Last Updated on 4 months by Francis
Infrared cameras, also known as thermographic cameras, have revolutionized the way we perceive the world around us. By capturing images beyond the visible spectrum, they provide valuable insights into temperature variations, energy efficiency, and even celestial bodies. But can cameras detect wavelengths other than infrared? Let’s explore the sensing capabilities of cameras and their spectrum detection.
While the human eye can detect only a limited range of wavelengths, cameras have the ability to see beyond what our eyes can perceive. In addition to capturing infrared radiation, cameras can pick up other wavelengths such as near infrared (NIR), short-wave infrared (SWIR), and long-wave infrared (LWIR). Each of these wavelengths has its own unique applications and benefits in various industries.
NIR, the closest to the visible range, is used in fields like industrial inspection and quality control. SWIR is popular for moisture detection, making it valuable in applications like agriculture and food processing. LWIR, with its thermal imaging capabilities, plays a vital role in areas such as firefighting and perimeter surveillance.
By expanding the range of detectable wavelengths, cameras enable us to explore new possibilities and gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. Whether it’s identifying energy inefficiencies in homes, navigating through smoke-filled buildings, or uncovering mysteries of the universe, cameras have proven to be invaluable tools.
Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Infrared cameras can detect wavelengths beyond the visible spectrum.
- Cameras can pick up wavelengths such as near infrared, short-wave infrared, and long-wave infrared.
- Each wavelength has specific applications in various industries.
- Expanding the range of detectable wavelengths allows for improved energy efficiency, enhanced emergency response, and exploration of celestial bodies.
- Cameras offer valuable insights into our environment and help us make informed decisions.
Understanding Infrared and Thermal Imaging

Infrared radiation, also known as heat, is a form of thermal radiation that extends beyond the visible spectrum. While our eyes are limited to detecting visible light, infrared cameras have the remarkable capability to detect wavelengths beyond what we can see. These cameras, also referred to as thermographic cameras, can identify near infrared (NIR), short-wave infrared (SWIR), and long-wave infrared (LWIR) wavelengths, opening up a world of applications in various fields.
NIR is the closest to the visible range, with wavelengths ranging from 650 to 1050 nm. It finds applications in a wide range of industries, including security systems and quality control processes.
SWIR, on the other hand, operates within a range of 1050 to 2500 nm. This wavelength is particularly useful for moisture detection and imaging through fog, smoke, and certain materials.
LWIR encompasses wavelengths from 8000 to 12000 nm and is frequently utilized in thermal imaging. This technology allows for the detection of heat and contrasting levels of heat between different objects. It has extensive applications in fields such as building inspections, electrical inspections, and security monitoring.
To truly grasp the capabilities of thermal imaging, it’s important to understand that it goes beyond mere visualization. Instead, thermal imaging is a powerful tool that enables us to perceive heat differences and patterns that are not discernible to the naked eye. By detecting and analyzing thermal radiation, thermographic cameras enhance our ability to monitor, diagnose, and make informed decisions across various industries and applications.
Thermal imaging allows us to see the world in a completely different way, unveiling a hidden realm of heat and temperature variations that are otherwise invisible to us.
The Benefits of Thermal Imaging
The advantages of thermal imaging are vast and encompass applications in numerous sectors. By harnessing the power of infrared technology, thermographic cameras offer:
- Enhanced safety and situational awareness in firefighting and search and rescue operations
- Improved energy efficiency through the identification of heat loss and areas of high energy consumption in buildings
- Efficient fault detection and preventive maintenance in electrical and mechanical systems
- Cost-effective and non-intrusive inspection of HVAC systems for performance optimization
- Effective detection of insulation defects, water leaks, and structural issues in buildings
- Accurate identification of anomalies in industrial processes and manufacturing quality control
These are just a few examples, highlighting the widespread utility of thermal imaging technology. As advancements continue to push the boundaries of thermographic cameras, the potential for new applications and discoveries in diverse fields only continues to grow.
Applications in Home Inspection and Energy Efficiency
Thermal imaging plays a crucial role in conducting thorough home inspections and improving energy efficiency. By utilizing thermal imaging inspections, homeowners and businesses can identify areas of heat loss or gain, leading to significant energy savings and improved comfort.
Identifying Heat Loss and Gain
Thermal imaging is particularly useful in identifying areas of heat loss or gain within a property. During the winter months, thermal imaging inspections can pinpoint areas where heat escapes, such as poorly insulated walls, windows, or doors. By addressing these areas, homeowners can reduce energy consumption and lower their heating bills.
