Last Updated on 4 months by Francis
Have you ever wondered if an infrared camera can see through glass? Infrared cameras are powerful tools that detect temperature differences in objects by capturing the infrared radiation they emit. However, when it comes to seeing through glass, these cameras face limitations.
Glass, with its poor heat conductivity and lack of significant infrared radiation emission, acts as a barrier for infrared cameras. It reflects infrared radiation back, making it difficult for the camera to capture temperature differences on the other side of the glass. This means that an infrared camera cannot see through glass like it can with other materials.
But why is glass a challenge for infrared cameras? Glass is a poor conductor of heat and does not emit a substantial amount of infrared radiation. Additionally, certain types of glass, such as low-emissivity (low-e) glass, are designed to reflect infrared radiation, further hindering the camera’s ability to see through it.
While infrared cameras cannot see through most types of glass, there are certain circumstances where they may detect temperature differences. For example, if there is a significant temperature contrast between the inside and outside of a building, the camera may capture this difference through the windows. However, this is only possible when there is a notable temperature variation.
Contents
Key Takeaways:
- An infrared camera cannot see through glass due to its poor heat conductivity and lack of significant infrared radiation emission.
- Glass acts as a mirror for infrared radiation and reflects it back, making it challenging for the camera to capture temperature differences on the other side.
- Certain types of glass, like low-emissivity (low-e) glass, are designed to reflect infrared radiation, further hindering the camera’s ability to see through it.
- In certain circumstances, such as significant temperature differences, infrared cameras may detect temperature variations through windows.
- While glass poses challenges for infrared cameras, they have applications in various industries, such as agriculture, appliances overhaul, fire rescue, and building maintenance.
Why Can’t Infrared Cameras See Through Glass?
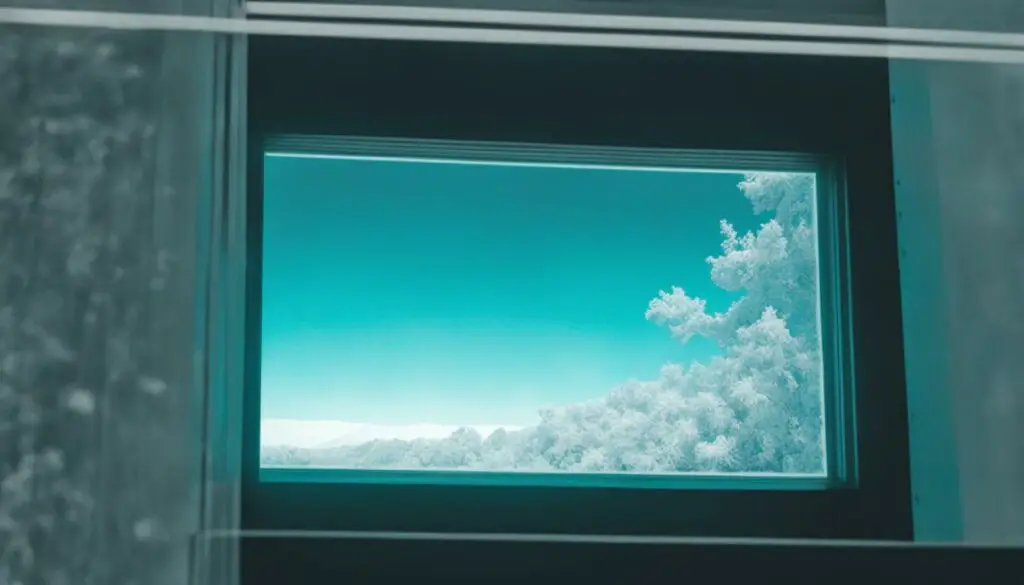

Glass visibility with infrared cameras poses a significant challenge due to the nature of glass as a poor conductor of heat and its low emission of infrared radiation. Infrared cameras, also known as IR cameras or thermal cameras, are designed to detect temperature differences in objects by capturing their infrared radiation. However, glass inhibits this process, preventing infrared cameras from effectively seeing through it.
The lack of significant infrared radiation emission from glass limits the ability of thermal cameras to detect temperature differences on the other side of the glass. As a result, when an infrared camera is pointed at a glass surface, it is unable to capture clear images or provide accurate temperature readings of objects on the other side.
Moreover, certain types of glass, such as low-emissivity (low-e) glass, further impede the visibility through an infrared camera. These glasses are specially designed to reflect infrared radiation rather than allow it to pass through, complicating the process of detecting temperature differences on the opposite side of the glass.
Overall, the combination of glass’s poor heat conductivity and its limited infrared radiation emission, along with the reflective properties of low-e glass, make it difficult for infrared cameras to see through glass. Consequently, glass remains an obstacle for thermal imaging technology.
