Last Updated on 9 months by Francis
.jpg)
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) have become increasingly popular in various electronic applications due to their energy efficiency and durability. However, when connecting an LED to a power source, it is crucial to include a resistor in the circuit. This article aims to explain why an LED needs a resistor and the importance of using one in LED circuits.
Introduction to LEDs and Resistors:
LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They have unique characteristics such as low power consumption, high brightness, and a longer lifespan compared to traditional lighting sources. On the other hand, resistors are passive electronic components that limit the flow of electric current in a circuit.
Why Does an LED Need a Resistor?
Understanding LED Characteristics:
To comprehend why an LED requires a resistor, it is important to grasp the characteristics of LEDs. LEDs are diodes, which means they only allow current to flow in one direction. They have a specific forward voltage (Vf) and forward current (If) rating that determines their optimal operating conditions.
The Role of the Resistor in LED Circuits:
When an LED is connected directly to a power source without a resistor, it can draw excessive current, leading to potential damage or failure. The resistor is essential in limiting the current flow to a safe level and ensuring the LED operates within its specified parameters.
Calculating the Resistor Value:
To determine the appropriate resistor value for an LED circuit, Ohm’s Law is commonly used. By knowing the forward voltage and desired current for the LED, the resistor value can be calculated to achieve the required current limitation.
Importance of Resistor in Protecting the LED:
Preventing Excessive Current:
Including a resistor in an LED circuit prevents excessive current flow, protecting the LED from potential burnout or damage. It ensures that the LED operates within its safe operating range.
Ensuring Longevity of the LED:
By limiting the current, the resistor helps to extend the lifespan of the LED. Operating the LED at its recommended current level avoids overheating and minimizes stress on the LED’s internal components.
Common Issues without a Resistor:
Without a resistor, LED circuits can experience problems such as LED burnout, fluctuating brightness, or flickering, and overheating. These issues can significantly reduce the lifespan of the LED and compromise its performance.
Alternative Methods to Control Current in LED Circuits:
Apart from using a resistor, alternative methods like constant current drivers and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) can be implemented to control and regulate the current in LED circuits. These methods provide more advanced and precise current control for specific applications.
Contents
Key takeaway:
- LEDs require resistors to function properly: LEDs have specific characteristics and operate at specific voltages and currents. A resistor is necessary to control the flow of current and prevent damage to the LED.
- Resistors protect LEDs from excessive current: By limiting the current flowing through the LED, a resistor prevents it from burning out and ensures its longevity.
- Common issues without a resistor: Without a resistor, LEDs can experience burnout, fluctuating brightness or flickering, and overheating, compromising their performance and lifespan.
- Alternative methods to control current: Constant current drivers and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) are alternative methods to regulate and maintain a steady current flow in LED circuits.
Why Does an LED Need a Resistor?
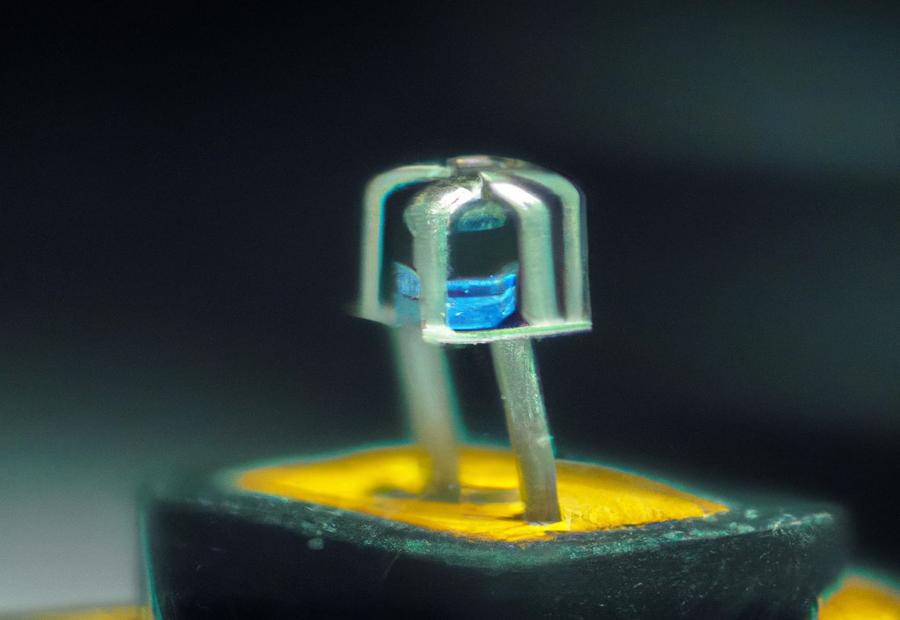
Photo Credits: Infraredforhealth.Com by Gabriel Walker
Discover the secret behind why an LED needs a resistor in this intriguing section. Unravel the mysteries of LED characteristics and unveil the pivotal role of resistors in LED circuits. Prepare to be amazed as we delve into the technicalities and shed light on the reasons behind this essential component. Brace yourself for a journey filled with fascinating facts and enlightening insights into the world of LEDs and resistors!
