Last Updated on 7 months by Francis
Did you know that drinking alcohol can potentially affect the accuracy of blood tests for tuberculin in resistant tuberculosis patients? When preparing for a tuberculosis test, many people have questions about informed consent and the blood tests involved. It’s important to be well-informed and aware of any potential problems that may arise during the procedure.
It is crucial to follow certain guidelines. One such guideline is avoiding alcohol consumption and smoking before undergoing blood tests. It is important to refrain from drinking ethanol or any alcoholic beverages prior to the test. While it may be tempting to unwind with a drink or two, studies have shown that alcohol can interfere with the immune system and impact the accuracy of tuberculosis screenings, such as the tuberculin skin test and blood test, which are important for detecting tb infection and ensuring public health.
In the following sections, we will explore why drinking alcohol should be avoided before a resistant tuberculosis treatment test, how it affects your body’s response to antituberculosis drugs, and what steps you can take to ensure reliable results for resistant tuberculosis cases. So if you’re curious about whether drinking alcohol can influence your TB test outcome and the attributable tuberculosis incidence, resistant tuberculosis cases, and the attributable tuberculosis burden, keep reading to learn more about resistant tuberculosis treatment!

Contents
Alcohol consumption as a risk factor for tuberculosis
Excessive drink of alcohol, or ethanol intake, can have detrimental effects on our health, and one area where it poses a significant risk is in relation to tuberculosis (TB) disease control. TB is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs of patients. One way to assess the severity of TB and predict mortality is through a blood test. Additionally, multidrug therapy is often used to treat TB. It is important to understand how alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing active TB, as it can contribute to the attributable tuberculosis burden. Additionally, alcohol consumption may also impact the resistant tuberculosis cases and their treatment.
Weakening the immune system
One of the key reasons why excessive alcohol consumption increases the risk of tuberculosis is its impact on the immune system. Drinking can worsen the resistant tuberculosis treatment and contribute to the overall attributable tuberculosis burden and incidence. Alcohol weakens our body’s natural defense mechanisms, making us more susceptible to infections like resistant tuberculosis. Regular heavy drinking can compromise our immune response, impairing its ability to fight off pathogens effectively. This can contribute to the disease burden and incidence of attributable tuberculosis.
Increased risk of active tuberculosis
Studies have shown that regular heavy drinking significantly increases the likelihood of developing active tuberculosis (TB), leading to a higher attributable tuberculosis incidence and burden. In fact, alcohol abuse is considered one of the major modifiable risk factors for this disease, impacting resistant tuberculosis treatment and contributing to tuberculosis mortality. The more alcohol an individual drinks, the higher their chances are of developing active TB if they come into contact with the bacteria. This can contribute to an increase in the attributable tuberculosis incidence and burden. It is important to consider the impact of alcohol consumption on resistant tuberculosis treatment.
Impact on resistant tuberculosis
Alcohol consumption also plays a role in increasing drug-resistant cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) disease. Drinking ethanol can contribute to the development of drug resistance in TB. When patients who drink excessive amounts of alcohol contract TB, they are less likely to adhere to treatment regimens for multidrug-resistant disease and complete their prescribed course of antituberculosis drugs. This non-compliance can lead to drug resistance in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, making it more challenging to treat and control the spread of the disease burden of tuberculosis.
High burden countries and attributable mortality
In countries with a high burden of tb disease, excessive alcohol consumption exacerbates the problem further for tb patients. These regions often face challenges in terms of healthcare infrastructure and resources, which are already strained due to the high tuberculosis burden and incidence rates. Alcohol-related behaviors significantly contribute to the incidence and mortality of tb disease in areas with multidrug-resistant tb patients, increasing the risk for tb patients.
Addressing the issue
To combat the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption and its impact on tuberculosis (TB), it is crucial to raise awareness about TB disease among TB patients. Additionally, it is important to address the issue of multidrug-resistant TB and promote the use of the TB skin test. Public health initiatives should focus on educating individuals about the dangers of heavy drinking and its connection to tuberculosis (TB), especially in regions with a high tuberculosis burden and incidence. Encouraging responsible alcohol use is crucial in preventing the spread of drug-resistant tuberculosis and ensuring effective tuberculosis treatment.
