Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Are you wondering if sugar is polar or nonpolar? If so, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the molecular structure of sugar and how it affects its polarity. By the end, you’ll understand why sugar is a special molecule, and why it’s neither polar nor nonpolar.

Contents
Sugar: A Polar or Nonpolar Molecule?
Sugar, or saccharose, is a naturally occurring molecule that is an important source of energy for living organisms. It is found in many foods and beverages and is a major component of many sweets. The question of whether sugar is a polar or nonpolar molecule is a frequently asked one. In order to answer this question, we must first understand the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules.
Polar molecules are molecules that have an unequal distribution of electrons, meaning that one side of the molecule has a slightly higher concentration of electrons than the other. This unequal distribution results in a slight positive and negative charge in different areas of the molecule. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, have an equal distribution of electrons, meaning that the molecule does not have any positive or negative charge.
Sugar: A Polar Molecule
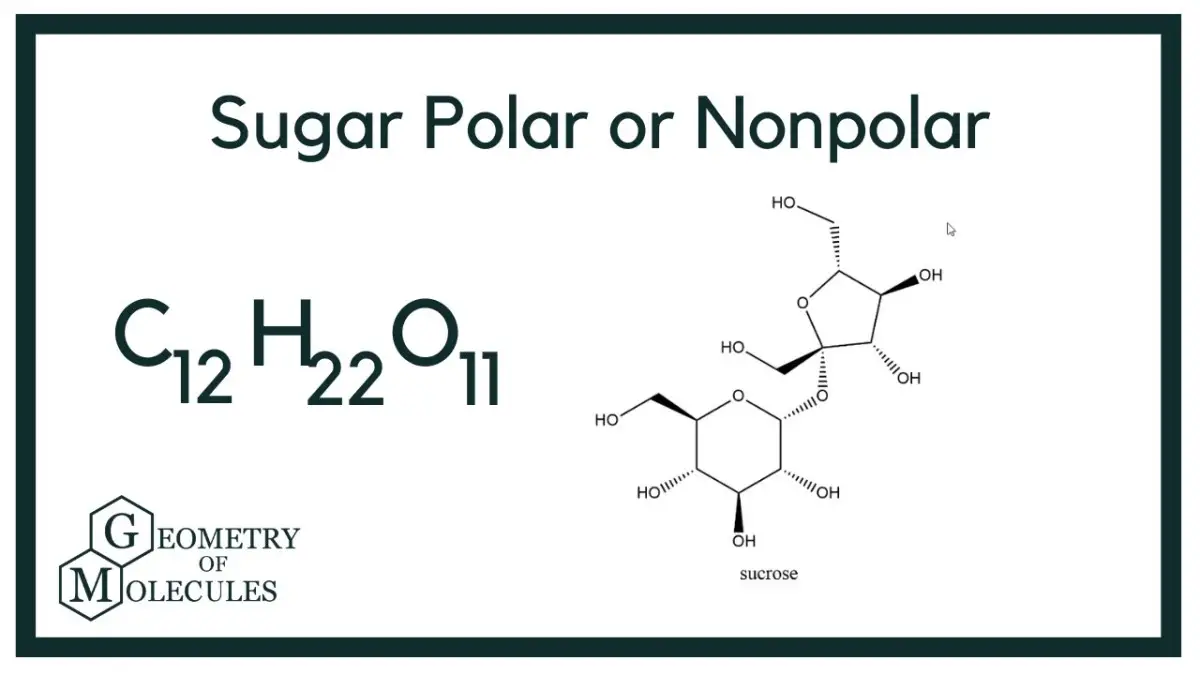
Sugar is generally considered to be a polar molecule. The molecule is composed of a ring of six carbon atoms and six oxygen atoms, with 12 hydrogen atoms attached. The slightly higher concentration of electrons on the oxygen atoms results in polar covalent bonds, which cause the molecule to have a slightly positive charge on one side and a slightly negative charge on the other. This makes sugar a polar molecule.
The Impact of Polar Molecules
Molecules that are polar in nature can have a great impact on their environment. For example, polar molecules are attracted to one another and can form strong hydrogen bonds with other molecules. This means that polar molecules are able to dissolve in water and other polar solvents, allowing them to mix and interact with other molecules.
Polar molecules can also be more easily absorbed by other molecules. This is because the positive and negative charges attract each other, allowing the polar molecule to easily bind to the other molecule. This can be seen in the human body, where polar molecules such as glucose can easily be absorbed and used for energy.
The Different Types of Polar Molecules
Polar molecules can be classified into two different types: ionic and covalent. Ionic polar molecules are molecules that have an unequal distribution of electrons, resulting in a positive and negative charge. Covalent polar molecules, on the other hand, are molecules that have an unequal distribution of electrons, but do not have a positive and negative charge.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sugar is a polar molecule. This is because it has an unequal distribution of electrons, resulting in a slight positive and negative charge. This polar nature allows sugar to easily dissolve in water and other polar solvents, and to be easily absorbed by other molecules. Additionally, polar molecules can be classified into two different types: ionic and covalent.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is sugar polar or nonpolar?
A1. Sugar is a polar molecule due to its molecular structure. It is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together in a ring-shaped structure. The oxygen and hydrogen atoms have different electronegativities, meaning they have different affinities for electrons. This causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge, leading to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Q2. What causes sugar to be polar?
A2. Sugar is a polar molecule due to the arrangement of its atoms. In its ring-shaped structure, the oxygen and hydrogen atoms have different electronegativities, meaning they have different affinities for electrons. This causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge, leading to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Q3. What is the structure of sugar?
A3. Sugar is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together in a ring-shaped structure. The oxygen and hydrogen atoms are arranged in a tetrahedral arrangement, with the oxygen atom at the center and the hydrogen atoms at the corners. This arrangement allows for the different electronegativities of the atoms to cause the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge, leading to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Q4. What are the components of sugar?
A4. Sugar is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms are bonded together in a ring-shaped structure, while the carbon atoms are located in the center. The oxygen and hydrogen atoms have different electronegativities, meaning they have different affinities for electrons. This causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge, leading to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Q5. How does the structure of sugar cause it to be polar?
A5. The structure of sugar causes it to be polar due to the arrangement of its atoms. In its ring-shaped structure, the oxygen and hydrogen atoms have different electronegativities, meaning they have different affinities for electrons. This causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge, leading to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Q6. What is the polarity of sugar?
A6. The polarity of sugar is due to its molecular structure. It is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together in a ring-shaped structure. The oxygen and hydrogen atoms have different electronegativities, meaning they have different affinities for electrons. This causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge, leading to the overall polarity of the molecule.
Sugar Polar or Nonpolar
In conclusion, sugar is a nonpolar molecule due to its molecular structure and the fact that it does not contain any hydrogen bonds. Although sugar is nonpolar, it is still soluble in water due to its molecular structure and the strong intermolecular forces of attraction between the water molecules and the sugar molecules. Therefore, sugar is an essential part of our diet, and it is important to understand its molecular structure and polarity in order to make informed decisions about our diet and health.