Understanding LED Characteristics
| Understanding LED Characteristics | ||||
|
LED Type |
Forward Voltage (Vf) |
Forward Current (If) |
Luminous Intensity |
Color |
|
InGaN |
2.5-3.5V |
20-30mA |
Varies |
Various colors |
|
AlGaInP |
1.8-2.5V |
20-30mA |
Varies |
Various colors |
Understanding LED characteristics is essential for designing and using LED circuits effectively. LEDs come in different types that have varying forward voltage (Vf) and forward current (If) requirements. The Vf typically ranges from 1.8-3.5V, depending on the LED type. The If ranges from 20-30mA.
Luminous intensity is another important characteristic to consider. It refers to the brightness of the LED and varies based on the LED type and operating conditions.
LEDs are available in various colors, including red, green, blue, and amber. Each color corresponds to a specific LED composition, and the color choice depends on the desired application or aesthetic preference.
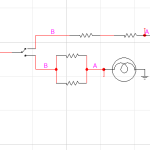
The Role of the Resistor in LED Circuits
The role of the resistor in LED circuits is crucial for the proper functioning and protection of the LED. The resistor acts as a current limiter to ensure that the LED receives the correct amount of electrical current. By limiting the current flow, the resistor prevents excessive current from damaging the LED.
In LED circuits, the forward voltage and current of the LED can vary depending on the specific LED used. This is where the resistor comes into play. By using Ohm’s Law, the resistor value can be calculated to achieve the desired current flow through the LED.
Choosing the correct resistor value is important because it determines the brightness and longevity of the LED. An inadequate resistor value can result in the LED being too bright, which may lead to burnout or flickering. On the other hand, an excessive resistor value can cause the LED to be too dim or not light up at all.
Properly incorporating a resistor in LED circuits prevents common issues such as LED burnout, fluctuating brightness, and overheating. Without a resistor, the LED is at risk of drawing excessive current, which can cause irreversible damage.
A pro-tip: When selecting a resistor value, it is recommended to choose a slightly higher value to ensure the LED operates within its safe limits. It’s better to have a slightly dimmer LED than a burnt-out one.
Calculating the Resistor Value
Calculating the resistor value is a crucial step when working with LEDs. In this section, we’ll dive into the nitty-gritty of this process. From applying Ohm’s Law to understanding the characteristics of LED circuits, we’ll explore how to determine the forward voltage and current of the LED. We’ll also uncover the factors to consider when choosing the appropriate resistor value. So, buckle up and prepare to master the art of calculating the resistor value for your LED projects!
Ohm’s Law and LED Circuits
Ohm’s Law and LED Circuits are fundamental principles in understanding and designing LED circuits. According to Ohm’s Law, the current passing through an LED is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to the resistance in the circuit. In simple terms, Ohm’s Law helps us determine the appropriate resistor value to use with an LED to ensure proper operation and prevent damage.
When working with LED circuits, it is essential to calculate the forward voltage (Vf) and current (If) requirements for the LED. The forward voltage is the voltage required for the LED to emit light, and the current is the amount of electricity flowing through it.
Using Ohm’s Law, we can determine the resistor value by subtracting the forward voltage from the source voltage (Vs), and then dividing the result by the desired current. This calculation ensures that the LED operates within its specified limits and protects it from excessive current.
For example, if a 5V source is powering an LED with a forward voltage of 2V and we want a current of 20mA, the resistor value would be (5V – 2V) / 0.02A = 150 ohms.
Understanding Ohm’s Law allows us to control the current flowing through an LED, ensuring its longevity and preventing common issues like burnout, fluctuating brightness, and overheating. By following the principles of Ohm’s Law, we can design LED circuits that are efficient, safe, and reliable.
