Last Updated on 6 months by Francis
Have you ever wondered if humans emit infrared radiation? The answer might surprise you! Infrared radiation, also known as thermal radiation, is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is produced by the movement of molecules. Thermal radiation is produced by all objects, including the human body, and it is an essential factor in understanding human physiology.
While the human body does emit infrared radiation, the amount and intensity of the emission can vary depending on several factors, such as physical activity, body temperature, and environmental conditions.
In this article, we will explore the concept of infrared radiation and its relevance to human physiology. We will uncover the truth behind human infrared emissions, their unique signature, how they are detected and measured, their potential applications in various fields, and their health implications. We will also address any controversies or misconceptions surrounding human infrared emissions. So, are you ready to dive deeper into the world of infrared radiation and the human body? Let’s get started!
Contents
Key Takeaways
- Humans emit infrared radiation as a result of their thermal emissions.
- The amount and intensity of human infrared emissions can vary depending on several factors.
- Infrared radiation is essential in understanding human physiology and has significant applications in fields such as medicine, security, and environmental monitoring.
- There are potential health implications associated with human infrared emissions.
- Advancements in infrared detection technology will lead to new insights and developments in human physiology.
Understanding Infrared Radiation

Before delving into the details of human infrared emissions, it is essential to understand what infrared radiation is and how it works.
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has longer wavelengths than visible light. It is produced by the thermal motion of atoms and molecules, which causes them to emit energy in the form of photons. In simpler terms, any object with a temperature above absolute zero radiates infrared energy.
When it comes to the human body, infrared radiation is produced by the process of thermoregulation. Our bodies maintain a constant internal temperature of around 98.6°F (37°C) by balancing the heat we produce with the heat we lose to the environment. This heat loss occurs primarily through radiation, convection, and conduction.
One of the biggest sources of heat loss from the human body is through radiation. In fact, around 60% of the body’s heat is lost through infrared radiation. This radiation is produced by the skin’s surface, which emits energy in the form of photons.
The Relationship Between Infrared Radiation and Human Body Heat Emissions
The heat that is lost through our skin’s surface is a result of our body’s natural processes, such as metabolism and physical activity. When these processes occur, they generate heat, which is then transferred from the body to the skin’s surface.
When the heat reaches the skin’s surface, it is released into the environment through infrared radiation. The amount of radiation emitted by the body is directly proportional to the amount of heat generated by the body.
Therefore, the more active we are or the higher our body temperature, the more infrared radiation we emit. This is why infrared cameras can be used to detect physical activity, such as running or jumping.
Human Thermal Emissions
Infrared radiation is just one form of thermal emissions from the human body. Thermal emissions also include convection and conduction, which are the transfer of heat through the movement of air molecules and direct contact, respectively.
These thermal emissions are critical to our understanding of human physiology, as they provide valuable information about our body’s metabolic rate, energy expenditure, and overall health.
In the next section, we will explore the unique infrared signature emitted by the human body and its significance in various fields.