Similarly, in the summer, thermal imaging can help detect areas of heat gain, such as air leaks around windows and cracks in the building envelope. By addressing these issues, homeowners can improve energy efficiency and lower cooling costs.
Assisting HVAC Systems
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) professionals rely on thermal imaging to assess the efficiency of HVAC systems. By using thermal imaging cameras, they can identify and address issues such as air leaks, faulty insulation, or improperly sealed ductwork.
“Thermal imaging allows us to visualize heat flow and temperature variations, enabling us to locate potential problems in HVAC systems quickly.”
Promoting Energy Efficiency
By identifying and addressing sources of heat loss or gain, thermal imaging inspections significantly contribute to improving energy efficiency. When combined with proper insulation, sealing, and HVAC system maintenance, homeowners can effectively reduce their energy consumption and create a more sustainable living environment.
| Benefits of Thermal Imaging in Home Inspections |
|---|
| Detects areas of heat loss or gain |
| Identifies air leaks and insulation issues |
| Assists in optimizing HVAC system performance |
| Contributes to energy savings and lower utility bills |
The Role of Thermal Imaging in Firefighting
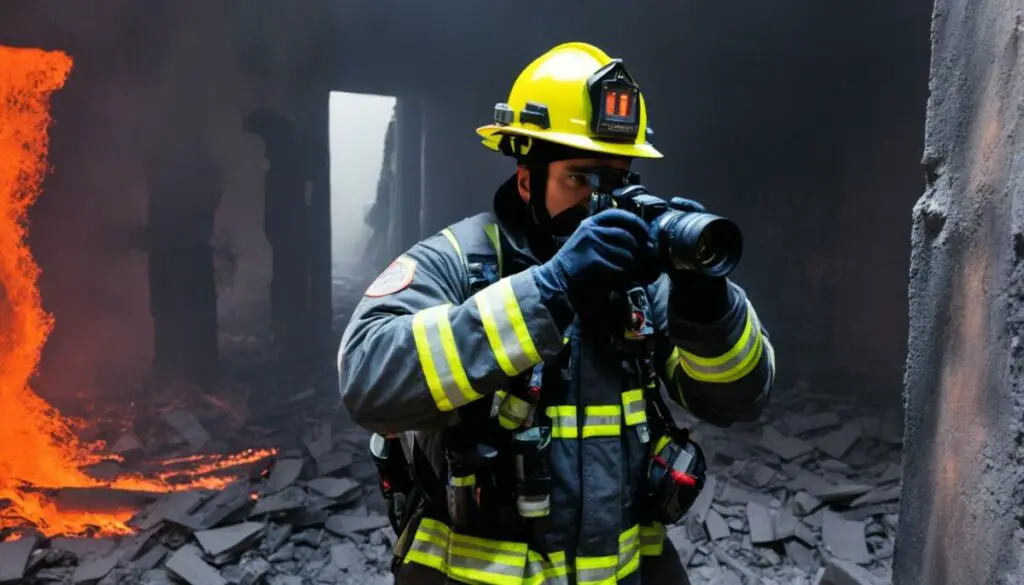

Thermal imaging cameras play a vital role in the firefighting industry, particularly in smoke-filled buildings where visibility is severely limited. These cameras utilize infrared imaging technology to detect differences in heat and help firefighters navigate through thick walls of smoke.
With thermal imaging cameras, firefighters can quickly identify burning surfaces and locate individuals amidst the chaos of smoke and flames. The cameras provide real-time visual feedback, enabling emergency responders to make informed decisions and execute effective rescue operations.
The infrared imaging capabilities of these cameras are instrumental in mapping out the fire, assessing its size and spread, and identifying potential hazards. By visually highlighting areas of intense heat, thermal imaging helps firefighters prioritize their efforts and allocate resources where they are most needed.
To enhance their situational awareness, firefighters can also deploy drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras. These aerial platforms provide invaluable perspectives and enable emergency responders to assess the situation from a safe distance, leading to more effective emergency response strategies.
By accurately detecting heat sources and assisting in the navigation of smoke-filled environments, thermal imaging cameras contribute to thorough fire suppression. They help prevent smaller flames from going undetected and ensure the safety of both firefighters and the public.
