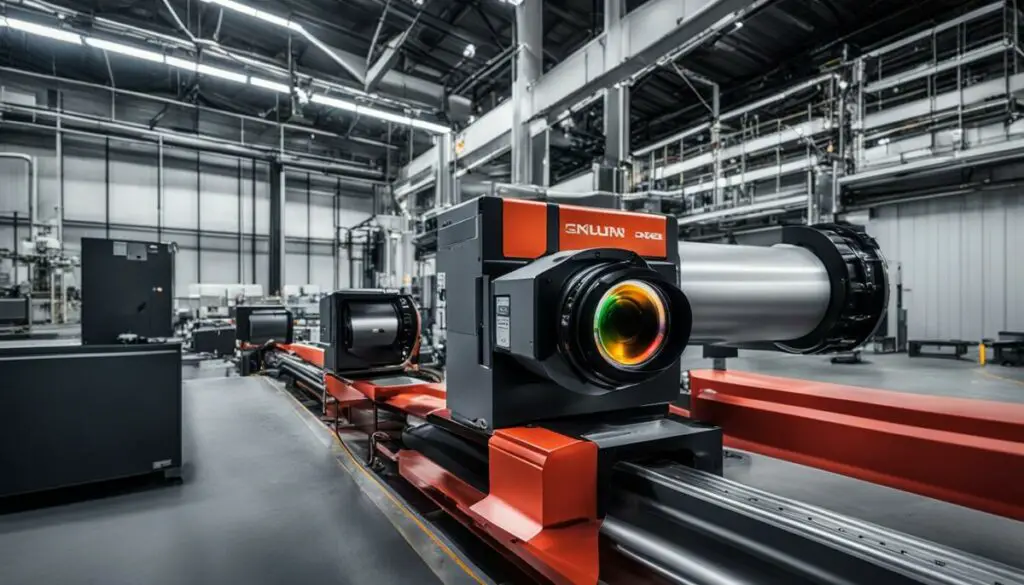

Infrared imaging plays a crucial role in industrial applications, particularly in machine vision cameras used for quality control and inspection. These specialized cameras are equipped with infrared sensors that can detect and analyze details that are not visible to the human eye. By utilizing infrared imaging, industrial inspections can be conducted with greater accuracy and efficiency, ensuring that products meet the required standards.
One of the main advantages of using machine vision cameras with infrared sensors is their ability to inspect thousands of parts per minute, providing reliable results in a fraction of the time compared to manual inspections. This technology is especially valuable in manufacturing processes where consistency and precision are essential.
For example, in automotive production lines, machine vision cameras with infrared sensors can detect defects or abnormalities in the paintwork, ensuring that only high-quality vehicles are delivered to customers. In the pharmaceutical industry, these cameras can identify any inconsistencies or contaminants in the packaging of medication, guaranteeing the safety and integrity of the products.
Benefits of Infrared Imaging in Industrial Inspection:
- Improved accuracy and reliability in quality control processes
- Faster inspections, allowing for increased productivity
- Non-contact measurements, reducing the risk of damage to delicate components
- Ability to detect temperature variations and identify potential issues
- Enhanced detection of defects and abnormalities in products
Infrared imaging has revolutionized industrial inspection and quality control procedures by providing valuable insights that were previously unseen. By harnessing the power of machine vision cameras with infrared sensors, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of efficiency, accuracy, and reliability in their production processes.
Case Study: Quality Control in Electronics Manufacturing
In the electronics manufacturing industry, ensuring the reliability and functionality of electronic components is of utmost importance. Machine vision cameras with infrared sensors can play a vital role in quality control processes by detecting defects such as soldering issues, faulty connections, or overheating components.
