Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Electrons are the building blocks of matter, yet why are they called negative? This seemingly simple question has many answers and a few misconceptions that can be easily dispelled with a little knowledge about the nature of electricity and the way electrons behave. In this article, we’ll explore why electrons are referred to as negative and what this means for the way we understand electricity. So let’s dive in and take a closer look at why electrons are labeled as negative and the significance of this for our lives.

Contents
What Is the Reason Behind Electrons Being Called Negative?
Electrons are a fundamental part of the universe and are found in every atom. They are negatively charged particles that are responsible for the chemical bonding between atoms. Electrons are called negative because of their charge and the way they interact with other particles. This article will explore the reasons why electrons are called negative and the implications of this charge.
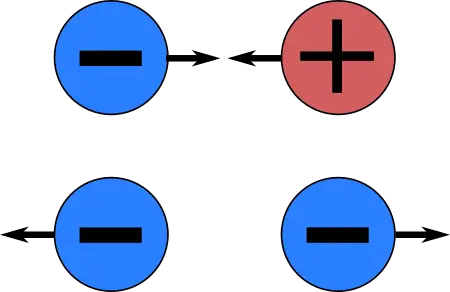
In order to understand why electrons are called negative, it is important to understand the basics of electricity and how it works. Electricity is the flow of electrons through a conductor, such as a wire. Electrons carry a negative charge, meaning they are attracted to positively charged particles and repelled by negatively charged particles. This charge is why electrons are called negative.
The implications of electrons being negative are far-reaching. This charge allows electrons to interact with other particles, forming strong chemical bonds between atoms. This is the basis of all chemical reactions and the basis of life itself. Furthermore, the negative charge of electrons allows them to be used as a source of energy in electrical circuits.
What Are Positively Charged Particles?
Positively charged particles are the opposite of negatively charged particles, such as electrons. These particles are attracted to negatively charged particles and repelled by positively charged particles. Examples of positively charged particles include protons and positrons.
Positively charged particles are found in the nucleus of atoms and are responsible for the stability of the atom. They are also responsible for the chemical properties of atoms, such as their reactivity and ability to form bonds with other atoms.
Positively charged particles are important for many reasons. They are essential for the formation of chemical bonds and thus the basis of all life on Earth. They are also essential for the stability of atoms, as well as for the transmission of energy in electrical circuits.
What Are the Implications of Electrons Being Negative?
The implications of electrons being negative are far-reaching. This charge allows electrons to interact with other particles, forming strong chemical bonds between atoms. This is the basis of all chemical reactions and the basis of life itself. Furthermore, the negative charge of electrons allows them to be used as a source of energy in electrical circuits.
Electrons being negative also has implications for the stability of atoms. Negatively charged electrons are attracted to positively charged particles, such as protons. This attraction helps to keep the nucleus of atoms stable, as the positively charged particles are held in place by the negatively charged electrons.
Finally, electrons being negative has implications for the transmission of energy. Electrons can be used as a source of energy in electrical circuits, as they can flow through conductors and be used to power devices. This is because of their negative charge, as they are attracted to positively charged particles.
What Are the Implications of Positively Charged Particles?
Positively charged particles are essential for the formation of chemical bonds and thus the basis of all life on Earth. They are also essential for the stability of atoms, as well as for the transmission of energy in electrical circuits.
Positively charged particles also have implications for the transmission of energy. When these particles are present in an electrical circuit, they create a voltage difference between two points. This voltage difference can then be used to move electrons through the circuit, allowing energy to be transmitted.
Finally, positively charged particles can also be used to create magnetic fields. When a current is run through a coil of wire, the positively charged particles create a magnetic field that can be used to power a variety of devices.
Conclusion
Electrons are called negative because of their charge and the way they interact with other particles. This charge allows electrons to form strong chemical bonds between atoms, which form the basis of all life on Earth. Electrons are also essential for the stability of atoms and for the transmission of energy in electrical circuits. Positively charged particles are also important, as they are essential for the formation of chemical bonds and for the transmission of energy.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Electron?
An electron is a subatomic particle with a negative electrical charge. Electrons are found in all atoms, and they are the primary carrier of electricity in solids. Electrons are the smallest and most abundant of the known particles. They are also the least massive, with a mass of 9.11 x 10-31 kilograms.
What is the Source of Electron’s Negative Charge?
The source of the electron’s negative charge is the fact that it has a negative charge relative to the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus by the electromagnetic force and are responsible for the chemical properties of atoms. The negative charge of the electron is due to the imbalance between the number of protons and the number of electrons.
Why are Electrons Called Negative?
Electrons are called negative because of their negative charge relative to the nucleus of an atom. Electrons have a negative charge because they have fewer protons than electrons, resulting in an overall negative charge. This imbalance between the number of protons and electrons is responsible for the attraction between atoms, which creates chemical bonds.
Are There Positively Charged Electrons?
No, there are no positively charged electrons. Electrons have a negative charge, which means they are attracted to positively charged particles, such as protons. When electrons and protons combine, they form atoms.
What is the Significance of the Negative Charge of Electrons?
The negative charge of electrons is significant because it is responsible for the attraction between atoms, which leads to chemical bonding and the formation of molecules. Furthermore, the negative charge of electrons is responsible for the flow of electricity in solids.
Are Electrons Always Negative?
Yes, electrons are always negatively charged. Electrons can gain or lose energy, which affects their movement and the attraction between atoms, but their charge remains the same. Electrons cannot change their charge from negative to positive.
Why Is An Electron Negative In Charge
In conclusion, electrons are called negative because of their negative charge. Electrons have a lower energy level than protons, which causes them to be attracted to higher energy levels. This attraction makes electrons move toward positive charges, making them a negative force in the universe. Electrons are also the smallest particles in an atom, which makes them more difficult to detect than protons. By understanding the physics behind why electrons are called negative, scientists are able to better understand the nature of electricity and how it works.

.jpg)
.jpg)