Despite the limitations with glass visibility, infrared cameras have a wide range of applications in various industries such as building maintenance, fire rescue, appliances overhaul, and agriculture. While they may not be able to see through glass, they excel at detecting temperature differences in other materials and environments, making them indispensable tools in many scenarios.
When Can Infrared Cameras Detect Temperature Differences Through Glass?

In certain circumstances, thermal cameras may be able to detect temperature differences through glass. For example, if there is a significant temperature difference between the inside and outside of a building, thermal cameras may be able to detect this difference through the windows. This is because some heat is transferred through the glass due to the temperature difference. However, this is only possible when there is a notable difference in temperature.
Thermal imaging glass transparency is influenced by the temperature contrast between the inside and outside of a building. When there is a significant distinction in temperature, some of the heat will be transferred through the glass. In such cases, an infrared camera may be able to detect temperature differences by capturing the heat transmitted through the glass surface.
Despite the limitations imposed by glass, certain conditions can enable visibility through glass with an IR camera. When there is a substantial temperature difference allowing heat transfer through the glass, thermal cameras can pick up on these variations. This can be particularly useful for monitoring energy efficiency, identifying areas of heat loss, or detecting anomalies in temperature distribution.
By leveraging the thermal conductivity of glass and the contrasting temperatures on either side, thermal cameras may successfully penetrate and capture temperature differences. However, it is important to note that this capability depends on the specific circumstances, as the degree of temperature contrast plays a crucial role in the visibility through glass with an IR camera.
Having a clearer understanding of the conditions under which thermal cameras can detect temperature differences through glass can help determine their applicability in various scenarios. While glass remains a challenge for infrared cameras, there are situations where they can be effective in identifying temperature variations on the other side of the glass.
Thermal Imaging and Other Materials
While glass poses challenges for thermal cameras, there are other materials that thermal cameras can detect and analyze effectively. These materials include:
- Smoke
- Fog
- Concrete
- Metal
- Trees
- Certain types of plastic
Thermal cameras have the ability to see through smoke, which makes them valuable tools in firefighting and search and rescue operations. They can also detect objects through fog, even better than visible light cameras, due to their ability to capture thermal differences. Thermal cameras can reveal temperature variations on the surface of concrete, helping identify areas of structural concern. They are also effective in identifying hot spots or cold spots on metal objects, which is useful in industrial inspections.
Thermal cameras can even help spot people or animals in forested areas, thanks to their ability to detect the heat signatures emitted. Additionally, these cameras can pass through thin, opaque sheets of certain types of plastic, providing valuable insights in various industries.
“Thermal cameras have a wide range of applications in different fields, where their ability to analyze temperature differences across various materials is crucial. While glass remains a significant obstacle for thermal cameras, they still offer significant utility in detecting and analyzing other materials.”
To illustrate the application of thermal cameras in different scenarios, the following table provides a comparison of the materials mentioned:
| Material | Thermal Imaging Capability |
|---|---|
| Smoke | Possibility to see through |
| Fog | Possibility to see through, better than visible light cameras |
| Concrete | Ability to detect temperature variations on the surface |
| Metal | Reveal hot spots or cold spots |
| Trees | Possibility to spot heat signatures of people or animals |
| Certain types of plastic | Possibility to pass through thin, opaque sheets |
As the table illustrates, thermal cameras have applications beyond glass, offering valuable insights in various industries and scenarios. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that their capabilities may be limited when it comes to glass visibility and penetration.
As we explore the laws of physics that govern glass and infrared radiation in Section 5, we will uncover more insights into the challenges it poses for thermal cameras.
The Physics Behind Glass and Infrared Radiation

Glass plays a fascinating role in how it interacts with infrared radiation. Unlike visible light, which can pass through glass with relative ease, infrared radiation behaves differently. Glass acts as a mirror for infrared wavelengths, reflecting the radiation instead of allowing it to penetrate through. This unique behavior of glass has a significant impact on the ability of thermal imaging cameras to see through it.
When a thermal imaging camera is directed at a window, it captures a blurred reflection of its own lens rather than providing a clear image of what is on the other side of the glass. The infrared reflections from the glass obscure the view, resulting in varying degrees of opacity. Although some infrared frequencies can pass through glass, the majority of the image is compromised by these reflections, limiting the camera’s visibility through the glass surface.
To overcome the limitations imposed by glass, thermal imaging camera lenses are often crafted from materials like germanium or zinc selenide instead. These materials possess properties that allow them to transmit infrared radiation more efficiently compared to glass. By using lenses made from these specialized materials, thermal cameras can capture clearer and more accurate images without the interference caused by glass reflections.