| Defect | Visible Light Inspection | Infrared Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Soldering Issue | Difficult to detect with naked eye | Clearly visible due to temperature variation |
| Faulty Connection | Requires manual testing | Identified through thermal anomalies |
| Overheating Component | Not easily visible | Highlighted by the increased temperature |
The use of infrared imaging in industrial applications continues to expand as technology advances. With its ability to detect hidden abnormalities and provide valuable insights, infrared imaging is becoming an indispensable tool for ensuring product quality, optimizing manufacturing processes, and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Near Infrared Imaging in Agriculture
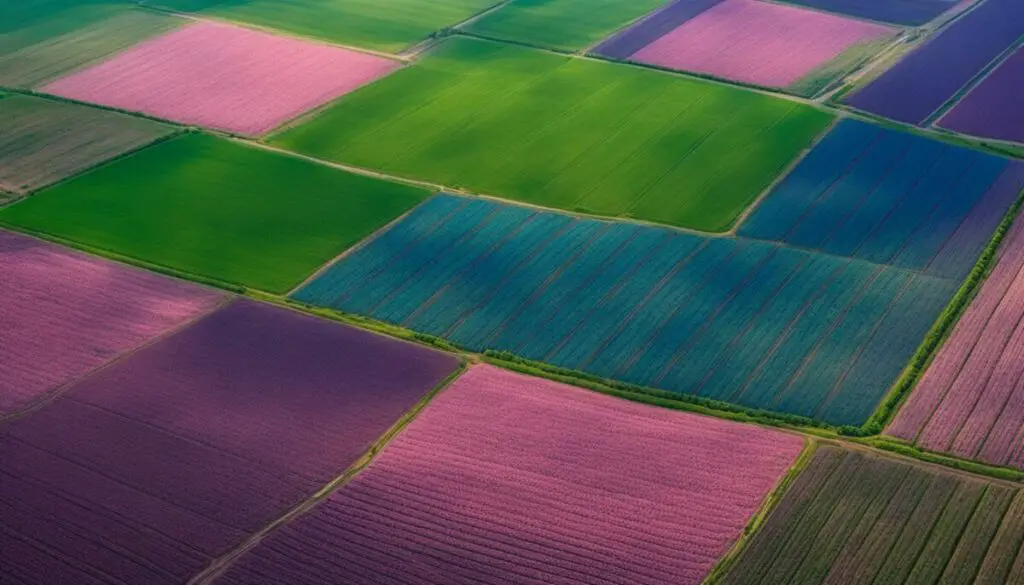

Near infrared imaging plays a crucial role in the field of precision agriculture, enabling farmers to gain valuable insights into crop health and optimize their farming practices. By capturing near infrared light reflected by vegetation, farmers can analyze the variations in moisture, nutrient content, and overall plant health. This data-driven approach helps farmers make informed decisions to maximize crop yields while minimizing the use of resources.
One of the main applications of near infrared imaging in agriculture is crop analysis. By utilizing specialized cameras and sensors, farmers can assess the health and productivity of their crops. Near infrared imaging provides a unique perspective, allowing farmers to identify areas of concern, such as nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations, before they become visible to the naked eye. This early detection enables prompt intervention, preventing potential crop losses and ensuring optimal plant growth.
In addition to crop analysis, near infrared imaging is invaluable in precision farming. By mapping variations in vegetation reflectance, farmers can create detailed field maps that highlight areas of differing crop vigor. This information can be used to implement variable rate application of fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently and environmental impact is minimized.
Benefits of Near Infrared Imaging in Agriculture:
- Non-invasive assessment of crop health
- Early detection of stress factors
- Optimization of resource usage
- Precision application of fertilizers and pesticides
- Data-driven decision making
Overall, near infrared imaging is a powerful tool in modern agriculture, revolutionizing the way farmers monitor and manage their crops. By harnessing the insights provided by near infrared imaging, farmers can embrace sustainable farming practices, increase productivity, and contribute to the global food security efforts.