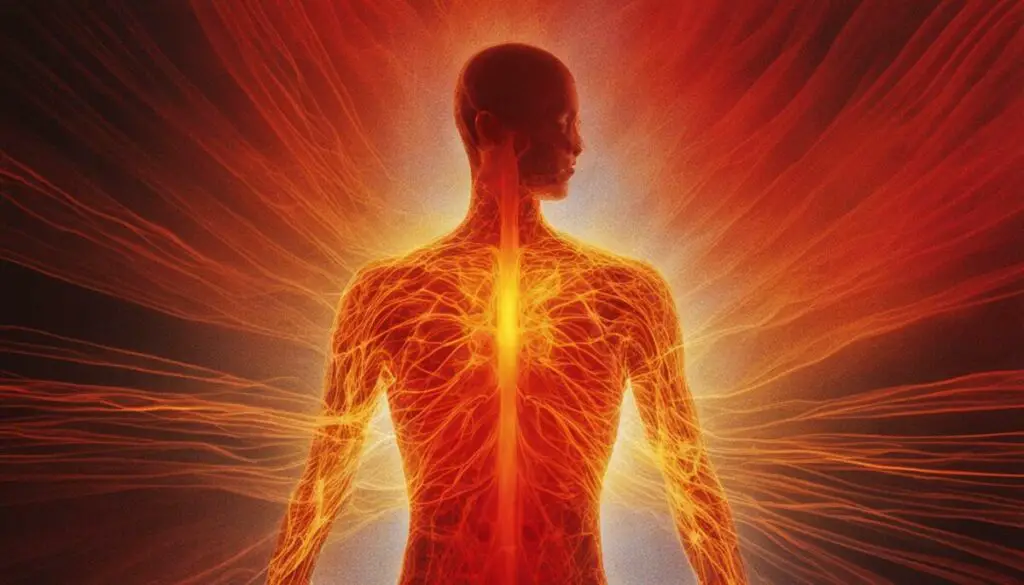
The Human Infrared Signature

Every object emits a certain amount of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation, including infrared radiation. Humans are no exception and emit infrared radiation as a result of heat emission by their bodies. The human infrared signature is a unique pattern of infrared emissions that can be detected and analyzed for various purposes.
When we think of detecting human infrared radiation, we often think of thermal imaging cameras. These cameras can detect the differences in temperature between objects and produce an image that highlights these temperature variations. In the case of humans, thermal imaging cameras can detect the heat emissions from the body and produce an image of the human infrared signature.
The human infrared signature can be used in various fields, such as medicine and security. For example, medical professionals can use thermal imaging to detect abnormalities in body temperature that may indicate an injury or illness. Security systems can also use thermal imaging to detect individuals who may be hiding, as their heat emissions will be different from their surroundings.
“The unique infrared signature emitted by the human body can be detected and analyzed for various purposes.”
Interestingly, the human infrared signature can also be used to differentiate between individuals. Each person has a unique pattern of heat emissions, making it possible to identify them based on their infrared signature. This concept is becoming increasingly important in fields such as biometrics and forensics.
Overall, the human infrared signature is an important concept in the study of human physiology. By understanding the unique infrared emissions produced by the human body, we can gain insight into various aspects of human health and behavior. As technology continues to advance, we can expect new and exciting applications of the human infrared signature to emerge.
Measuring Human Infrared Emissions

Measuring human infrared emissions requires specialized technology and equipment capable of capturing and analyzing the heat signature of the human body. There are several methods employed in measuring human heat signature, each with its advantages and limitations.
One of the most commonly used techniques is thermography, which uses a thermographic camera to capture images of the heat radiating from the human body. These images are then analyzed to identify regions of increased or decreased heat emission, which can help detect underlying medical conditions such as tumors or inflammation.
Another method is radiometry, which uses sensors to detect the heat emitted by the human body and convert it into electrical signals. These signals can then be analyzed to determine the temperature and intensity of the heat signature.
Electrodermal activity (EDA) is another technique used to measure human heat signature. EDA measures the changes in the electrical conductance of the skin, which can be influenced by factors such as emotion, stress, and physical activity. By analyzing these changes, researchers can gain insight into the physiological effects of these factors on the human body.
Limitations of Infrared Emission Measurement
While measuring human infrared emissions has many potential applications, it also has some limitations. One major limitation is the variability in human thermal emissions based on individual factors such as age, sex, and health status. Additionally, environmental factors such as ambient temperature and humidity can also influence the intensity and pattern of human heat signature.
Another limitation is the cost and technical expertise required to use infrared detection equipment. These tools can be expensive and require trained professionals to operate them properly, making it challenging to implement them in certain settings.
Applications of Human Heat Signature Measurement
Despite the limitations, measuring human infrared emissions has numerous potential applications. One such application is in the field of medical imaging, where infrared technology can be used to detect and monitor various medical conditions, including breast cancer, skin tumors, and musculoskeletal injuries.