Insightful Quote:
“Glass acts as a mirror for infrared radiation, reflecting it back instead of letting it pass through. This makes it challenging for thermal imaging cameras to provide clear images when pointed at glass surfaces.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson, Leading Expert in Infrared Technology
The Impact of Infrared Imaging Glass Penetration on Visibility
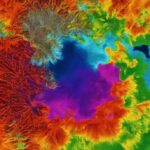
The limited transparency of glass to infrared radiation affects the visibility obtained through thermal imaging cameras. The reflections and opacity caused by glass hinder the camera’s ability to accurately detect and capture temperature differences on the other side. While some thermal energy may penetrate the glass, allowing certain infrared frequencies to transmit, the resulting image quality is compromised. The presence of glass introduces uncertainty and distortion, making it difficult to discern detailed features and contrasts on the thermal image.
The image above demonstrates the challenges faced by thermal cameras when attempting to see through glass. The reflections and opaqueness obscure the clarity and definition of the objects observed on the other side of the glass.
Comparing Infrared Cameras and Night Vision

When it comes to seeing in the dark, both infrared cameras and night vision technologies offer unique capabilities. While night vision relies on visible light to form images, infrared cameras function by visualizing heat. This fundamental difference allows infrared cameras to excel in situations where visibility is limited or non-existent, such as complete darkness or adverse weather conditions.
Unlike night vision, which requires some level of ambient light, infrared cameras can capture thermal images regardless of the lighting conditions. They detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, converting it into a visual representation of heat signatures. This ability to see heat makes them extremely useful in various applications, including surveillance, search and rescue operations, wildlife observation, and more.
However, it is important to note that infrared cameras do have limitations when it comes to seeing through certain materials, particularly glass. Glass acts as a barrier for infrared radiation, reflecting it instead of allowing it to pass through. As a result, the images captured by thermal cameras are often obscured or distorted when pointed at glass surfaces.
“Infrared cameras provide unparalleled visibility in complete darkness, but glass remains a challenge for thermal imaging.”
The limited transparency of glass for infrared radiation affects the overall performance of thermal cameras. While they can detect temperature differences on the surface of opaque objects, their ability to penetrate transparent materials like glass is significantly reduced.
Comparing Infrared Cameras and Night Vision: Key Differences
To summarize the differences between infrared cameras and night vision:
| Infrared Cameras | Night Vision |
|---|---|
| Visualize heat signatures | Rely on visible light |
| Work in complete darkness | Require some level of light |
| Not affected by adverse weather | Can be impacted by environmental conditions |
| Can’t see through glass | Able to see through glass |
By understanding the distinctions between infrared cameras and night vision systems, you can choose the most suitable technology for your specific use case. While infrared cameras excel in darkness and challenging environments, including situations where glass is present, night vision offers the benefit of providing detailed images in low-light conditions where visible light is available.
Application of Thermal Cameras in Different Situations

While thermal cameras may not be able to see through glass, they have numerous other applications in various industries. Here are some key areas where thermal cameras are widely used:
Agriculture
In the agricultural industry, thermal cameras play a critical role in monitoring crop health and detecting irrigation issues. By identifying temperature variations in plants, farmers can determine areas that require attention and optimize their crop management strategies.
Appliance Overhaul
Thermal cameras are valuable tools for technicians during appliance repair and maintenance. By detecting temperature anomalies in electrical appliances, such as overheating components or insulation failures, technicians can diagnose and address issues efficiently, preventing potential hazards or malfunctions.
Fire Rescue
Thermal cameras greatly aid firefighters in search and rescue operations, especially in environments filled with smoke and poor visibility. These cameras detect heat signatures, allowing firefighters to locate trapped individuals and navigate through hazardous conditions with enhanced safety.
Building Maintenance
In building maintenance, thermal cameras are indispensable for identifying energy inefficiencies and identifying areas with missing insulation. By detecting temperature differences in walls, windows, and roofs, thermal cameras help building owners and managers optimize energy consumption and improve overall energy efficiency.
(Image: Thermal camera)
Despite their limitations in seeing through glass, thermal cameras continue to be essential tools in various industries, enabling professionals to detect temperature differences, identify issues, and improve safety and efficiency. Their versatility and ability to navigate through challenging environments make them invaluable assets in a range of applications.
Limitations of Thermal Cameras and Reflective Surfaces
When it comes to capturing accurate readings, thermal cameras face certain limitations when dealing with reflective surfaces such as glass, polished metal, and specific types of plastic. These surfaces have the ability to reflect infrared radiation, posing challenges for the cameras to accurately detect temperature differences.
One major limitation is the inability of thermal cameras to see through glass or provide detailed images of objects on the other side. Glass acts as a mirror for infrared radiation, reflecting it back and making it difficult for the cameras to capture accurate readings. This means that when using a thermal imaging camera to look through a window, for example, the resulting image will typically show a blurred reflection of the camera lens rather than a clear view of objects on the other side.