Effects of alcohol on TB test results
Drinking alcohol before a tuberculosis treatment (TB) skin test or blood test does not directly impact the accuracy of the results for resistant tuberculosis patients, according to studies. However, it is important to understand how chronic alcohol use may affect the reliability of certain tests and why disclosing your alcohol consumption habits to healthcare providers is crucial for proper interpretation of results. Numerous studies and analyses have shown that chronic alcohol use can cause problems with test accuracy, making it essential to inform healthcare providers about your drinking habits for accurate interpretation of results.

Weakened Immune Response
Chronic alcohol use can weaken the immune response, increasing the risk of infections, including multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, according to studies. This weakened immune system can potentially affect the reliability of certain tuberculosis (TB) tests, such as sputum smear tests, in patients with resistant tuberculosis. This is concerning given the high tuberculosis burden and incidence rates. These tests involve examining a sample of sputum smear, or mucus coughed up from the lungs, for the presence of resistant tuberculosis bacteria. This is an important step in assessing the tuberculosis burden and tuberculosis incidence in a population.
Impact on Sputum Smear Results
When someone consumes excessive amounts of alcohol over an extended period, they may be at risk for developing multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, according to a study. Their immune system may become compromised. As a result, tb patients’ body’s ability to fight off multidrug-resistant infections, including tuberculosis, may be impaired. This can be determined through a tb skin test or sputum smear. This weakened immune response can lead to false-negative sputum smear results in patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, increasing the burden of tuberculosis incidence.
A false-negative sputum smear result means that even if tb patients have active tuberculosis, the test fails to detect it. Multidrug analyses. Consequently, this could delay diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, potentially posing risks not only to the individual but also to those around them. The tuberculosis burden is a significant concern in this context.
Threshold Effect
It’s important to note that while chronic alcohol use may weaken the immune response and affect certain TB tests’ reliability, it can pose a higher risk for patients with resistant tuberculosis. Additionally, this can contribute to the overall tuberculosis burden. However, there is often a threshold effect. This means that moderate alcohol consumption or occasional drinking is unlikely to have a significant impact on test results for patients. Multiple studies and risk analyses have shown this.
However, when patients regularly consume excessive amounts of alcohol or suffer from alcoholism, their risk of tuberculosis burden increases substantially, according to studies on multidrug-resistant strains. In these cases, it becomes even more crucial for healthcare providers to be aware of their patients’ alcohol use and drinking habits in order to interpret test results accurately. Healthcare providers should consider conducting thorough analyses and studies on the patients’ alcohol dosage.
Importance of Disclosure
To ensure accurate interpretation and appropriate treatment decisions regarding tuberculosis infection, it is vital for patients undergoing sputum smear testing to honestly disclose their alcohol consumption habits. This is crucial in assessing the risk and determining the appropriate multidrug treatment. By providing healthcare providers with this information, they can consider the potential impact of alcohol on patients’ test results and make informed decisions based on the risk analyses accordingly.
Disclosing alcohol consumption allows healthcare providers to assess the patients’ overall health status more comprehensively. This is important for conducting analyses and studies on tuberculosis burden. The analyses of sputum smear in patients help them understand any potential factors that may affect test results and tailor treatment plans accordingly. These meta-analyses provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals.
Managing side effects of a TB test
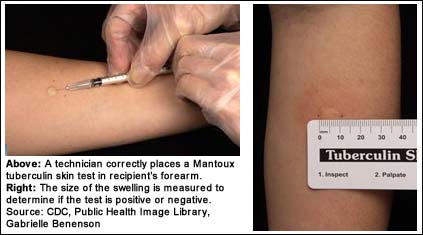
Common side effects after a TB skin test include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site.
After undergoing a TB skin test, patients with resistant tuberculosis may experience certain side effects, such as sputum smear positivity. It is important for healthcare providers to inquire about alcohol use in these patients. These symptoms can occur in patients who have alcohol use disorder and are diagnosed with resistant tuberculosis. The symptoms can include redness, swelling, and itching at the site where the sputum smear injection was given. This immune response occurs in patients with resistant tuberculosis due to the tuberculin protein that was injected under your skin. The reaction can be analyzed through sputum smear analyses. It is important to note that these side effects of alcohol use are generally mild and temporary. These side effects have been studied through meta-analyses, which analyze the effects of alcohol dosage on the body.