In the field of security, infrared detection technology can be used to identify individuals based on their unique heat signature, providing an additional layer of security in high-risk areas such as airports and government buildings.
Finally, measuring human infrared emissions can also be useful in environmental monitoring, providing insights into the impact of climate change on human health and wellbeing.
Factors Affecting Infrared Emissions

Various factors can influence the amount and intensity of infrared emissions from the human body. These factors can be broadly categorized into internal and external factors.
Internal Factors
Internal factors refer to physiological processes within the body that affect thermal emissions, such as physical activity and body temperature.
Physical activity is a significant determinant of the amount of heat emissions from the human body. The more physically active a person is, the higher the intensity of their thermal emissions. For instance, a person engaged in a strenuous exercise will have a higher heat signature than someone who is sitting still.
Body temperature is another important internal factor that can influence infrared emissions. The human body maintains a constant internal temperature of around 98.6°F (37°C) through a process called thermoregulation. When the body temperature rises above this level, it triggers an increase in the thermal emissions from the body. This is why a person with a fever will have a higher heat signature than someone with a normal body temperature.
External Factors
External factors refer to environmental conditions that affect thermal emissions, such as ambient temperature and humidity.
Ambient temperature is a crucial external factor that can affect the heat signature of the human body. When the temperature around a person is high, their body will emit less thermal radiation, as there is less of a temperature gradient between the body and the environment. Conversely, when the temperature is low, the body will emit more thermal radiation, as it attempts to maintain its internal temperature.
Humidity is another external factor that can influence infrared emissions. When the air is humid, it reduces the rate at which the human body can dissipate heat through perspiration. This can result in a higher heat signature, as the body attempts to maintain its internal temperature by emitting more infrared radiation.
In conclusion, various internal and external factors can affect the amount and intensity of infrared emissions from the human body. These factors must be taken into account when analyzing thermal images or using infrared technology to detect and measure human thermal emissions.
Applications of Human Infrared Radiation

Human infrared radiation has numerous applications in various fields. Medical imaging is one such field where it is extensively used to detect and diagnose various conditions. It is also used in environmental monitoring to detect heat emissions from industries and other sources.
Medical Imaging: Infrared imaging is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that helps in identifying various medical conditions. It is used to detect breast cancer, skin cancer, and other conditions that affect blood flow or change the temperature of affected areas. Infrared cameras can detect the heat emitted by cancer cells, which can help doctors identify the location and extent of the cancer.
Environmental Monitoring: Human infrared radiation is also used in environmental monitoring to detect heat emissions from various sources. It is used to monitor industrial emissions and detect any anomalies or irregularities in the heat patterns. Infrared cameras are also used to monitor forest fires and to detect hotspots that may indicate the early stages of a fire.
The use of infrared technology has revolutionized many fields, including medicine and environmental monitoring.
