Ions are one of the building blocks of chemistry and physics, but have you ever stopped to wonder why they are called ions? This article will explore the origin of the term ‘ion’ and explain why this small particle has such an important role in our daily lives. Discover the intriguing history of ions and how they play a vital role in modern life.
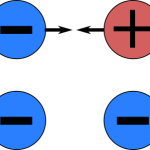
Ions are molecules that have a positive or negative charge. This charge is created when electrons are transferred between two atoms. The name comes from the Greek words “ion” and “on”, which means to go. Ions are important in many processes including chemical reactions, electric currents, and energy transfer.
Contents
What Are Ions?
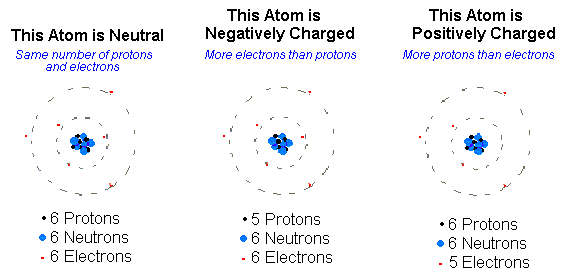
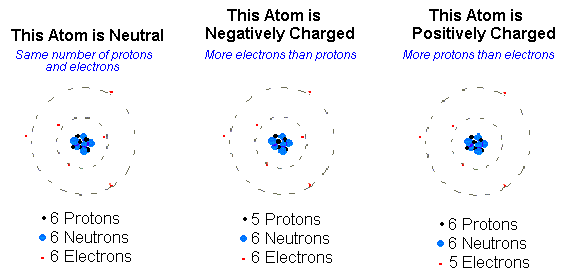
Ions are atoms or molecules with an electric charge. They can either be positively or negatively charged and are created when an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons. Ions are an important part of chemistry and are found in many everyday objects, such as salt, and they play an important role in many biological processes.
How Are Ions Formed?
Ions are formed when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons. This can happen when the atom or molecule is exposed to a source of energy, such as radiation or heat. This process is known as ionization. The atom or molecule gains or loses an electron, which then gives it an electric charge. This process can also happen when atoms or molecules interact with other atoms or molecules.
What Is the Meaning of the Word ‘Ion’?
The word ‘ion’ comes from the Greek word ‘ion’, which means ‘going’. The name was given to atoms and molecules that have an electric charge because of the way they move. The movement of ions is an important part of many chemical reactions and processes.
What Are the Different Types of Ions?
There are two main types of ions: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. Cations are formed when an atom or molecule gains electrons, while anions are formed when an atom or molecule loses electrons.
Cations
Cations are positively charged ions that are formed when an atom or molecule gains electrons. They are typically smaller than anions and have a greater attraction for other ions. Examples of cations include sodium, potassium, and magnesium ions.
Anions
Anions are negatively charged ions that are formed when an atom or molecule loses electrons. They are typically larger than cations and have a greater attraction for other ions. Examples of anions include chloride, bromide, and sulfate ions.
What Are the Properties of Ions?
Ions have several properties that make them important in chemistry and biology. They are electrically charged, which means they can interact with other ions, and they are capable of forming bonds with other molecules. Ions also have a greater attraction for other ions than atoms and molecules without an electric charge.
Electrical Charge
The most important property of ions is their electric charge. This charge allows ions to interact with other ions and molecules. Ions with opposite charges are attracted to each other, while ions with the same charge repel each other. This is an important property for many chemical reactions and processes.
Bonding Ability
Ions are also able to form bonds with other molecules. This is because the electric charge of the ion allows it to form a bond with the molecules it interacts with. This is an important property in biology, as it allows cells to form complex structures and carry out important functions.
What Are the Applications of Ions?
Ions are used in a wide range of applications, from medicine to industry. They are used in medicine to diagnose and treat diseases, and they are used in industry to create products such as batteries and semiconductors. Ions are also important in biology, as they are involved in many biological processes and help to maintain the balance of ions in cells.
Medicine
Ions are used in medicine to diagnose and treat diseases. They are used in imaging techniques such as MRI, which uses magnetic fields to create images of the body. They are also used in treatments such as chemotherapy, where ions are used to target and kill cancer cells.
Industry
Ions are also used in industry to create products such as batteries and semiconductors. Batteries use ions to store and release energy, while semiconductors use ions to create electrical signals. Ions are also used in the production of plastics, which use ions to form strong bonds between molecules.
What Are the Dangers of Ions?
While ions are important in many applications, they can also be dangerous. Exposure to high levels of certain ions can be harmful to humans and the environment. For example, exposure to high levels of chlorine ions can be toxic and can cause respiratory problems.
Human Health
Exposure to high levels of certain ions can be toxic to humans. Inhaling high levels of chlorine ions can cause respiratory problems, while exposure to high levels of sulfur ions can cause skin irritation. Ions can also react with other molecules in the body, which can cause damage to cells and tissues.
Environmental Damage
Exposure to high levels of certain ions can also be harmful to the environment. For example, high levels of nitrogen ions can cause eutrophication, which is an increase in the nutrients in a body of water that can cause an increase in algae growth. High levels of sulfur ions can also cause acid rain, which can damage plants and animals.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What are Ions?
Ions are atoms or molecules which have an electric charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. An ion can be either positively or negatively charged, depending on whether it has lost or gained electrons. Ions can form when an atom is exposed to heat, light, radiation, or chemical reactions.
What is the Difference Between Ions and Atoms?
Atoms are the smallest unit of matter that retain their chemical properties. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons. This causes the atom or molecule to have an electric charge. This change in the number of electrons changes the chemical properties of the atom or molecule.
Why is It Called Ions?
Ions are named after the Greek word ‘εἰων’, which means ‘to go’. This refers to the movement of electrons in an atom or molecule, causing a charge to be created. The prefix ‘ion’ is also used to describe an atom or molecule which has gained or lost electrons, such as in the words ‘cations’ and ‘anions’.
What are the Different Types of Ions?
There are two main types of ions – cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions which have lost electrons, while anions are negatively charged ions which have gained electrons. Other types of ions include polyatomic ions, which are composed of two or more atoms, and chelated ions, which are ions which have been bound to a metal ion.
How are Ions Formed?
Ions are formed when an atom or molecule is exposed to heat, light, radiation, or chemical reactions. When exposed to these external factors, the atom or molecule can gain or lose electrons, resulting in a charge. This charge can then cause the ion to interact with other atoms, molecules, and ions.
What are Ions Used For?
Ions are used in a wide range of applications, from medical treatments to industrial processes. Ions are used in the medical field to detect, diagnose, and treat diseases. In the industrial field, ions are used in chemical reactions to create products such as fertilizers and pharmaceuticals. Ions are also used in batteries and fuel cells, which use the energy generated by the movement of ions to create electricity.
What Are Ions | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
In conclusion, it’s clear that the term ‘ions’ is used to describe atoms or molecules that have an unequal number of protons and electrons, meaning they have an overall electrical charge. This charge is what makes ions so useful in a variety of applications, from industrial processes to medical treatments. Understanding why ions act the way they do and why they are called ‘ions’ is essential to making the most of their properties.

.jpg)

.jpg)