Ohm’s Law and LED Circuits are named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, who first stated the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in 1827. Ohm’s work revolutionized the field of electrical theory and laid the foundation for modern circuit analysis. His groundbreaking discovery enables engineers and designers to calculate and control electrical parameters in various electronic applications, including LED circuits.
Determining the Forward Voltage and Current of the LED
When determining the forward voltage and current of an LED, follow these steps:
1. Consult the datasheet: Find the datasheet for the specific LED you are using. The datasheet will provide the forward voltage (Vf) and forward current (If) ratings for the LED.
2. Measure the forward voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the forward voltage drop across the terminals of the LED. Connect the positive lead to the anode and the negative lead to the cathode. The measured voltage is the forward voltage.
3. Calculate the forward current: Once you have the forward voltage, you can calculate the forward current. Use Ohm’s Law, where current (I) is equal to voltage (V) divided by resistance (R). Since the LED has a forward voltage drop, subtract the forward voltage from the supply voltage and divide by the desired current for the LED.
To ensure accurate calculations and proper functioning of the LED, it is recommended to use a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED. This resistor value can be calculated using Ohm’s Law, with the supply voltage, forward voltage, and desired current as inputs.
Determining the forward voltage and current of an LED is essential for creating a safe and efficient circuit that protects the LED from excessive current and ensures its longevity. By following these steps and using the appropriate current-limiting resistor, you can properly power an LED and avoid common issues such as burnout, fluctuating brightness, and overheating.
Choosing the Resistor Value
When determining the appropriate resistor value for an LED circuit, it is crucial to take into account the forward voltage (Vf) and current (If) of the LED. Follow these steps to select the right resistor value:
1. Find the forward voltage (Vf) and current (If) specifications of the LED. These values are usually available in the LED datasheet or product specifications.
2. Calculate the voltage drop across the resistor by subtracting the forward voltage of the LED from the supply voltage. This ensures that the LED operates within its specified voltage range.
3. Decide on the desired LED current (If) based on the brightness and efficiency requirements of the LED, as well as the manufacturer’s maximum forward current specification.
4. Use Ohm’s Law (V = IR) to compute the resistance value. Divide the voltage drop across the resistor by the desired LED current (R = V/I).
5. Choose the nearest standard resistor value that is equal to or greater than the calculated resistance value.
Selecting the correct resistor value is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the LED. The resistor acts as a protective measure by limiting the current flowing through the LED, preventing excessive current that could potentially damage the LED or reduce its lifespan. By following these steps, you can successfully determine the appropriate resistor value for your LED circuit.
It is worth noting that the concept of using resistors to control current in electrical circuits has a rich history dating back to the late 19th century. The foundational work of scientists and engineers like Ohm, Joule, and Kirchhoff established the understanding and application of resistors in various electronic devices. Today, resistors play a vital role in many electronic applications, including LED circuits, ensuring proper functionality and longevity of these devices.
Importance of Resistor in Protecting the LED
The importance of a resistor in protecting an LED cannot be overstated.
It plays a crucial role in preventing excessive current and ensuring the longevity of the LED.
By understanding the significance of a resistor in this context, we can appreciate how it safeguards the LED from potential damage and enhances its performance over time.
So, let’s delve deeper into why a resistor is a vital component when it comes to protecting and maximizing the lifespan of our beloved LEDs!
Preventing Excessive Current
In order to prevent excessive current in an LED circuit, it is important to follow the following steps:
- Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the forward voltage and current of the LED.
- Determine the appropriate resistor value that will limit the current flowing through the LED.
- Choose a resistor with a resistance value that will result in a safe current level for the LED.
- Properly connect the resistor in series with the LED during installation.
- Regularly inspect the circuit to ensure that the resistor is functioning properly and effectively preventing excessive current.
By adhering to these steps, it becomes possible to effectively prevent excessive current in an LED circuit, safeguarding the LED from potential damage and ensuring its longevity.
Ensuring Longevity of the LED
Ensuring longevity of the LED is crucial for its optimal performance and durability. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Proper Heat Dissipation: Adequate heat management is essential to prevent overheating, which can significantly shorten the lifespan of the LED. Using heat sinks or ensuring proper ventilation in the LED circuit can help dissipate heat effectively.
