Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Earth is a fascinating planet full of mysteries, and one of the most interesting questions we can ask is: what is Earth’s charge? We have known for centuries that the Earth is electrically charged, but what causes this charge and how does it affect our everyday lives? In this article, we will explore the science behind Earth’s charge, how it has been studied, and what its effects are on our world. We will also consider some of the potential implications of Earth’s charge for the future. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of Earth’s charge and its role in the environment.
Earth has a net negative charge due to the abundance of electrons relative to protons in its components. It is mainly caused by the attraction of electrons to the positive charge of the protons. This overall negative charge is balanced out by the positive charge of the Earth’s surface. The Earth’s charge can also be affected by solar wind, cosmic rays, and other external influences.
The Earth’s charge helps to create the atmosphere, by controlling the flow of ions and electrons, and it also plays a role in the formation of lightning and other electrical phenomena. Additionally, it affects the levels of radiation on the planet and the rate at which the atmosphere is heated.
Contents
Overview of Earth’s Charge
Earth’s charge is an important part of the electrical environment of our planet. It is the total electric charge that is held by the Earth and its atmosphere. This charge is generated by the continual bombardment of cosmic rays, lightning strikes and other sources. Earth’s charge is also affected by the magnetosphere, which is created by the Earth’s magnetic field. The charge is constantly changing due to the interaction of the Earth with the Sun, Moon, and other bodies in the Solar System.
Earth’s charge consists of both positive and negative charges. The positive charges are held in the atmosphere by air molecules, while the negative charges are held in the Earth’s outer layers. This charge is constantly changing in response to the forces of nature. For instance, during an electrical storm, the charge of the atmosphere increases due to the billions of electrons and protons that are generated by lightning strikes.