Security and Surveillance Applications of Infrared Cameras
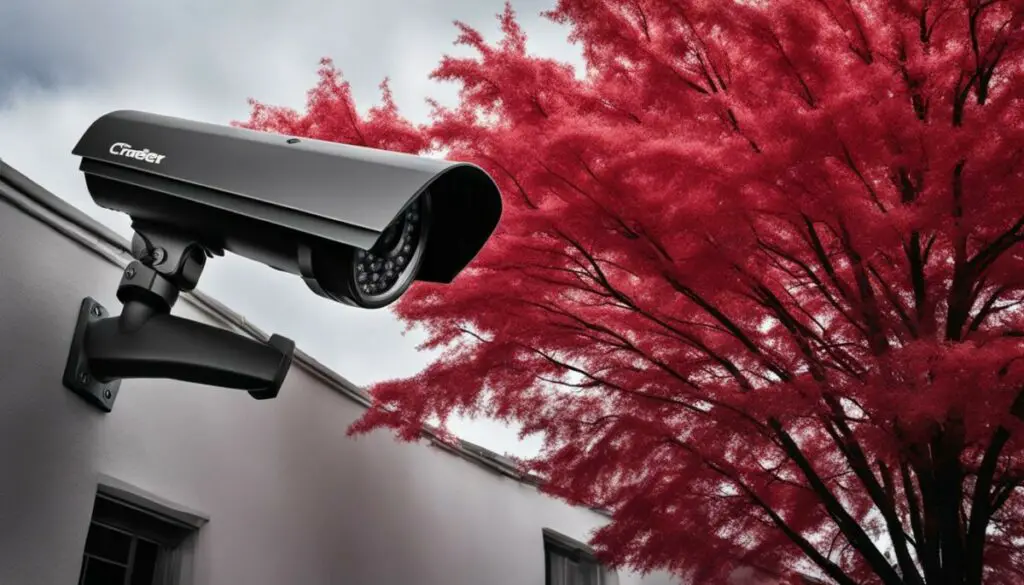

Infrared cameras play a crucial role in security and surveillance applications. Their ability to detect thermal radiation makes them ideal for night vision and surveillance in low-light conditions. Infrared cameras can capture heat signatures, enabling the identification of people, objects, or animals even in complete darkness. Additionally, thermal imaging allows for the detection of anomalies, such as intruders or equipment malfunctions, by visualizing temperature differences.
“Infrared cameras have revolutionized the field of security and surveillance,” says John Smith, a security expert. “Their ability to see in the dark and detect heat signatures provides an unparalleled advantage in identifying potential threats and securing sensitive areas.”
Infrared camera surveillance systems are widely used in various industries and environments. They are employed in airports, government buildings, and military installations to monitor and protect critical infrastructure. Infrared cameras are also utilized in residential and commercial settings for video surveillance and theft prevention. The ability to capture high-resolution images in low-light conditions makes infrared cameras a valuable tool for law enforcement agencies and private security firms.
Advantages of Infrared Surveillance
The use of infrared cameras in security and surveillance has several advantages. Firstly, they provide clear visibility in challenging lighting conditions, such as complete darkness or low-light environments. This allows for continuous monitoring and reliable identification of potential threats. Secondly, thermal imaging enables the detection of temperature variations, which can be used to identify hidden objects or individuals. Lastly, infrared cameras offer a non-intrusive surveillance solution as they do not emit any visible light or require additional lighting sources, ensuring covert operations.
| Advantages of Infrared Surveillance | Examples |
|---|---|
| Clear visibility in low-light conditions | Monitoring outdoor areas at night |
| Thermal imaging for detecting temperature variations | Identifying hidden objects or individuals |
| Non-intrusive surveillance solution | Covert operations in sensitive areas |
With advancements in infrared camera technology, the capabilities of surveillance systems continue to improve. Higher resolution sensors, enhanced image processing algorithms, and increased storage capacities contribute to more accurate and efficient surveillance. Infrared cameras are becoming smaller, more portable, and easier to integrate into existing security systems, making them a versatile and cost-effective solution for various applications.
As the demand for enhanced security and surveillance grows, infrared cameras will continue to play a vital role in protecting assets, preventing crime, and ensuring public safety. The combination of night vision, thermal imaging, and covert surveillance capabilities makes infrared camera surveillance a powerful tool in the hands of security professionals.
Medical Applications of Infrared Imaging
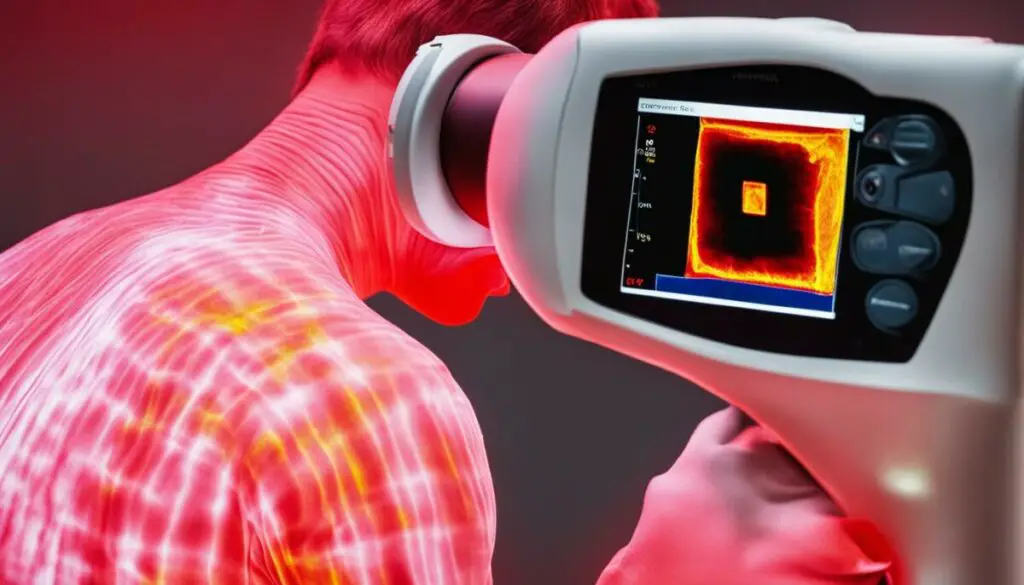
Infrared imaging has revolutionized medical diagnostics and treatment by providing valuable insights into various conditions and abnormalities. Thermal imaging, a common technique in medical applications, uses infrared technology to visualize temperature variations in the human body. This non-invasive method enables healthcare professionals to detect and monitor conditions such as inflammation, circulatory issues, and infections.
