Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Have you ever wondered what the white matter in the brain does? It’s an important part of the brain and plays a crucial role in the functioning of the nervous system. In this article, we’ll explore the functions of the white matter in the brain and how it works to regulate and control the body’s functions. We will also examine how white matter damage can affect the brain and body, and how it can be treated. So, if you’re curious about the white matter in the brain and want to learn more about its role in the body, then read on!
The white matter in the brain is responsible for communication between different regions of the brain. It consists of nerve fibers that connect the neurons together and enable them to communicate with each other. The white matter also helps in controlling the timing and intensity of neural signals. It is also important for memory formation and learning.

Contents
What Does White Matter do in the Brain?
White matter is an essential component of the brain that helps it communicate and function properly. It is composed of nerve fibers that carry signals from one part of the brain to another and is responsible for the transmission of information between different areas of the brain. White matter serves as a bridge between the gray matter (where most of the neurons are located) and the rest of the nervous system. It is essential for the proper functioning of the brain and plays a crucial role in cognition, learning, and memory.
Role of White Matter in Cognitive Function
White matter is involved in the processing of information in the brain, allowing for the communication of signals between different areas of the brain. This is especially important for higher cognitive functions such as learning, decision-making, and problem-solving. By aiding in the transmission of signals, white matter enables the brain to form new connections, allowing for better communication between different parts of the brain.
White matter also plays a role in the formation of memories. The transmission of signals between neurons is essential for the recall of memories, and the white matter ensures that these signals are efficiently sent and received. Without white matter, the brain would be unable to store and retrieve memories, making it difficult to learn and remember new information.
Role of White Matter in Motor Function
White matter is also responsible for the transmission of signals from the brain to the rest of the body. Specifically, it is involved in the control of motor functions such as movement and coordination. Without white matter, these signals would not be able to travel from the brain to the body, resulting in a lack of motor control.
White matter is also important for the control of fine motor skills, such as those needed for writing or playing an instrument. The transmission of signals between different areas of the brain helps to ensure that these skills are executed accurately and with precision. Without white matter, these skills would be much more difficult to learn and execute.
Role of White Matter in Emotional Regulation
White matter is involved in the emotional regulation of the brain, allowing for the efficient transmission of signals related to emotional responses. This helps to ensure that the brain is able to respond appropriately to situations, and to regulate emotional responses in a healthy manner. Without white matter, it would be difficult for the brain to process and respond to emotions in a healthy way.
White matter also plays a role in the formation of relationships and social interactions. By aiding in the transmission of signals related to emotions and social cues, white matter helps to ensure that these interactions are carried out in a healthy manner. Without white matter, it would be difficult for the brain to recognize and respond to social cues, making it difficult to form and maintain relationships.
Role of White Matter in Disease
White matter is essential for the proper functioning of the brain, and any disruption to white matter can have a significant impact on cognition, motor function, and emotional regulation. Diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic brain injuries can all lead to white matter damage, resulting in cognitive, motor, and emotional deficits.
White matter damage can also occur as a result of aging, with the white matter of the brain becoming increasingly damaged as people age. This can lead to age-related cognitive decline, as well as an increased risk of dementia. It is important to take steps to protect the white matter of the brain, such as engaging in physical activity and eating a healthy diet, in order to reduce the risk of white matter damage.
Related Faq
What is White Matter in the Brain?
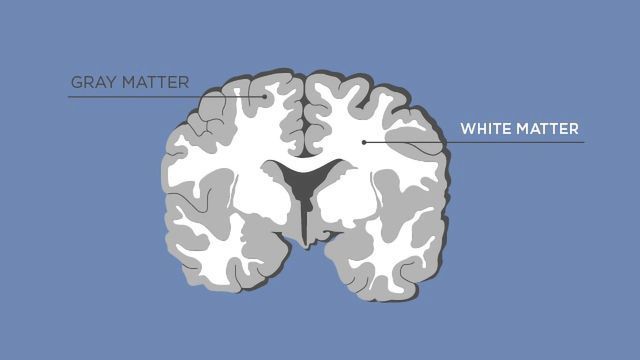
White matter in the brain is a type of neural tissue that consists of bundles of nerve fibers, which are covered by a protective sheath called myelin. These nerve fibers are responsible for sending signals from one part of the brain to another. They are also responsible for communication between different parts of the body. White matter is found in the brain and spinal cord, and makes up about half of the total volume of the brain.
What Does White Matter Do in the Brain?
White matter in the brain plays a crucial role in the transmission of signals from one part of the brain to another. It is responsible for relaying information from one area to another, which is essential for complex cognitive processes, such as thinking, learning, and memory. White matter is also important for motor functions, as it helps to coordinate movement of the body. Additionally, it helps to regulate the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for involuntary functions such as heart rate and breathing.
What Are the Different Types of White Matter in the Brain?
White matter in the brain is divided into two main types: myelinated and unmyelinated. Myelinated white matter consists of nerve fibers surrounded by a protective sheath called myelin. This type of white matter helps to speed up the transmission of signals, as the myelin helps to insulate the nerve fibers and allow for more efficient transmission of signals. Unmyelinated white matter, on the other hand, consists of nerve fibers without a myelin sheath. These nerve fibers are responsible for slower signals, such as those involved in the autonomic nervous system.
How Does White Matter Affect the Brain?
White matter in the brain is essential for proper functioning of the brain. It helps to ensure that signals are sent from one part of the brain to another efficiently, which is essential for cognitive processes such as thinking, learning, and memory. Additionally, white matter is important for coordinating movement of the body and regulating the autonomic nervous system. As such, an impairment of white matter can have a significant impact on brain functioning and overall health.
How Does White Matter Develop in the Brain?
White matter in the brain develops during early childhood, and continues to develop throughout adolescence and into adulthood. During this time, myelination of the nerve fibers occurs, which increases the speed of signal transmission. Additionally, new synapses are formed, which further increases signal transmission. Finally, white matter continues to mature throughout adulthood, with the amount of white matter increasing with age.
What Are the Diseases Associated with White Matter in the Brain?
There are various diseases that are associated with white matter in the brain, such as multiple sclerosis and leukodystrophy. Multiple sclerosis is a degenerative disorder that affects the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers, which can cause a range of symptoms, including difficulty with walking, vision loss, and fatigue. Leukodystrophy is a group of genetic disorders that affect the white matter in the brain, which can cause issues with motor skills, vision, and hearing. Other diseases associated with white matter include stroke, traumatic brain injury, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Brain white matter
The white matter in the brain is a complex and fascinating part of the human body. It helps to connect different areas of the brain, allowing us to think, reason, and feel. Without it, we would not be able to move, process information, create memories, and experience emotions. The white matter is a vital part of the brain and it is essential to our lives. Understanding how it works and how to protect it is essential for a healthy and successful life.


.jpg)