Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
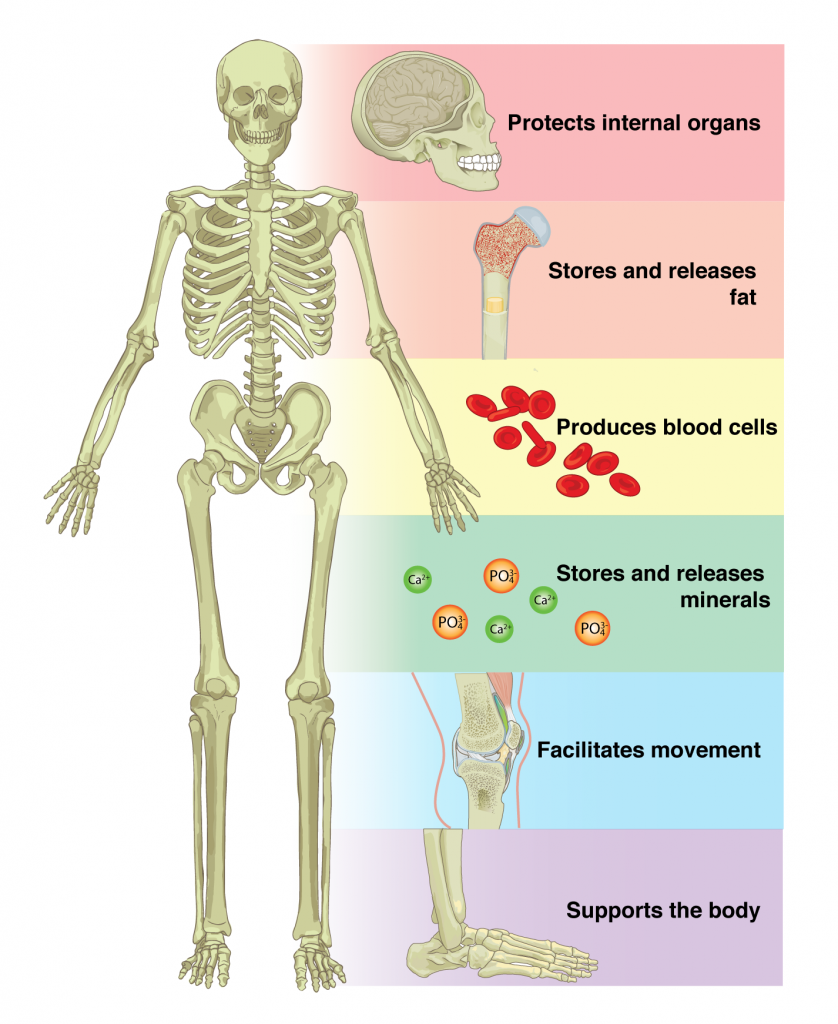
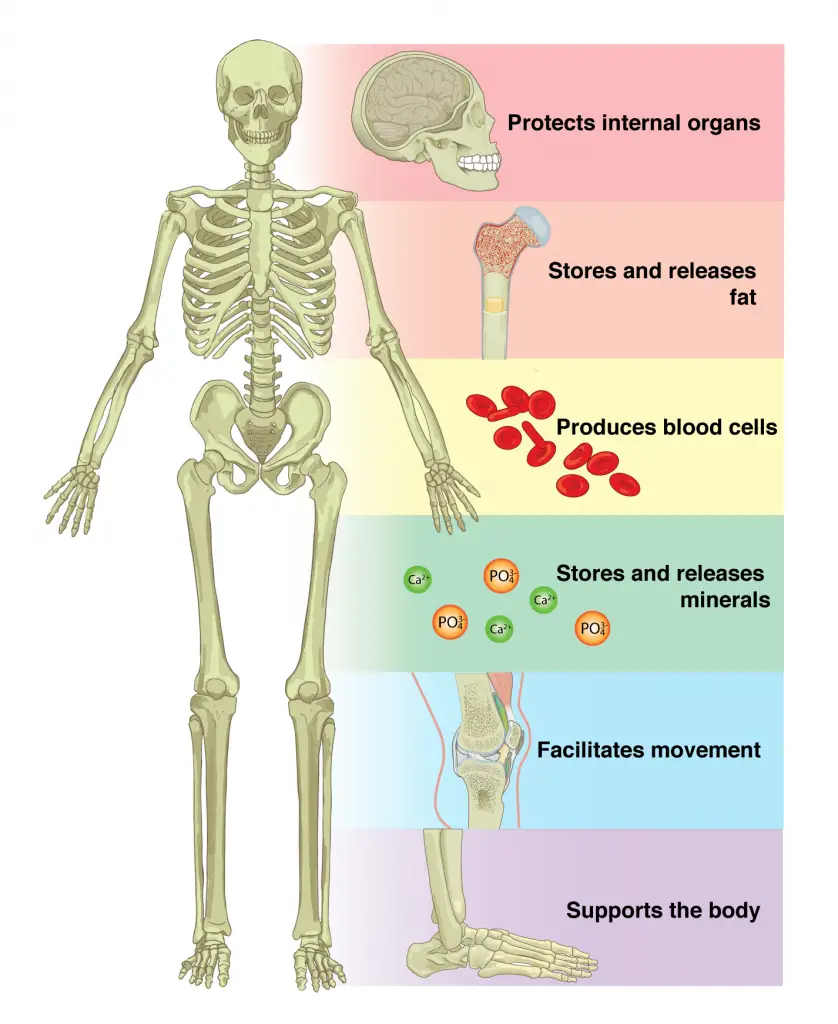
The skeletal system plays a vital role in the functioning of our body. It is the framework that provides structure, support, and protection to our organs and tissues. It is also responsible for movement, producing red blood cells, and storing minerals. In this article, we will explore the various functions of the skeletal system and how they affect our lives.