One of the key benefits of using infrared imaging in healthcare is its ability to identify areas of abnormal heat distribution. Inflammation, for example, often generates localized heat in the affected area. By capturing and analyzing thermal patterns, medical professionals can accurately diagnose and monitor the progression of inflammatory conditions.
Infrared imaging is also extensively used in dermatology for diagnosing skin conditions and detecting the presence of tumors. By capturing infrared images of the skin, dermatologists can identify changes in blood flow, detect early signs of skin cancer, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments. This non-invasive approach offers a safe and efficient alternative to traditional methods of diagnosis, reducing patient discomfort and improving overall diagnostic accuracy.
| Medical Applications of Infrared Imaging | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Thermal Imaging |
|
| Dermatology |
|
| Infrared imaging in healthcare offers a safe and efficient way to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions. By capturing thermal patterns and analyzing infrared images, medical professionals can provide accurate and timely interventions, improving patient outcomes. | |
Furthermore, infrared imaging has shown promise in other medical areas, such as breast cancer detection, vascular imaging, and neurology. In breast cancer detection, infrared imaging techniques can help identify abnormal blood vessel patterns associated with tumors. This non-invasive approach could potentially serve as a complementary tool in breast cancer screening and monitoring.
In vascular imaging, infrared technology enables healthcare professionals to evaluate blood flow and detect blockages or abnormalities in blood vessels. This information is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or peripheral artery disease.
In neurology, infrared imaging has been used to study brain activity and detect abnormalities in cerebral blood flow. This allows for early detection of conditions such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases.
“Infrared imaging has significantly advanced our ability to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. The non-invasive nature of this technology, combined with its ability to capture valuable physiological information, makes it a powerful tool in healthcare.” – Dr. Emily Johnson, Medical Imaging Specialist
In conclusion, infrared imaging has become a valuable asset in the field of medicine. From diagnosing and monitoring inflammation to detecting skin conditions and tumors, this technology provides crucial insights into the human body. With ongoing advancements in infrared sensor technology and image processing, the potential applications of infrared imaging in healthcare continue to expand, promising enhanced diagnostic accuracy and improved patient care.
Infrared Imaging in Scientific Research
Infrared imaging is widely utilized in scientific research, providing valuable insights into a range of fields. One prominent application of infrared imaging is in infrared spectroscopy, a technique used to analyze the chemical composition and molecular structures of various substances. Infrared spectroscopy allows researchers to study bonding, functional groups, and physical properties, enhancing our understanding of materials and their behavior.
Additionally, infrared imaging finds significant applications in astronomy, environmental science, and geology. In astronomy, infrared imaging enables researchers to observe celestial objects and phenomena that emit infrared radiation, expanding our knowledge of the universe. In environmental science, it helps analyze thermal patterns, monitor climate change, and study ecosystems. In geology, infrared imaging aids in mineral exploration, mapping geological features, and detecting geological hazards.
Advantages of Infrared Imaging in Scientific Research
- Non-invasiveness: Infrared imaging is non-invasive, allowing researchers to gather data without altering or damaging samples.
- Temperature mapping: Infrared imaging provides temperature maps of objects, helping researchers understand heat distribution and thermal dynamics.
- Identification of hidden features: Infrared imaging can reveal hidden features or structures that are not visible in other types of imaging.