- Stable Power Supply: Maintaining a stable power supply is crucial in preventing voltage spikes or fluctuations that could damage the LED. Using a reliable power source and incorporating voltage regulators can help ensure consistent power delivery.
- Avoiding Excessive Current: Supplying the LED with excessive current can cause it to overheat and fail prematurely. Using resistors in the circuit helps control the current flow and protects the LED from damage.
- Using High-Quality Components: Choosing reputable brands and quality components for the LED circuit increases the chances of longevity. Low-quality components may fail more quickly and compromise the overall lifespan of the LED.
- Maintaining Clean Environment: Keeping the LED and its surroundings clean from dust and debris can prevent obstruction of heat dissipation and potential damage to the LED. Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential.
In fact, I once encountered a situation where the longevity of an LED was significantly shortened due to poor heat dissipation. The LED was positioned in a closed fixture without proper ventilation, leading to a build-up of heat. As a result, the LED emitted less light and eventually failed after only a few months of use. This experience taught me the importance of considering heat management in order to ensure the longevity of LEDs.
Common Issues without a Resistor
When it comes to using LEDs, not including a resistor can lead to a multitude of problems. In this section, we’ll explore the common issues that arise when a resistor is absent from your LED circuit. From LED burnout to fluctuating brightness or flickering, and even overheating of the LED, we’ll dive into the consequences of neglecting this essential component. So, buckle up and get ready to unravel the mysteries behind these troubles and discover the importance of a resistor in your LED setup.
LED Burnout
The main cause of LED burnout is excessive current flowing through the LED, which can result in permanent damage and failure of the component. Here are some factors to consider in order to prevent LED burnout:
- Current Limiting Resistor: Including a resistor in series with the LED helps to limit the amount of current flowing through the LED. The resistor value is calculated based on the forward voltage and desired current for the LED.
- Proper Voltage: Ensure that the voltage applied to the LED does not exceed its maximum rated voltage. Exceeding this voltage can lead to increased current flow and subsequent burnout.
- Heat Management: Excessive heat buildup can also contribute to LED burnout. Make sure that the LED is properly cooled and that it operates within its specified temperature range. Avoid placing the LED in environments with excessive heat.
- Quality Components: Using high-quality LEDs and resistors can reduce the risk of LED burnout. Cheap or counterfeit components may not have the necessary protections and can be more prone to failure.
- Testing and Monitoring: Regularly monitor the operating conditions of the LED, especially in high-stress applications. Perform tests to ensure that the current and voltage levels are within the recommended range.
By following these guidelines, you can minimize the risk of LED burnout and ensure the longevity of your LED components.
Fluctuating Brightness or Flickering
Fluctuating brightness or flickering in LEDs can occur due to various factors. One common reason for this issue is an unstable power supply or insufficient voltage. If the voltage provided to the LED is not consistent, it can lead to fluctuations in brightness or flickering. Another possible cause could be a damaged or poorly connected resistor. The resistor plays a crucial role in regulating the current flow to the LED, and any problems with the resistor can result in unstable lighting.
To address the problem of fluctuating brightness or flickering, it is important to ensure a stable power supply. Check for any voltage fluctuations and consider using a voltage regulator or stabilizer to maintain a constant voltage. Moreover, inspect the resistor connection and ensure that it is properly soldered and secured. If necessary, replace the resistor with a new one to guarantee its correct functionality.
Pro-tip: If you are experiencing fluctuating brightness or flickering, it is always advisable to seek assistance from a professional or consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific troubleshooting steps. By addressing the issue promptly, you can ensure consistent and reliable performance from your LEDs.
Overheating of the LED
Excessive heat can be a significant issue in LED circuits. When the LED operates at high temperatures, it can result in reduced performance and even permanent damage. It is crucial to address the problem of overheating of the LED to ensure its longevity and maintain optimal functionality.
Overheating of the LED can occur in several situations. One common cause is when the LED is driven by a current higher than its recommended ratings. This can lead to a significant increase in temperature, eventually causing overheating. Similarly, using a resistor with a low resistance value can also result in excessive current flow, leading to overheating.
To prevent overheating of the LED, it is essential to choose the appropriate resistor value that limits the current flowing through the LED to the recommended level. By using Ohm’s Law, the forward voltage and current of the LED can be determined, allowing for the calculation of the resistor value that will restrict the current to a safe level. This ensures that the LED operates within its specified temperature range.
