Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Have you ever heard of Stockholm Syndrome? You may be familiar with the term, but do you know the actual definition? Stockholm Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon where hostages or victims of a traumatic event develop an emotional bond with their captors or perpetrators. It is an intriguing concept with a long and complicated history. In this article, we will explore the definition of Stockholm Syndrome and delve into the psychology behind it.

Contents
Definition of Stockholm Syndrome
Stockholm Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon in which hostages form a strong emotional bond with their captors. It is named after the 1973 hostage situation in Stockholm, Sweden, in which four people were held hostage by bank robbers for six days. The hostages began to sympathize with their captors, even defending them when police arrived.
This phenomenon can be seen in other hostage situations, such as when victims of domestic violence become attached to their abuser, or in cases of child abuse in which the child feels loyal to the perpetrator. Stockholm Syndrome is a form of trauma bonding and is seen as a defense mechanism in which hostages or victims become attached to their captors or abusers in order to survive.
Causes of Stockholm Syndrome
The exact causes of Stockholm Syndrome are not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of several factors. The most important factor is a feeling of helplessness and dependence on the captor. This can lead to the victim feeling that they must rely on the captor for their survival.
Another factor is the fear of retaliation. Victims may feel that if they do not cooperate with the captor, they could be harmed. This fear can lead to the victim developing a bond with the captor, as they believe that the captor is their only source of protection.
Finally, Stockholm Syndrome can be caused by the captor showing kindness and understanding towards the victim. This can lead the victim to feel that the captor is not all bad, and they may develop feelings of gratitude and loyalty towards them.
Examples of Stockholm Syndrome
One of the most well-known examples of Stockholm Syndrome is the 1973 Stockholm bank robbery. During the six-day standoff, the hostages became emotionally attached to their captors, even defending them when police arrived.
Another example is the 2002 Moscow theatre hostage crisis, in which 129 hostages were held by Chechen rebels for three days. During this time, the hostages formed a bond with their captors and defended them when the siege was eventually over.
Risks of Stockholm Syndrome
One of the risks of Stockholm Syndrome is that the victim may become attached to their captor or abuser and may be reluctant to seek help or leave the situation. This can lead to further abuse or even death in extreme cases.
Another risk is that the victim may have difficulty adjusting to life outside of the situation. They may have difficulty forming relationships or may have flashbacks of the traumatic situation. This can lead to long-term psychological issues, such as depression and anxiety.
Treatment for Stockholm Syndrome
The most important step in treating Stockholm Syndrome is for the victim to be removed from the dangerous situation. This means that the victim must be encouraged to seek help and be protected from further abuse.
Once the victim is safe, they should be provided with psychological support and counseling to help them process the trauma they have experienced. This may include cognitive-behavioral therapy and talk therapy to help the victim process their emotions and experiences.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help with anxiety and depression. However, it is important to note that medication should not be used as a substitute for therapy and should be used in conjunction with therapy.
Related Faq
What Is the Definition of Stockholm Syndrome?
Answer: Stockholm Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon in which hostages develop strong emotional bonds with their captors, often to the point of defending them. It is thought to be caused by the captives believing their captors are their only chance of survival, which can lead to feelings of loyalty and sympathy towards them. Stockholm Syndrome was first identified in 1973 after a failed bank robbery in Stockholm, Sweden, in which the hostages ended up sympathizing with their captors.
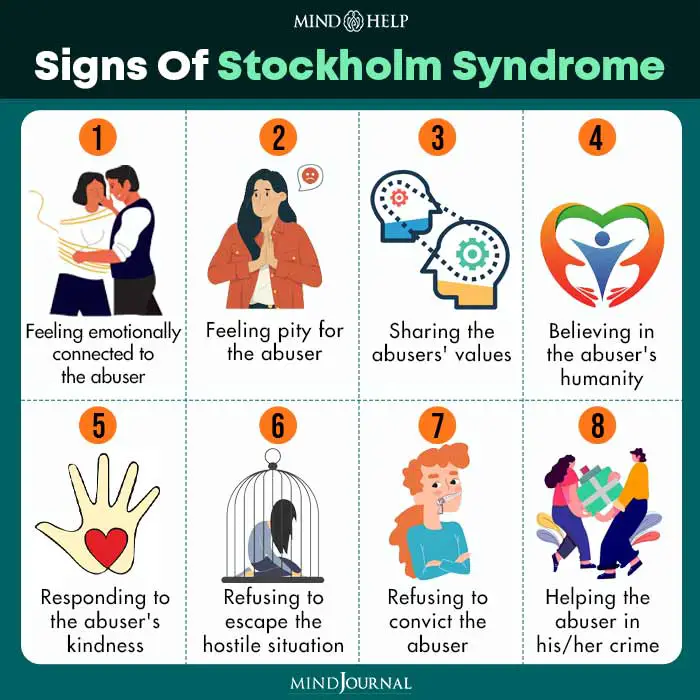
What Are the Symptoms of Stockholm Syndrome?
Answer: The primary symptoms of Stockholm Syndrome include a strong emotional connection to one’s captor, a feeling of helplessness, and difficulty feeling empathy for those outside of the captor-captive relationship. Other symptoms may include feeling a sense of guilt or shame for being a victim, difficulty trusting other people, and avoiding talking about the traumatic experience.
What Causes Stockholm Syndrome?
Answer: Stockholm Syndrome is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, such as the victim’s perception of their captor as a source of survival, the development of a bond between the captor and victim, and the captor’s display of kindness and understanding towards the victim. It is believed that these factors can lead to feelings of loyalty and sympathy towards the captor, even in extreme cases of abuse.
How Is Stockholm Syndrome Treated?
Answer: The treatment of Stockholm Syndrome typically involves psychotherapy, which may involve cognitive-behavioral therapy, trauma-focused therapy, or a combination of both. The goal of therapy is to help the individual identify and process their traumatic experience, and learn how to cope with the resulting emotions. Medication may also be used to help treat symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Stockholm Syndrome?
Answer: The long-term effects of Stockholm Syndrome can vary from person to person, but can include feelings of guilt and shame, difficulty trusting other people, difficulty feeling empathy for those outside of the captor-victim relationship, and difficulty with forming healthy relationships. In some cases, individuals may also experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, or depression.
Are There Any Preventative Measures for Stockholm Syndrome?
Answer: While there is no way to completely prevent Stockholm Syndrome, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of it occurring. These include providing support and resources to victims of abuse or captivity, ensuring that victims feel safe and secure, and encouraging victims to talk about their experiences. Additionally, education about the signs and symptoms of Stockholm Syndrome can help victims identify the condition and seek help if needed.
What is STOCKHOLM SYNDROME?
Stockholm Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when a hostage or captive develops strong emotional ties to their captor. The condition is characterized by positive feelings towards the captor, including a sense of loyalty, as well as a reluctance to cooperate with law enforcement. Although it is not fully understood, Stockholm Syndrome is believed to be a coping mechanism used by victims of traumatic situations. It is important to recognize the signs of Stockholm Syndrome in order to provide victims with the appropriate treatment and support.

.jpg)