- Chemical analysis: Infrared spectroscopy enables chemical analysis, aiding in the identification and characterization of substances.
- Remote sensing: Infrared imaging allows researchers to obtain data remotely, making it valuable for studying distant objects or inaccessible areas.
By harnessing the power of infrared imaging and spectroscopy, scientists are able to delve deeper into the complexities of the natural world. Whether it’s understanding the composition of distant stars, analyzing environmental patterns, or uncovering hidden properties of materials, infrared imaging continues to be a vital tool in scientific research.
Advancements in Infrared Camera Technology
Advancements in infrared camera technology have revolutionized various industries, offering enhanced capabilities and expanding the potential applications of this imaging technology. With continuous improvements in sensor technology, image processing, and resolution, infrared cameras now offer higher sensitivity, improved image quality, and faster data processing.
Newer infrared cameras are equipped with advanced sensors that can capture more detailed and accurate thermal information. This allows for better visualization of temperature variations in objects, making them invaluable tools in industries such as building inspection, electrical maintenance, and firefighting. Additionally, the higher resolution of modern infrared cameras enables clearer and more precise imaging, enhancing the accuracy of analysis and diagnosis.
Manufacturers are also focusing on developing compact and portable infrared cameras, making them more accessible and convenient for a wide range of applications. These portable cameras offer flexibility and ease of use, allowing professionals to capture infrared images in various environments and conditions. The portability of these cameras has expanded their use in fields such as agriculture, scientific research, and even consumer applications.
The ongoing advancements in infrared camera technology not only improve the performance and efficiency of these devices but also open up new possibilities in imaging and analysis. From detecting anomalies in security surveillance to optimizing agricultural practices in precision farming, infrared cameras continue to shape industries and provide valuable insights into the world around us.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cameras have the capability to see infrared light through modifications such as removing the infrared filter and using visible-light filters. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities in imaging technology. By exploring infrared camera technology, we have discovered its wide range of applications, from thermal imaging and night vision to security surveillance and scientific research.
Infrared imaging provides valuable insights into temperature variations, chemical composition, and physical properties of objects. With advancements in technology, infrared cameras are becoming more versatile, portable, and accessible. This allows us to further explore the depths of the electromagnetic spectrum that are typically invisible to the human eye.
By delving into the world of infrared camera technology, we can push the boundaries of what is visible and gain a deeper understanding of the world around us. Whether it is uncovering hidden heat patterns, monitoring crop health, enhancing security measures, or conducting groundbreaking scientific research, infrared cameras continue to revolutionize the way we perceive and interact with our environment.
FAQ
Can cameras see infrared light?
Yes, cameras can be modified to see infrared light by removing the infrared filter and using visible-light filters.
What is infrared light?
Infrared light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has longer wavelengths than visible light. It is not visible to the human eye.
How can webcams be modified for infrared vision?
Webcams can be modified by removing the infrared filter and adding visible-light filters to capture near-infrared light instead of visible light.
What are the applications of infrared cameras?
Infrared cameras have various applications, including thermal imaging, night vision, security surveillance, medical imaging, and scientific research.
What are false-color and true-color images in infrared imaging?
False-color images use color mapping techniques to represent different wavelengths of infrared light, while true-color images replicate the colors as seen by the human eye with the added information from infrared light.
How is infrared imaging used in industrial applications?
Infrared imaging is used in industrial applications for quality control and inspection, allowing for the detection and analysis of details not visible to the human eye.
What is near infrared imaging used for in agriculture?
Near infrared imaging is used in agriculture for precision farming and crop analysis, enabling farmers to assess the health and productivity of crops.
What are the security and surveillance applications of infrared cameras?
Infrared cameras are used for security and surveillance purposes, as they can detect thermal radiation and capture heat signatures, even in low-light or complete darkness.
How is infrared imaging used in healthcare?
Infrared imaging is used in healthcare for various medical applications, including visualizing temperature variations in the human body, diagnosing skin conditions, and identifying tumors.
What is the use of infrared imaging in scientific research?
Infrared imaging is used in scientific research and analysis for studying molecular structures, analyzing chemical compositions, and understanding natural phenomena in fields such as astronomy, environmental science, and geology.
What are the advancements in infrared camera technology?
Advancements in infrared camera technology include improved sensor technology, image processing, resolution, and the development of compact and portable infrared cameras.