Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Do you ever find yourself getting confused between glucose and glycogen? Well don’t worry – you aren’t alone! Glucose and glycogen are two compounds that are very similar in appearance and structure, yet have some distinct differences. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the similarities and differences between glucose and glycogen, so you can understand the difference between the two.
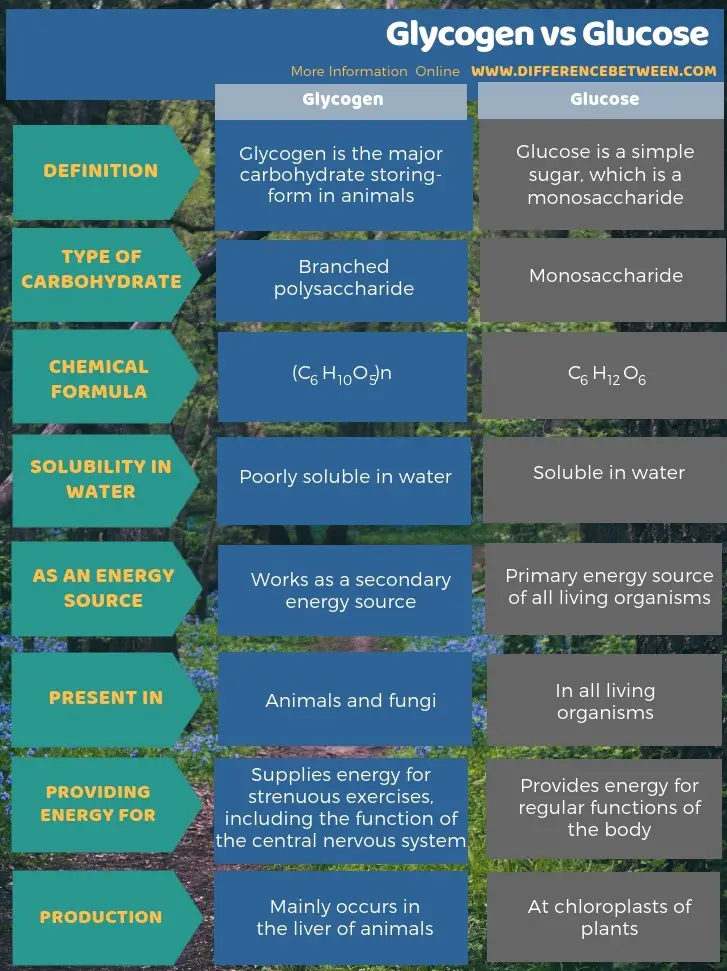
The primary difference between glucose and glycogen is the purpose for which they are used by the body. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body. It is a single molecule and is readily available for use. Glycogen, on the other hand, is a storage form of glucose. It is made up of multiple molecules and is stored in the muscles and liver.

Contents
What’s the Difference between Glucose and Glycogen?
Glucose and glycogen are both simple sugars and are the body’s main sources of energy. Glucose is the primary energy source used by the body and is found in many foods, while glycogen is a storage form of glucose, primarily stored in the liver and muscles. Although they are both forms of sugar, there are some distinct differences between the two.
Glucose Characteristics
Glucose, also known as dextrose or blood sugar, is a monosaccharide or simple sugar. It is the body’s main source of energy and is used to fuel all of the cells in the body. Glucose is found in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, breads, pastas, and grains. It is also produced in the body from the breakdown of carbohydrates and is released into the bloodstream. Once it is in the bloodstream, insulin helps transport it to the cells for energy.
Sources of Glucose
Glucose is found in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, breads, pastas, and grains. It is also found in sodas and other sugary drinks. Glucose can also be produced in the body from the breakdown of carbohydrates.
Uses of Glucose
Glucose is the body’s main source of energy and is used to fuel all of the cells in the body. It is used by the brain and nervous system, as well as muscles and other organs. Insulin helps transport glucose to the cells for energy.
Glycogen Characteristics
Glycogen is a polysaccharide, or complex sugar, and is the body’s main storage form of glucose. It is stored in the liver and muscles and is released into the bloodstream when needed. Glycogen is produced in the liver from glucose and can also be produced from other sources, such as lactose and proteins.
Sources of Glycogen
Glycogen is primarily produced in the liver from glucose. It can also be produced from other sources, such as lactose and proteins.
Uses of Glycogen
Glycogen is the body’s primary storage form of glucose and is stored in the liver and muscles. It is released into the bloodstream when needed for energy. Glycogen is also used by the brain and nervous system, as well as muscles and other organs.
Related Faq
What is Glucose?
Glucose is a simple sugar molecule which is the primary energy source for most of the cells in the body. It is found in many foods, and is also produced by the body from the breakdown of carbohydrates. Glucose is also known as dextrose. It is an important fuel for the brain, muscles, and other organs and is used for energy production. The body has a limited capacity to store glucose, so it must be constantly replenished.
What is Glycogen?
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the body. It is a complex branching chain of glucose molecules found mainly in the liver and muscles. It is the body’s main storage form of energy and can be rapidly broken down into glucose when the body needs more energy. Glycogen is also known as animal starch as it is found in most animals.
What is the Difference Between Glucose and Glycogen?
The main difference between glucose and glycogen is their structure and function. Glucose is a simple sugar molecule which is used immediately by the body for energy, while glycogen is a complex branching chain of glucose molecules which is used as a storage form of energy. Glucose is found in many foods and can also be produced by the body, while glycogen is only produced by the body and is stored in the liver and muscles. Glucose is used for energy production and can be quickly depleted, while glycogen can be rapidly broken down into glucose when the body needs more energy.
How Are Glucose and Glycogen Used by the Body?
Glucose is used by the body for energy production, and is the primary energy source for most of the cells in the body. It is used by the brain, muscles and other organs for energy. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the body and is used by the body when more energy is needed. It is stored in the liver and muscles and is broken down into glucose when the body needs more energy.
What Is the Maximum Amount of Glucose and Glycogen That Can Be Stored by the Body?
The body has a limited capacity to store glucose, so it must be constantly replenished. The maximum amount of glucose that can be stored in the body is about 2,000 kcal, or about 5% of total body weight. The maximum amount of glycogen that can be stored in the body is about 100 to 120 g, or about 400 kcal, and is stored mainly in the liver and muscles.
What Happens if the Body Does Not Have Enough Glucose and Glycogen?
If the body does not have enough glucose, it will be unable to produce energy and the body will become weak and sluggish. If the body does not have enough glycogen, it will be unable to break down into glucose when the body needs more energy, leading to fatigue and decreased performance. In both cases, it is important to replenish glucose and glycogen levels to maintain energy levels.
Glucose vs Glycogen
In conclusion, it is evident that there are significant differences between glucose and glycogen. Glucose is a monosaccharide molecule which is the primary energy source for the body, while glycogen is a polysaccharide chain that is stored in the liver and muscles as a complex form of stored energy. Glucose is more readily available to the body, while glycogen requires more energy to break down and access. Both glucose and glycogen are important components of the body’s metabolism and energy production.

.jpg)


.jpg)