The charge of the Earth is also affected by the cycle of the seasons. During the summer months, the temperature of the atmosphere increases, which results in a higher charge in the atmosphere. During the winter months, the temperature decreases and the charge in the atmosphere decreases.
The Magnitude of Earth’s Charge
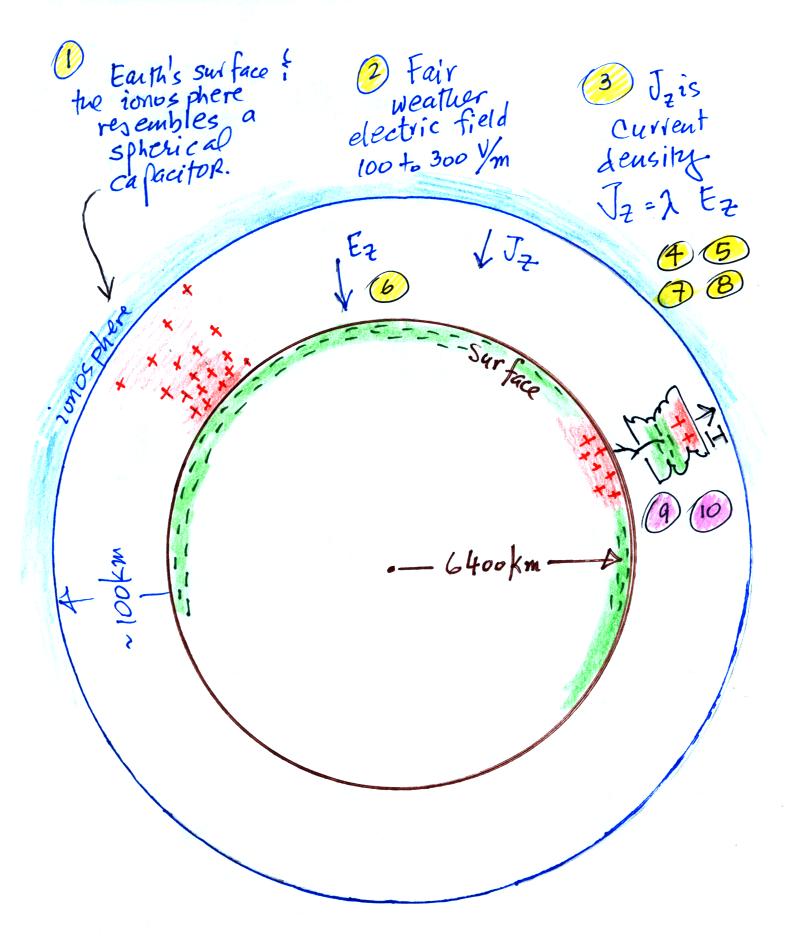
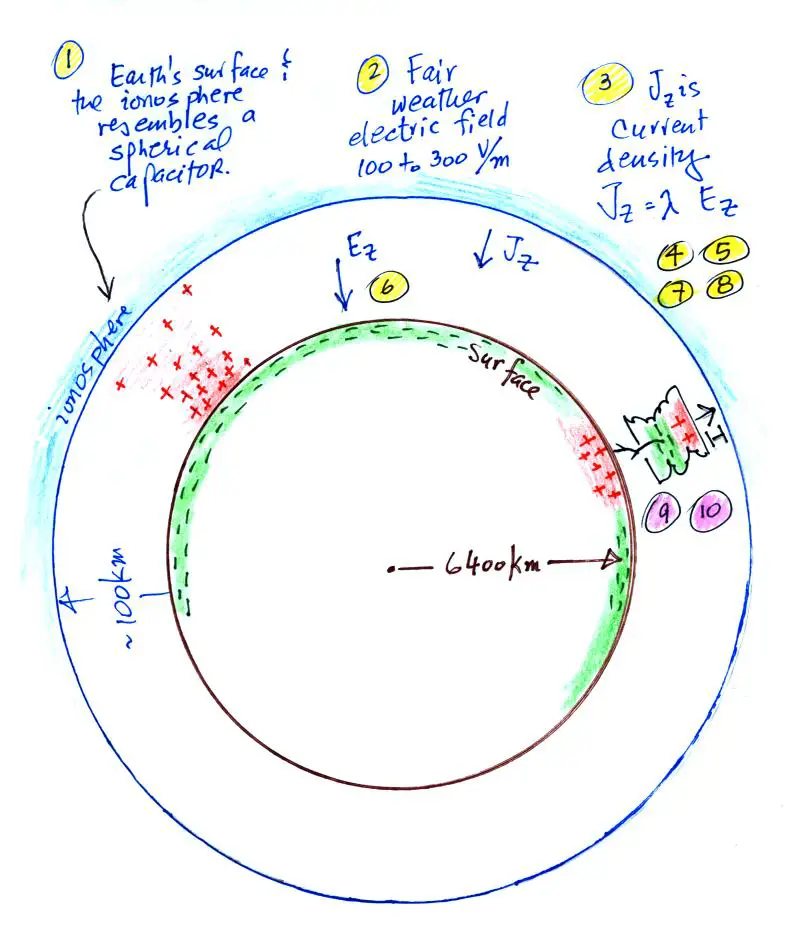
The magnitude of Earth’s charge can be measured by the electric field strength. This is measured in volts per meter (V/m). The average electric field strength at the Earth’s surface is about 150 V/m. This is about one-tenth the strength of the electric field of a small battery.
The Earth’s charge can also be measured by its electric potential. This is measured in volts (V). The electric potential of the Earth’s surface is around 220 V. This is about one-sixth the electric potential of a small battery.
The charge of the Earth is also affected by the magnetosphere. The magnetosphere is created by the Earth’s magnetic field, which is generated by the Earth’s spinning core. The strength of the magnetosphere decreases with distance from the Earth, so the magnetosphere is strongest near the Earth’s surface.
Impact of Earth’s Charge on Life
The charge of the Earth has a significant effect on all forms of life. Plants, animals, and humans all rely on the electrical environment of the Earth to maintain their physiological functions. The electric field of the Earth helps to create the electrochemical reactions that drive the processes of life.
The electric field of the Earth also plays an important role in the navigation of animals. Many animals, such as birds, use the Earth’s electric field to help them find their way. The electric field of the Earth is also important for the migration of animals, as it helps them determine the direction they need to travel.
The Space Environment and Earth’s Charge
The space environment has a major influence on Earth’s charge. The space environment is filled with charged particles, such as protons and electrons, which can interfere with the Earth’s electric field. These particles can reduce the electric field of the Earth and can also cause fluctuations in the electric potential of the Earth.
The space environment also affects the Earth’s magnetosphere. The space environment is filled with magnetic fields, which can disrupt the magnetosphere of the Earth. This can result in changes in the electric potential of the Earth and can also cause fluctuations in the electric field of the Earth.