Health Implications of Infrared Emissions
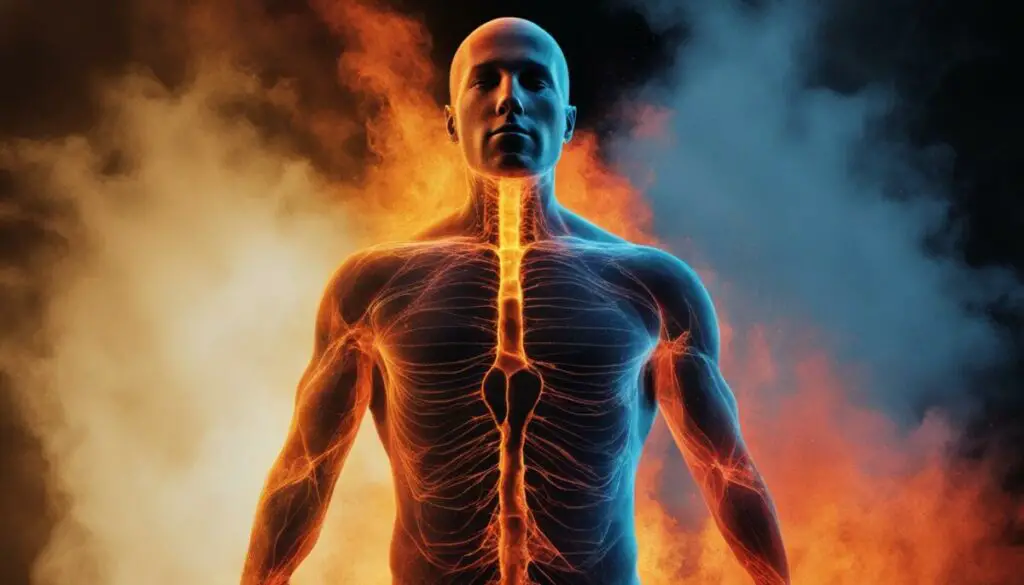
The role of infrared radiation in human thermoregulation is essential. Our bodies maintain a constant internal temperature within a narrow range of about 97.7°F to 99.5°F (36.5°C to 37.5°C). When our bodies produce excess heat from metabolic processes, the thermoregulatory system relies on sweat evaporation and radiation of heat to maintain an optimal temperature. Infrared radiation is one of the primary means by which our bodies radiate heat.
But why is this important? The ability of our bodies to regulate internal temperatures is crucial for a range of physiological functions, including enzyme activity, immunity, and metabolism. Infrared radiation plays a significant role in this process, and any disruption or abnormality of this system can result in serious health consequences.
An example of this is hyperthermia, a condition in which our body temperature rises above the normal range. This can occur due to environmental factors or an underlying medical condition. Hyperthermia can result in dehydration, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke, all of which can have severe consequences, including organ damage and death.
On the other hand, hypothermia (a condition in which our body temperature falls below the normal range) can also have significant health implications. It can result in fatigue, confusion, and even cardiac arrest in severe cases. This further emphasizes the role of infrared radiation in maintaining optimal body temperature and its significance in overall human health.
Controversies and Misconceptions
Despite the numerous scientific studies confirming the existence of human infrared emissions, there are still controversies and misconceptions surrounding this topic.
One common myth is that human infrared radiation is harmful to our health. While excessive exposure to certain types of radiation can be harmful, the level of infrared radiation emitted by the human body is relatively low and is not considered to be harmful.
Another misconception is that infrared technology can be used to diagnose illnesses or detect diseases in the human body. While infrared imaging can be a useful diagnostic tool in certain cases, it is not a substitute for traditional medical examinations and should not be relied upon as the sole means of diagnosis.
“Infrared imaging is a useful diagnostic tool, but it is not a substitute for traditional medical examinations.”
There are also controversies surrounding the use of infrared technology in security systems. Critics argue that these systems violate privacy rights and can be subject to abuse by those in positions of power. Proponents of the technology argue that it plays a crucial role in maintaining public safety and preventing crime.
Ultimately, it is important to recognize the potential benefits and limitations of infrared technology and to use it responsibly and ethically.
Future Developments in Infrared Detection
With the increasing importance of human thermal emissions in various fields, we can expect further advancements in infrared detection technology in the coming years.
One area of development is the use of wearable sensors that can measure body temperature and other physiological parameters in real-time. These sensors can provide valuable insights into the body’s thermal emissions and help detect any abnormalities or anomalies that may indicate underlying health issues.
In addition, advancements in machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence are making it possible to analyze large amounts of thermal data from human emissions. This can lead to new discoveries and insights into human physiology, as well as improve medical diagnostics and treatment.