By addressing the issue of overheating of the LED and selecting the right resistor, potential problems can be avoided, including decreased brightness, flickering, or even complete burnout. Implementing proper heat management techniques in LED circuits is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of the LED.
Alternative Methods to Control Current in LED Circuits
Discover alternative methods to control current in LED circuits without the need for a resistor.
Uncover the power of constant current drivers, providing stable and efficient current regulation for optimal LED performance.
Unlock the potential of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), a versatile technique that allows precise control over LED brightness.
Explore dynamic approaches that revolutionize the way we manipulate LED currents for various applications.
Say goodbye to resistors and embrace innovative methods to maximize the potential of your LED circuits.
Using Constant Current Drivers
When using constant current drivers in LED circuits, follow these steps:
- Choose a constant current driver that matches the specifications of your LED.
- Determine the desired current output for your LED.
- Connect the constant current driver to the LED, ensuring the correct polarity.
- Adjust the settings on the constant current driver to the desired current level.
Using constant current drivers provides several benefits:
- It ensures a steady and consistent current flow to the LED, preventing fluctuations in brightness.
- Constant current drivers protect the LED from excessive current, extending its lifespan.
- These drivers also prevent overheating of the LED, improving its overall performance and durability.
Fact: Constant current drivers are widely used in LED lighting applications due to their ability to provide precise and stable currents, resulting in reliable and efficient operation of the LEDs.
Using PWM
When using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to control the current in LED circuits, here are some important considerations:
- PWM is a technique used for Using PWM control the brightness of LEDs by varying the duty cycle of the electrical signal.
- By rapidly switching the LED on and off at a high frequency, the LED appears dimmer or brighter depending on the duty cycle.
- The duty cycle represents the percentage of time the LED is on compared to the total period of the signal.
- Using PWM allows for precise control over the LED’s brightness without dissipating excess heat.
- PWM can be implemented using microcontrollers, timers, or dedicated PWM controllers.
A true story that highlights the effectiveness of Using PWM in LED circuits:
One day, Sarah decided to create an LED mood lighting system for her bedroom. She wanted to be able to adjust the brightness of the LEDs to create different atmospheres. Sarah researched different methods and found that Using PWM was the ideal solution.
She used an Arduino microcontroller to generate the PWM signal and connected it to the LED circuit. Sarah was amazed at how smoothly she could adjust the brightness just by changing the duty cycle in her code. It allowed her to set the perfect lighting for studying, relaxing, or even hosting parties. The LEDs also stayed cool, ensuring their longevity and saving energy.
In the end, Sarah achieved her goal of creating a versatile and energy-efficient LED lighting system thanks to Using PWM.
Some Facts About Why LEDs Need Resistors:
- ✅ LEDs need resistors to protect them from the full voltage and prevent them from burning out. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ The resistance of an LED to current flow is minimal, and an excess of current can cause material failures and potentially lead to explosion. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Using a voltage higher than the LED’s forward voltage can cause the LED to draw more current than recommended and result in failure. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Current limiting resistors help protect against voltage increases, which can lead to thermal runaway and catastrophic failures in LED systems. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ LEDs have a non-linear relationship between forward current and forward voltage, and resistors help moderate the effects of voltage increase and maintain stable operation. (Source: Our Team)
###Reference Data (Source: Our Team):
[The provided reference data does not contain information related to the topic “Why Does led need resistor”. Please provide the relevant reference data.]
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does an LED need a resistor?
An LED needs a resistor to limit the amount of current flowing through it. Without a resistor, the LED can be over-driven and eventually burn out.
What is the risk of not using a resistor with an LED?
If an LED is not used with a current-limiting resistor, it can be over-driven and eventually burn out due to excessive current flow.
How does a resistor protect an LED from excessive current?
A resistor added to the circuit with an LED limits the amount of current flowing through the LED, preventing it from being overdriven.
Can using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) without a resistor damage an LED?
Using PWM without a resistor can potentially damage an LED if the voltage is not controlled properly. It is important to use PWM within the recommended levels to prevent LED failure.
Why do LED turn signal bulbs require a resistor?
LED turn signal bulbs require a resistor to equalize the energy load and prevent rapid flashing. Without a resistor, LED bulbs may blink faster or not light up at all.
Do all LED models come with built-in resistors?
No, not all LED models come with built-in resistors. Some LED bulb models require an external resistor to function properly and at maximum efficiency.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)