In addition to glass, thermal cameras may also struggle to accurately measure temperatures on shiny or reflective metal surfaces. Due to the reflective nature of these surfaces, infrared radiation bounces off them, making it challenging for the cameras to capture precise temperature readings. As a result, the accuracy of temperature measurements may be compromised when dealing with such materials.
It’s important to note that while thermal cameras may have limitations when it comes to reflective surfaces, their capabilities extend far beyond. These cameras are widely used in various industries, from detecting issues like water leaks and missing insulation in walls to assisting firefighters in navigating through smoke-filled environments. However, it’s crucial to understand the limitations surrounding the use of thermal cameras and reflective surfaces to ensure accurate and reliable results.
The Role of Glass Type in Infrared Penetration
When it comes to infrared camera glass penetration, the type and configuration of glass play a significant role. While standard household glass may hinder thermal imaging, certain types of glass, like car windshields, can yield better results.
Car windshields are designed to have better infrared imaging glass transparency compared to regular glass. They are constructed with specific materials and coatings that allow a higher degree of infrared radiation to pass through. As a result, thermal cameras may be able to detect temperature differences more accurately when looking through car windshields.
However, it’s important to note that even with specialized glass, infrared reflections can still occur from the “wrong” side of the glass. These reflections can obscure the image seen through the glass, leading to varying degrees of opacity and a lack of noticeable detail and contrast.
In summary, while certain types of glass may offer better infrared camera penetration capabilities, infrared imaging through glass remains challenging due to reflections. The type and configuration of glass should be considered when using thermal cameras, but the limitations of glass visibility for infrared cameras should also be taken into account.
| Glass Type | Infrared Penetration |
|---|---|
| Standard Household Glass | Limited or no penetration |
| Car Windshields | Better infrared penetration compared to standard glass, but still affected by reflections |
| Specialized Infrared-Transparent Glass | Higher degree of infrared penetration with reduced reflections |
Conclusion
Infrared cameras are highly effective tools for detecting temperature differences in a wide range of materials and environments. However, when it comes to glass, their capabilities are limited. Glass has poor heat conductivity and reflects infrared radiation, making it difficult for thermal cameras to see through. As a result, these cameras cannot capture accurate images or detect temperature differences on the other side of the glass.
Despite this limitation, thermal cameras still offer a multitude of applications. They excel at identifying issues in walls, such as water leaks or missing insulation, and can navigate through smoke-filled environments. Additionally, thermal cameras are useful for spotting heat signatures in forested areas, which can be crucial for search and rescue operations or wildlife monitoring.
While infrared cameras are not able to penetrate glass and provide detailed visibility through it, their overall versatility makes them indispensable in various industries. From agriculture to building maintenance, these cameras play a crucial role in identifying temperature variations and potential issues. Although glass remains a challenge for infrared cameras, their remarkable capabilities continue to be harnessed for a wide range of other applications.
FAQ
Can an infrared camera see through glass?
No, infrared cameras cannot see through glass due to its poor heat conductivity and ability to reflect infrared radiation.
Why can’t infrared cameras see through glass?
Glass acts as a mirror for infrared radiation, reflecting it back and making it difficult for infrared cameras to detect temperature differences on the other side.
When can infrared cameras detect temperature differences through glass?
Infrared cameras can detect temperature differences through glass when there is a notable temperature difference between the inside and outside of a building.
Can infrared cameras see through other materials?
Infrared cameras can see through smoke, detect objects through fog, reveal temperature differences on the surface of concrete and metal, and identify heat signatures in forested areas, but they have limitations with glass.
What is the physics behind glass and infrared radiation?
Glass reflects infrared radiation instead of allowing it to pass through, making it challenging for thermal imaging cameras to capture accurate images.
How does infrared camera compare to night vision?
Thermal imaging is not affected by darkness and does not require visible light, unlike night vision. However, infrared cameras cannot see through glass, while night vision requires some level of visible light to form an image.
What are the applications of thermal cameras?
Thermal cameras are used in various industries for detecting issues in walls, navigating through smoke-filled environments, and spotting heat signatures in forested areas, among other applications.
What are the limitations of thermal cameras with reflective surfaces?
Reflective surfaces like glass, polished metal, and certain types of plastic can obscure the image seen through thermal cameras, making it difficult to capture accurate readings.
How does the type of glass affect infrared penetration?
Certain types of glass, like car windshields, may yield better results for thermal imaging compared to standard household glass, but in most cases, infrared reflections from the “wrong” side of the glass obscure the image, resulting in varying degrees of opacity.
Can infrared cameras see through glass?
No, infrared cameras cannot see through glass due to its poor heat conductivity and ability to reflect infrared radiation.