Applying a cold compress can help alleviate discomfort from these side effects.
If you find yourself experiencing discomfort from the side effects of a TB skin test for resistant tuberculosis, there are simple steps you can take to alleviate it. These steps include managing sputum and smear conversion, as well as avoiding alcohol use. One effective method for promoting alcohol use is applying a cold compress to the injection site in patients with resistant tuberculosis. This can help with smear conversion. Alcohol use can help reduce redness, swelling, and itching by constricting blood vessels in the area. This is especially beneficial for individuals with alcohol use disorder who may experience these symptoms. Additionally, alcohol use can also be effective in reducing the smear and sputum production associated with respiratory infections. Furthermore, it has been found that alcohol use can play a role in the conversion of tuberculosis infection to active disease. You can use a clean cloth or ice pack wrapped in a towel and gently apply it to the affected area for short intervals. This method is particularly useful for patients undergoing smear analyses or sputum tests to detect resistant tuberculosis.
If experiencing severe symptoms or an allergic reaction, seek medical attention immediately.
While most individuals only experience mild side effects after a TB skin test, there is still a possibility of more severe symptoms or even an allergic reaction occurring, especially in cases of resistant tuberculosis. It is important to note that the test requires a smear of sputum, and alcohol use may affect the accuracy of the results. If you notice any alarming signs such as intense pain, excessive swelling, difficulty breathing, or hives developing on your body after undergoing the sputum smear test for resistant tuberculosis, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate an adverse reaction related to alcohol use that requires prompt evaluation and treatment by healthcare professionals. This is particularly important when dealing with resistant tuberculosis, as alcohol use can complicate the analyses of sputum smear samples.
It’s important not to ignore any unusual reactions following a TB skin test, especially for individuals at risk of resistant tuberculosis. These reactions could be indicative of other underlying conditions or allergies that need medical intervention. Therefore, thorough analyses should be conducted to determine the cause of the reactions and appropriate actions taken accordingly. Additionally, it’s essential to consider factors such as alcohol use, as it can potentially impact the test results and overall diagnosis.
Risks and contraindications of alcohol consumption before a TB test
Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol before undergoing a tuberculosis (TB) test can smear the results and hinder conversion. This can pose potential risks and contraindications. It is important to be aware of factors such as smear and alcohol use to ensure accurate test results and proper diagnosis for resistant tuberculosis.
Masking Symptoms and Delayed Diagnosis
Excessive alcohol consumption prior to a smear test for tuberculosis may mask the symptoms of resistant tuberculosis, potentially leading to delayed diagnosis and hindered conversion. Alcohol can suppress the immune system, making it difficult for the body to fight off infections effectively, including resistant tuberculosis. This can delay the conversion of smear-positive patients. This suppression can hide the symptoms of resistant tuberculosis, such as coughing, chest pain, fatigue, and weight loss. It is important to note that alcohol use can also contribute to the development of resistant tuberculosis. Additionally, the smear test is commonly used to diagnose tuberculosis and monitor treatment progress, including conversion from positive to negative results. As a result, individuals with resistant tuberculosis who consume alcohol heavily before getting tested may not exhibit clear signs of the infection during the smear diagnostic process. However, it is important to monitor their progress and ensure timely conversion.
Adverse Interactions with Medications
Certain medications used in conjunction with TB tests may have adverse interactions with alcohol, especially in cases of resistant tuberculosis. It is important to note that alcohol consumption can hinder smear conversion. Some diagnostic procedures for resistant tuberculosis require specific medications or contrast agents that are sensitive to alcohol consumption. These procedures often involve the examination of sputum samples for the presence of smear, which helps in diagnosing the disease accurately. Mixing alcohol with resistant tuberculosis medication or smear substances can lead to unpredictable reactions or interfere with the effectiveness of the medication. In some cases, consuming alcohol before a tuberculosis (TB) smear test may render certain medications for tuberculosis less potent or even ineffective.