The Benefits of Thermal Imaging in Firefighting
- Enhanced visibility in smoke-filled environments
- Detection of burning surfaces and heat sources
- Identification of individuals amidst smoke and flames
- Mapping out the fire and assessing its size and spread
- Drones equipped with thermal imaging for aerial views
- Thorough fire suppression and prevention
| Benefits | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced visibility | Allows firefighters to navigate through smoke-filled buildings with greater ease. |
| Detection of heat sources | Enables firefighters to quickly identify burning surfaces and sources of heat. |
| Identification of individuals | Helps locate and rescue individuals in smoke and flame-filled environments. |
| Mapping out the fire | Provides valuable insights into the size, spread, and potential hazards of the fire. |
| Aerial views with drones | Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras offer valuable aerial perspectives. |
| Thorough fire suppression | Ensures that all flames are identified and addressed properly. |
Exploring the Universe with Infrared Imaging

Infrared imaging plays a crucial role in the field of astronomy, allowing scientists to observe celestial bodies beyond what the human eye can see. By capturing the energy emitted by planets, stars, and galaxies in the infrared spectrum, astronomers can reveal details that would otherwise be obstructed by dust particles.
One of the key tools in infrared astronomy is the Hubble Space Telescope, which is equipped with near-infrared sensors. The Hubble space telescope has revolutionized our understanding of the universe by capturing breathtaking images and making groundbreaking discoveries. From detecting dark matter to uncovering potential exomoons, the Hubble space telescope has provided valuable insights into the mysteries of our universe.
“The combination of infrared imaging technology and space-based telescopes has opened up new frontiers in our exploration of the cosmos.” – Dr. Emily Smith, Astrophysicist
Infrared imaging also enables the discovery of new planets and stars outside our solar system. Space-based telescopes equipped with infrared sensors have the ability to detect the faint signatures of these celestial bodies, expanding our understanding of the universe and the possibilities for extraterrestrial life.
As technology continues to advance, infrared imaging will play an increasingly important role in unraveling the mysteries of the universe. By capturing images and data from celestial bodies in the infrared spectrum, astronomers can further explore the nature of distant galaxies, the formation of stars, and the evolution of our universe.
Exploring the Universe: Key Insights
- Infrared imaging allows astronomers to observe celestial bodies beyond the visible spectrum.
- The Hubble Space Telescope, equipped with near-infrared sensors, has made remarkable discoveries in the field of infrared astronomy.
- Infrared imaging enables the discovery of new planets and stars outside our solar system.
- Space-based telescopes equipped with infrared sensors provide valuable insights into the nature and evolution of our universe.
Industrial Applications of Machine Vision Cameras

Machine vision cameras play a crucial role in various industries, providing reliable and accurate inspection capabilities that go beyond what the human eye can perceive. These sophisticated cameras utilize a combination of visible light and invisible light, including infrared and X-rays, to assess object quality and identify defects.
One of the primary applications of machine vision cameras is in manufacturing, where they are used for the inspection of parts, robotics control, and surveillance. These cameras can detect fine details and anomalies that may not be visible to human inspectors, ensuring the highest quality standards are met.
Moreover, machine vision cameras find a wide range of applications beyond manufacturing. In the military and law enforcement sectors, these cameras aid in surveillance and monitoring activities, providing valuable insights and enhancing security protocols.
The healthcare industry also benefits from machine vision cameras, where they are used for medical imaging, diagnosis, and monitoring. These cameras enable healthcare professionals to capture precise images of internal structures and detect abnormalities for accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Entertainment is another field where machine vision cameras are employed. They are used for special effects, motion capture, and virtual reality applications, enhancing the overall visual experience and immersing audiences in virtual worlds.
Benefits of Machine Vision Cameras in Industrial Inspection
Machine vision cameras offer numerous advantages in the realm of industrial inspection. Here are some key benefits:
- Greater Accuracy: Machine vision cameras provide highly accurate measurements and inspections, reducing human error and ensuring consistent results.
- Improved Efficiency: These cameras can perform inspections at high speeds, significantly improving productivity and reducing manufacturing costs.
- Non-Destructive Testing: By utilizing non-invasive imaging techniques, machine vision cameras enable non-destructive testing, minimizing damage and waste.
- Real-Time Monitoring: These cameras can capture and analyze data in real-time, allowing for proactive decision-making and timely interventions.
With their ability to detect both visible and invisible light, machine vision cameras have become indispensable tools in various industries. They empower businesses to achieve higher levels of quality control, precision, and efficiency, ultimately driving growth and success.