Emerging Technologies
Several promising technologies are emerging in the field of infrared detection for human thermal emissions.
| Technology | Application |
|---|---|
| Quantum sensing | Highly sensitive detection of human thermal emissions for medical and security purposes |
| Thermography cameras | Non-invasive imaging of human thermal emissions for medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring |
| Fiber optic sensors | Real-time monitoring of body temperature and other physiological parameters |
These technologies have significant potential to advance our understanding of human thermal emissions and their role in human physiology and health.
Advantages and Limitations
Advances in infrared detection technology bring numerous advantages, including:
- Improved medical diagnostics and treatment
- Enhanced security systems
- Better environmental monitoring
- Increased understanding of human physiology
However, there are also limitations to these technologies. For example, wearable sensors may not be accurate under certain environmental conditions, and thermography cameras may not be suitable for certain medical imaging applications.
Conclusion
Infrared radiation is a significant part of the human body’s thermal emissions. As we explored in this article, humans do emit infrared radiation, and this knowledge has various applications in fields such as medicine, security, and environmental monitoring.
Emerging technologies are making it possible to measure human thermal emissions with increasing accuracy, and this has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of human physiology.
Implications for Health
The role of infrared radiation in human health is still a subject of ongoing research. However, we know that thermal emissions play a crucial part in thermoregulation, which is essential for maintaining optimal bodily functions.
Studying the patterns of human infrared emissions can provide valuable insights into the human body’s underlying physiological processes, leading to improved diagnostic techniques and treatments for various health conditions.
Misconceptions
Despite the scientific evidence supporting the existence of human infrared emissions, several misconceptions and myths surround the topic.
Some people believe that humans do not emit infrared radiation, while others claim that it can be used as a tool for weight loss. However, these beliefs are not backed by scientific evidence, and it is essential to base our understanding of human thermal emissions on robust research.
Future Developments
The field of infrared detection technology is advancing at a rapid pace, and we can expect significant developments in the coming years.
As we gain a better understanding of human thermal emissions and their implications, we can expect emerging technologies to lead to new insights and developments in human physiology. This could have significant implications for various fields, from medical diagnostics to environmental monitoring.
Overall, the study of human infrared radiation is an exciting and rapidly-evolving field, with various implications for human health and wellbeing. As technology advances, we can expect to learn more about this fascinating subject and its impact on our understanding of human physiology.
FAQ
Do humans emit infrared radiation?
Yes, humans do emit infrared radiation as a result of their thermal emissions. The human body produces heat, which is then radiated as infrared radiation.
What is infrared radiation?
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than visible light. It is associated with heat and is often referred to as “thermal radiation.”
How is infrared radiation produced by the human body?
Infrared radiation from the human body is produced through the process of thermal emissions. As the human body generates heat through metabolic processes, this heat is radiated as infrared radiation.
How is the human infrared signature detected?
The human infrared signature can be detected using specialized instruments and sensors that are sensitive to infrared radiation. These devices can analyze the heat emissions from the human body and capture the unique infrared signature.
What factors can affect the amount of infrared emissions from the human body?
Several factors can influence the amount and intensity of infrared emissions from the human body. Factors such as physical activity, body temperature, and environmental conditions can all affect the level of infrared radiation emitted.
What are the applications of human infrared radiation?
Human infrared radiation has various applications. It is utilized in medical imaging techniques such as infrared thermography, as well as in environmental monitoring and security systems that detect human heat signatures.
Are there any health implications associated with human infrared emissions?
Infrared emissions from the human body play a role in thermoregulation and can have implications for overall human health. Understanding the effects of infrared radiation on the body can help in areas such as temperature regulation and thermal comfort.
Are there any controversies or misconceptions about human infrared emissions?
There can be misconceptions and misinformation surrounding human infrared emissions. It is important to rely on scientifically-backed explanations to address any controversies or misconceptions that may arise.
What does the future hold for infrared detection technology and its impact on the study of human thermal emissions?
As technology continues to advance, we can expect further developments in the detection and analysis of human thermal emissions. Emerging technologies in infrared detection may lead to new insights and advancements in our understanding of human physiology.