Abstaining from Alcohol Before Diagnostic Procedures
To ensure accurate smear results and avoid any potential complications, it is advisable to abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages at least 24 hours before undergoing any tuberculosis diagnostic procedures. By refraining from alcohol consumption, individuals allow their bodies to function optimally without interference from substances like alcohol that could affect tuberculosis and smear test outcomes.
Abstaining from alcohol before a tuberculosis (TB) smear test helps healthcare professionals accurately assess an individual’s health condition by ensuring that symptoms are not masked by intoxication effects or compromised by medication interactions.
In addition to avoiding alcohol consumption prior to a tuberculosis (TB) smear test, there are other considerations individuals should keep in mind.
-
Always follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding pre-test preparations for tuberculosis, including dietary restrictions and medication guidelines.
-
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water before a tuberculosis (TB) smear test can help ensure accurate results and make the testing process smoother.
-
Communicate openly with healthcare providers: Inform your healthcare provider about any medications, supplements, substances, tuberculosis, or smear you have consumed recently to ensure they have a comprehensive understanding of your health status.
By being mindful of these factors and taking necessary precautions, individuals can contribute to the accuracy and effectiveness of their tuberculosis (TB) smear tests. It is important to prioritize one’s health by making informed decisions regarding alcohol consumption and following medical advice for tuberculosis and smear.
Can a person drink alcohol after taking a TB test?
After completing a standard tuberculosis (TB) skin or blood test, there are no specific restrictions on consuming alcohol. Smear tests are not necessary in this case. However, it is always best to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding post-test activities, especially if you have been tested for tuberculosis. While alcohol itself does not interfere with the accuracy of tuberculosis test results, there are a few factors to consider.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions
After taking a tuberculosis test, it is essential to follow the guidance provided by your healthcare provider. They may have specific recommendations based on your individual circumstances or any additional tests you may need for tuberculosis. It’s important to remember that everyone’s situation, including those affected by tuberculosis, can be different. So, what works for one person dealing with tuberculosis may not be suitable for another.
Medication interactions
If you have been prescribed tuberculosis medication as part of your TB treatment plan, it is essential to check for any potential interactions with alcohol. Some medications used in tuberculosis treatment can have adverse effects when combined with alcohol consumption. Alcohol can interfere with the effectiveness of tuberculosis drugs or increase their side effects.
To ensure the safety and efficacy of your tuberculosis treatment, consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist about any possible interactions between your medication and alcohol. They will provide you with accurate tuberculosis information and guidance tailored to your specific tuberculosis situation.
General considerations
While drinking alcohol after a tuberculosis (TB) test may not directly impact the accuracy of the results, it is essential to consider some general factors.
-
Moderation: If you choose to consume alcohol after taking a tuberculosis (TB) test, do so in moderation. Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system and make it harder for your body to fight infections, including tuberculosis.
-
Overall health: Consider whether drinking alcohol aligns with your overall health goals, lifestyle choices, and tuberculosis. If you have concerns or medical conditions related to tuberculosis, speak with your healthcare provider about how alcohol fits into your overall health plan.
-
Recovery process: If you are undergoing treatment for tuberculosis, it’s vital to prioritize rest and recovery. Alcohol can potentially disrupt your sleep patterns and hinder the healing process of tuberculosis.
Remember, it is always best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding alcohol consumption after a tuberculosis (TB) test. They can provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date information on tuberculosis based on your individual circumstances.
Understanding treatment outcome definitions for TB cases
In tuberculosis (TB) treatment, the outcomes of patients are classified into different categories to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and determine if it was successful. These tuberculosis treatment outcome definitions help healthcare professionals evaluate the progress made by individuals undergoing TB therapy.
Treatment Outcomes for TB Cases
The various treatment outcomes for tuberculosis can be categorized as follows:
-
Cured: This outcome indicates that the individual has successfully eliminated the tuberculosis bacteria from their body, effectively treating tuberculosis. It means that they have completed their prescribed course of tuberculosis medication and subsequent tuberculosis tests show no evidence of tuberculosis disease.
-
Completed Treatment: When a person completes their full course of tuberculosis (TB) treatment without any evidence of disease, they fall under this category. Although they may not have been cured of tuberculosis, completing the entire treatment regimen is still considered a positive outcome.