Solar Activity and Earth’s Charge
Solar activity has a major impact on Earth’s charge. Solar activity is the release of energy from the Sun, which results in the emission of charged particles. These particles can interfere with the Earth’s electric field and can also cause fluctuations in the electric potential of the Earth.
Solar flares and coronal mass ejections can also have a major impact on the Earth’s charge. These events can cause the electric field of the Earth to fluctuate and can also cause the electric potential of the Earth to fluctuate.
Effects of Human Activity on Earth’s Charge
Human activity can also have an effect on Earth’s charge. The use of technology, such as power lines, can interfere with the electric field of the Earth. This can cause the electric field of the Earth to fluctuate and can also cause the electric potential of the Earth to fluctuate.
The use of technology can also affect the magnetosphere of the Earth. The use of high-powered electromagnetic fields, such as cell phone towers, can interfere with the Earth’s magnetosphere. This can result in changes in the electric potential of the Earth and can also cause fluctuations in the electric field of the Earth.
Conclusion
Earth’s charge is an important part of the electrical environment of our planet. It is the total electric charge that is held by the Earth and its atmosphere. This charge is generated by the continual bombardment of cosmic rays, lightning strikes and other sources. Earth’s charge is also affected by the magnetosphere, which is created by the Earth’s magnetic field. The magnitude of Earth’s charge can be measured by the electric field strength and electric potential. The charge of the Earth has a significant effect on all forms of life, as it helps to create the electrochemical reactions that drive the processes of life. The space environment and human activity can also have an effect on Earth’s charge.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Earth’s Charge?
Earth’s charge is a term used to describe the net electrical charge of the Earth’s atmosphere and the Earth’s surface. It is the result of the accumulation of electrical charges from sources such as thunderstorms, lightning, solar radiation, and the static electricity generated by the Earth’s rotation.
What Factors Contribute to Earth’s Charge?
Earth’s charge is the result of several factors. Thunderstorms, lightning, and solar radiation all contribute to Earth’s charge. Additionally, the static electricity generated by the Earth’s rotation also plays a role in the accumulation of electrical charges. Additionally, the electric fields created by the Earth’s atmosphere, and the electric and magnetic fields created by the Earth’s core, both contribute to Earth’s charge.
What is the Impact of Earth’s Charge?
The impact of Earth’s charge is far-reaching. It affects the behavior of particles in the atmosphere, such as the formation of clouds and precipitation. It also affects the behavior of animals and humans, as it can cause humans to experience static electricity shocks. Additionally, Earth’s charge plays a role in the formation of Earth’s magnetic field, which serves to protect the planet from harmful cosmic radiation.
How is Earth’s Charge Measured?
Earth’s charge is typically measured using techniques such as radio wave measurements, satellite imagery, and radar measurements. Additionally, ground-based instruments such as magnetometers, electrostatic probes, and electrostatic field mills can be used to measure Earth’s charge.
What is the Difference Between Earth’s Charge and Global Electric Circuit?
Earth’s charge is the net electric charge of the Earth’s atmosphere and surface, while the global electric circuit is the path taken by electricity throughout the Earth’s atmosphere. In the global electric circuit, electricity is moved around the Earth by lightning, thunderstorms, and other electric phenomena. This electricity is then redistributed throughout the atmosphere and Earth’s surface.
What is the Significance of Earth’s Charge?
Earth’s charge is important for a variety of reasons. It affects the behavior of particles in the atmosphere, which in turn affects the formation of clouds and precipitation. Additionally, Earth’s charge plays a role in the formation of Earth’s magnetic field, which helps to protect the planet from cosmic radiation. Finally, Earth’s charge is important for the safety of humans and animals, as it can cause humans to experience static electricity shocks.
Is the Earth Negatively Charged – Answers to Questions – RSD Academy
Earth’s charge is a fascinating concept that raises many questions. Our planet is full of electricity and magnetism, and these forces are key to many of the world’s natural phenomena. We may never fully understand the complicated relationship between the Earth’s charge and its many effects, but it is an exciting field of exploration that has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the world around us. As we continue to learn more about Earth’s charge, we can move closer to unlocking its secrets and unlocking the potential of the world to come.


.jpg)
.jpg)