The skeletal system is the body’s framework that provides structure and support, allowing us to move in many ways. It also protects our internal organs and produces blood cells. The skeletal system is made up of bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments.
The bones provide strength and stability, while the cartilage and tendons allow us to move and flex our joints. The ligaments connect the bones together and keep them in place. The skeletal system also produces red and white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections and other diseases.
In addition, the skeletal system stores minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are important for keeping our bones strong and healthy. Without the skeletal system, we would be unable to move and our internal organs would be unprotected.
Contents
Overview of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is made up of bones, joints, and cartilage. It serves several important functions, including providing structure and support for the body, protecting vital organs, providing movement, and storing minerals. The bones of the skeletal system are held together by ligaments and tendons, which are flexible bands of tissue connecting the bones. The skeletal system also provides a framework for the attachment of muscles.
Support and Protection
The skeletal system provides structure and support for the body. It holds the body together and gives it shape. The bones also protect internal organs, such as the brain, heart, and lungs. The rib cage protects the heart and lungs, while the skull protects the brain. The vertebrae of the spinal column protect the spinal cord.
The skeletal system also provides stability and balance. It helps to absorb shock and reduces the risk of injuries from falls and other impacts.
Movement and Storage
The skeletal system enables movement by providing a frame for the attachment of muscles. Muscles, in turn, contract and relax to move the bones, which allows for body movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
The skeletal system also serves as a storage site for minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are essential for the growth and repair of bones and teeth.
Types of Skeletal Systems
The human skeletal system is made up of 206 bones. It is divided into two main parts: the axial skeleton, which consists of the skull, spine, and rib cage, and the appendicular skeleton, which consists of the arms, legs, and pelvis.
The axial skeleton provides the main support for the body and houses the major organs. The appendicular skeleton provides the frame for the attachment of the arms, legs, and pelvis, enabling movement.
Cartilage and Connective Tissue
The bones of the skeletal system are connected by ligaments and tendons, which are flexible bands of tissue connecting the bones. The skeletal system also includes cartilage, which is a type of connective tissue that cushions the joints and provides support.
The skeletal system also includes other connective tissues, such as ligaments and tendons, which give the body strength and flexibility.
Growth and Repair
The skeletal system is constantly growing and changing. During childhood and adolescence, bones grow and lengthen as the body develops. The bones also undergo remodeling and repair throughout life, as they are constantly being broken down and rebuilt.
The bones of the skeletal system are constantly renewing themselves. They are constantly being broken down and rebuilt to maintain healthy bones and joints.
Diseases and Disorders
The skeletal system can be affected by a variety of diseases and disorders, such as osteoporosis, arthritis, and bone cancer. These diseases and disorders can cause pain and discomfort and can lead to fractures and other complications.
The skeletal system can also be affected by injuries. Traumatic injuries such as fractures, sprains, and strains can cause pain and can interfere with normal function. It is important to receive prompt treatment for any injury to the skeletal system.
Conclusion
The skeletal system serves several important functions, including providing structure and support for the body, protecting vital organs, providing movement, and storing minerals. It is composed of bones, joints, and cartilage and is held together by ligaments and tendons. The skeletal system is constantly growing and changing throughout life and can be affected by a variety of diseases and disorders. It is important to take good care of the skeletal system to maintain good health and prevent injuries and other complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Function of the Skeletal System?
Answer: The skeletal system is the body’s structural framework that provides support, stability, and movement to the body. Its primary functions are to protect the vital organs, store minerals, produce blood cells, and provide a mechanical advantage for movement.
What Is the Structure of the Skeletal System?
Answer: The skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Bones are rigid and strong organs that form the structural framework of the body. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that cushions bones and joints. Ligaments are tough fibrous bands that connect bones together and hold them in place. Tendons are dense fibrous bands that attach bones to muscles.
What Are the Major Divisions of the Skeletal System?
Answer: The skeletal system is divided into two major divisions: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum. The appendicular skeleton includes the shoulder girdle, pelvic girdle, and the bones of the upper and lower limbs.
What Are the Functions of the Skeletal System?
Answer: The skeletal system has many important functions. It provides support and stability for the body, protects the vital organs, stores minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, produces blood cells, and provides a mechanical advantage for movement. It also houses the sensory organs of hearing and balance, and is the site of attachment for muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
What Are the Different Types of Bones?
Answer: Bones can be classified into four different types: long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones. Long bones are typically found in the arms and legs and are responsible for movement. Short bones are small and cube-like, and are found in the wrists and ankles. Flat bones are thin and curved, and are found in the skull and shoulder blades. Irregular bones have unique shapes, and are found in the vertebrae and hip bones.
What Are Joints and What Do They Do?
Answer: Joints are the points of connection between two or more bones. They are made up of ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, and they provide flexibility and movement to the body. Joints also allow for the absorption of shock and vibration, and they help to maintain posture. There are three main types of joints: immovable, slightly movable, and freely movable. Immovable joints are found in the skull, and slightly movable joints are found in the vertebrae. Freely movable joints are found in the limbs and allow for more complex movement.
The Skeletal System – Skeletal System Functions – Skeletal System Basics
The skeletal system is a complex and vitally important component of the human body. It provides us with the structure and support necessary for movement, protection for the body’s organs, and housing for bone marrow which produces red blood cells. The bones provide stability and strength, while the muscles and ligaments help to connect the skeleton to the body’s tissues. The skeletal system also serves as a reservoir for essential minerals and salts, and helps to regulate calcium levels in the blood. In short, the skeletal system is essential for life, and it is important to take care of it.



.jpg)