-
Tuberculosis Treatment Failure: Unfortunately, some individuals do not respond adequately to tuberculosis treatment, leading to an unsuccessful outcome. Treatment failure occurs when there is persistent or recurrent active tuberculosis (TB) disease despite receiving appropriate therapy.
-
Defaulting refers to individuals who interrupt their tuberculosis (TB) treatment for two consecutive months or more after starting therapy. This interruption in tuberculosis treatment can significantly impact tuberculosis treatment outcomes and may lead to increased tuberculosis drug resistance and potential tuberculosis complications.
Importance of Defining Treatment Outcomes
Defining clear-cut criteria for different treatment outcomes in tuberculosis cases is crucial for several reasons:
-
Evaluation: By establishing specific definitions, healthcare providers can effectively evaluate how well tuberculosis patients are responding to treatment and identify areas where adjustments may be necessary.
-
Comparisons: Standardized definitions enable consistent comparisons between different patient populations, settings, and time periods for tuberculosis. This allows tuberculosis researchers and public health officials to analyze tuberculosis trends and make informed decisions about tuberculosis interventions and tuberculosis resource allocation.
-
Monitoring Progress: Clear outcome definitions facilitate accurate monitoring of tuberculosis progress at both individual and population levels. They help track success rates, identify areas requiring improvement, and measure overall program effectiveness in combating tuberculosis.
Analyzing Treatment Outcome Data
To assess tuberculosis treatment outcomes, data from individuals undergoing tuberculosis treatment is collected and analyzed. This information provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of current tuberculosis treatment protocols and helps guide future interventions for tuberculosis. Some key aspects of analyzing treatment outcome data include:
-
Treatment outcome analyses often focus on incident tuberculosis cases, which are newly diagnosed TB patients who have initiated therapy. By examining these tuberculosis cases, researchers can determine the success rates of different tuberculosis treatment approaches.
-
Analyzing unsuccessful tuberculosis treatment outcomes, such as treatment failure or default, helps identify factors contributing to suboptimal results. This information can guide efforts to improve patient adherence, enhance healthcare delivery systems, and develop more effective treatments.
-
Results Interpretation: The interpretation of treatment outcome data requires careful consideration of various factors such as patient demographics, comorbidities, drug resistance patterns, and healthcare access. These factors influence the overall success rates observed in different populations.
Alcohol and TB testing: What you need to know
In conclusion, it is important to understand the impact of alcohol consumption on TB testing. Alcohol can affect the accuracy of the test results, potentially leading to false negatives or false positives. Alcohol can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to tuberculosis. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid drinking alcohol before a TB test to ensure accurate results and maintain a strong immune system.
To prioritize your health and obtain reliable results from a TB test, it’s crucial that you abstain from consuming alcohol beforehand. Remember, your well-being should always be your top priority. If you have any concerns or questions about alcohol and TB testing, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Stay informed and take proactive steps towards maintaining good health.
FAQs
Can I drink alcohol after taking a TB test?
After taking a TB test, it is generally safe to consume alcohol. However, it’s important to listen to your body and consider any potential side effects or interactions with medications you may be taking. It’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider for specific guidance based on your individual circumstances.
How long should I wait before drinking alcohol after a TB test?
There isn’t a specific waiting period mentioned regarding drinking alcohol after a TB test in general. However, if you have received any medication or treatment related to tuberculosis along with the test, it’s advisable to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding when you can resume consuming alcoholic beverages.
Can I drink in moderation before a TB test?
It is recommended to avoid consuming any amount of alcohol before a TB test as even moderate consumption can affect the accuracy of the results. To ensure reliable outcomes and minimize potential risks associated with tuberculosis detection, it is best practice not to drink any alcoholic beverages prior to the test.
Are there any alternative tests available that do not require abstinence from alcohol?
Currently, there are no alternative tests available for tuberculosis that do not require abstinence from alcohol. To ensure accurate and reliable results, it is necessary to follow the guidelines provided by healthcare professionals, which often include abstaining from alcohol consumption before undergoing a TB test.
Can drinking alcohol increase the risk of developing tuberculosis?
Yes, consuming alcohol can increase the risk of developing tuberculosis. Alcohol weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections such as TB. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of contracting tuberculosis and other diseases.

.jpg)