“Machine vision cameras revolutionize the way inspections are conducted in industries, providing unparalleled accuracy and enabling the detection of defects that would otherwise go unnoticed.”
Applications of Machine Vision Cameras
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Parts inspection, robotics control, quality assurance |
| Military and Law Enforcement | Surveillance, monitoring, security |
| Healthcare | Medical imaging, diagnosis, monitoring |
| Entertainment | Special effects, motion capture, virtual reality |
Visible, Infrared, and X-Ray Imaging

The world around us is filled with different forms of light, all part of the electromagnetic spectrum. While our eyes can detect visible light, there are other types of light that are beyond our perception. Infrared light, for example, extends beyond the visible range and enables us to detect thermal radiation or heat. Cameras equipped with infrared sensors can capture images in this wavelength range, opening up a wide range of applications in various industries.
Infrared cameras are extensively used in night vision systems, allowing us to see and navigate through low-light environments. These cameras are also utilized in security systems to detect anomalies and monitor areas where the human eye may fail to distinguish certain objects or individuals. In the field of medical imaging, infrared cameras provide valuable insights by detecting heat patterns, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions.
On the other end of the spectrum, we have X-ray imaging. X-rays have very short wavelengths, enabling them to penetrate solid objects and capture images of hidden structures. X-ray imaging is commonly used in medical diagnostics, allowing doctors to visualize bones, tissues, and other internal structures. In addition to healthcare, X-ray imaging plays a crucial role in industrial inspections, facilitating the detection of defects and contaminants in manufactured products.
By harnessing the power of different wavelengths, from visible light to infrared and X-rays, we gain a deeper understanding of our world. Each type of imaging provides unique insights and applications, contributing to various fields such as security, healthcare, and industrial inspection.
Comparison of Visible, Infrared, and X-Ray Imaging
| Aspect | Visible Light | Infrared | X-Ray |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Range | 400-700 nm | 700 nm – 1 mm | 0.01-10 nm |
| Penetration | Low | Medium | High |
| Applications | Photography, human vision | Night vision, medical imaging, security | Medical diagnostics, industrial inspections |
As the table above demonstrates, each type of imaging has its unique wavelength range, penetration capabilities, and applications. Visible light is essential for everyday photography and human vision, enabling us to perceive the world around us. Infrared imaging expands our sensing capabilities, allowing us to detect heat and navigate through low-light environments. X-ray imaging, with its high penetration capabilities, enables us to see through solid objects and uncover hidden structures.
Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum and the diverse imaging technologies it encompasses broadens our horizons and empowers us to explore the world in ways that were once unimaginable.
Exploring Infrared and X-Ray Technologies
Infrared cameras offer a wide range of capabilities, operating in different regions of the infrared spectrum. Let’s delve into the diverse applications of near infrared (NIR) imaging, short-wave infrared (SWIR) imaging, medium-wave infrared (MWIR) imaging, long-wave infrared (LWIR) imaging, and X-ray imaging.
Near Infrared (NIR) Imaging
In industries, NIR imaging plays a vital role in quality assurance and classification. This technology is extensively used to ensure the accuracy and reliability of various industrial processes.
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) Imaging
SWIR imaging offers unique advantages such as the ability to see through water vapors and haze. This makes it valuable for applications like port security and packaging inspection, where clarity is crucial.
Medium-Wave Infrared (MWIR) Imaging
MWIR imaging excels in long-distance surveillance and chemical identification. Its capabilities make it an invaluable tool in sectors that require precise identification and monitoring of substances.
Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) Imaging
LWIR imaging specializes in detecting thermal emissions. It is commonly used in perimeter surveillance and short-range surveillance, ensuring robust security and safety measures.
X-Ray Imaging
X-ray imaging provides unparalleled penetration capabilities, allowing it to examine solid objects. Its applications range from medicine, enabling precise diagnostic imaging, to food processing, ensuring optimal quality control.
By exploring these infrared and X-ray technologies, we unlock a multitude of possibilities across various industries. The utilization of different imaging techniques enables enhanced quality control, classification accuracy, and reliable surveillance, ultimately contributing to advancements in multiple fields.
Demonstrating the Capabilities of Infrared Cameras
An infrared camera allows us to see beyond the wavelengths detected by our eyes. By displaying the infrared spectrum on a false-color scale, an infrared camera can show us heat radiated from different objects. It can also detect differences in temperature and see through certain materials that visible light cannot penetrate.
