Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Electromotive force, also known as EMF, is a concept in physics that refers to the electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is often measured in volts and represents the force with which electrical charges are moved through the circuit. However, there is some misconception that EMF is the force in newtons acting on each individual electron, which we will explore in this discussion.
Contents
The Fundamentals of EMF
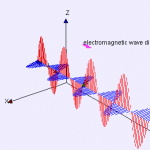
Electromagnetic fields (EMF) are waves of energy that can be found throughout the universe. These waves are created when charged particles, such as electrons and protons, move through space. EMF is measured in units of volts per meter (V/m) and can be found in a variety of forms, including radio waves, microwaves, and light waves.
The Relationship Between EMF and Electrons
EMF is not the force in newtons on each electron. The force in newtons on each electron is actually determined by the electric field in which the electron is located. The electric field is created by the presence of charged particles, such as protons or other electrons, which exert a force on the electron.
Understanding Newton’s Laws of Motion
To understand the relationship between EMF and electrons, it’s important to understand Newton’s laws of motion. Newton’s laws describe the behavior of objects in motion and how they interact with one another. They state that an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
How EMF Affects Our Bodies
EMF can affect our bodies in a variety of ways, including disrupting our sleep patterns, causing headaches, and increasing our risk of cancer. There is still much research to be done on the long-term effects of EMF exposure, but it’s important to be aware of the potential risks.
The Science of EMF
EMF is created by the movement of charged particles, such as electrons and protons. These particles create an electric field, which can then create a magnetic field when the particles are in motion. The combination of these fields creates an electromagnetic wave.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies that includes all types of EMF, from radio waves to gamma rays. Each type of EMF has a different frequency and wavelength, which can affect how it interacts with matter.
How EMF Can Be Measured
EMF can be measured using a variety of instruments, including Gaussmeters, which measure the strength of a magnetic field, and EMF meters, which measure the strength of an electric field. These instruments can be used to determine the level of EMF in a particular area.
Safe EMF Levels
There are currently no established safe levels of EMF exposure, but many experts recommend limiting exposure to EMF as much as possible. This can be done by limiting the use of electronic devices, such as cell phones and laptops, and by avoiding areas with high levels of EMF, such as power lines and cell phone towers.
EMF and Our Environment
EMF can affect our environment in a variety of ways, including disrupting wildlife and affecting the Earth’s magnetic field. It’s important to be aware of the potential environmental impacts of EMF and to take steps to limit our exposure.
The Effects of EMF on Wildlife
EMF can disrupt the behavior and migration patterns of wildlife, particularly birds and insects. This can have a cascading effect on ecosystems, as these animals play important roles in pollination and seed dispersal.
The Effect of EMF on the Earth’s Magnetic Field
EMF can also affect the Earth’s magnetic field, which plays an important role in protecting us from solar radiation. This can have a wide range of impacts, including increased rates of cancer and other health problems.
FAQs: Is EMF the Force in Newtons on Each Electron?
What is EMF in physics?
EMF stands for electromotive force, which is defined as the force that drives an electric current through a circuit. It is measured in volts and represents the potential difference between two points in a circuit. EMF can be generated by a variety of sources, including batteries, generators, and solar cells.
Is EMF the force in newtons on each electron?
No, EMF is not the force in newtons on each electron. Newtons are used to measure force, while EMF is used to measure voltage. The force on each electron in a circuit is represented by the electric field, which is also measured in newtons. The electric field is created by the potential difference (or voltage) between the two points in the circuit, which drives the flow of electrons.
How does EMF relate to electric current?
EMF is directly related to electric current, as it is the force that drives the flow of electrons through a circuit. When an EMF is applied to a circuit, it creates a potential difference between two points, which causes the electrons to flow from the higher potential point to the lower potential point. The rate at which this flow of electrons occurs is measured as electric current, which is measured in amperes.
Are EMF and voltage the same thing?
EMF and voltage are closely related, but they are not the same thing. EMF is the force that drives an electric current through a circuit, while voltage is the potential difference between two points in a circuit. EMF is a type of voltage, but it is specifically related to the energy conversion that drives the flow of electrons. Voltage is a more broad term that can refer to any potential difference in a circuit.