Infrared cameras have various applications in fields like research, building inspection, and climate studies. A demonstration can involve observing temperature gradients, testing transparency of materials, and exploring different objects’ thermal emissions.
Conclusion
Cameras have revolutionized the way we perceive the world by their ability to detect a wide range of wavelengths beyond infrared. With their sensitivity to different wavelengths, including near infrared, short-wave infrared, and long-wave infrared, cameras have become invaluable tools in various fields.
Infrared cameras, working in tandem with visible light and X-ray imaging, offer unique insights into different aspects of our environment. From home inspection to astronomy, these cameras enable us to better understand and manage natural disasters, improve energy efficiency, and explore the vast universe.
The spectral sensitivity and wavelength range of a camera play a crucial role in its response to non-IR wavelengths. By carefully calibrating these factors, we can optimize cameras for specific applications, such as identifying heat loss in a building or capturing celestial bodies in deep space.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect cameras to further expand their capabilities in detecting and capturing wavelengths beyond what our human eyes can perceive. Whether it’s uncovering hidden details, assessing energy consumption, or unraveling the mysteries of the universe, cameras with their spectral sensitivity and wavelength range hold the key to unlocking new possibilities and enriching our understanding of the world around us.
FAQ
Can cameras detect wavelengths other than infrared?
Yes, cameras can detect other wavelengths such as near infrared (NIR), short-wave infrared (SWIR), and long-wave infrared (LWIR) in addition to infrared. These different wavelengths have various applications in fields like home inspection, firefighting, and astronomy.
What is the difference between infrared and thermal imaging?
Infrared is a form of thermal radiation, also known as heat, that is beyond the visible spectrum. Thermal imaging refers to the use of cameras to detect and visualize these infrared wavelengths. Thermal imaging allows for the detection of heat and contrasting levels of heat between objects.
How is thermal imaging used in home inspections?
Thermal imaging is used in home inspections to identify areas of heat loss or gain. It helps identify spots where heat or air conditioning can leak out, such as faulty windows or cracks. By addressing these areas, energy efficiency can be improved, leading to cost savings for homeowners and businesses.
How are thermal imaging cameras used in firefighting?
Thermal imaging cameras are essential tools for firefighters in smoke-filled buildings. They can detect differences in heat, helping firefighters see through thick smoke. Firefighters can also use these cameras to identify burning surfaces and locate individuals amidst the smoke and flames. Infrared imaging aids in mapping out the fire and assessing its size, spread, and potential hazards.
What role does infrared imaging play in astronomy?
Infrared imaging is crucial in astronomy for observing celestial bodies. It allows scientists to capture images that would be obstructed by dust particles and other interstellar matter. Infrared sensors have enabled the discovery of new planets and stars outside our solar system, providing new insights into the universe.
How are machine vision cameras used in various industries?
Machine vision cameras are widely used for inspection purposes in industries such as manufacturing. These cameras can detect details that are not visible to the human eye and provide reliable and accurate inspections. They utilize visible light as well as invisible light, such as infrared and X-rays, to assess object quality and identify defects.
What is the relationship between visible light, infrared, and X-ray imaging?
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all forms of light. Visible light falls within a narrow range of wavelengths that can be detected by our eyes. Infrared light extends beyond the visible range, detecting thermal radiation or heat. X-rays, on the other hand, have very short wavelengths and are used for medical diagnostics and industrial inspections to detect defects and contaminants.
What are the different regions of the infrared spectrum used in imaging?
Infrared cameras can operate in different regions of the infrared spectrum. Near infrared (NIR) imaging is used for quality assurance and classification in industrial applications. Short-wave infrared (SWIR) imaging sees through water vapors and haze, enabling applications such as port security. Long-wave infrared (LWIR) imaging detects thermal emissions and is suitable for surveillance and monitoring applications.
What can be demonstrated using an infrared camera?
An infrared camera allows us to see beyond the wavelengths detected by our eyes. It can display the infrared spectrum on a false-color scale, showing heat radiated from objects and temperature differences. Infrared cameras can also see through certain materials that visible light cannot penetrate. Demonstrations can involve observing temperature gradients, testing material transparency, and exploring thermal emissions.
What are some factors that determine a camera’s sensitivity to different wavelengths?
A camera’s sensitivity to different wavelengths depends on its spectral sensitivity and wavelength range. Different cameras may have varying capabilities to detect and respond to certain wavelengths. Manufacturers provide specifications that detail the spectral range and sensitivity of cameras, enabling users to select the appropriate camera for their specific application.