Are you managing diabetes and looking for a reliable way to track your glucose levels? A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) could be the perfect solution. CGMs provide real-time data on your glucose levels, giving you a more complete picture of your health and helping you manage your diabetes more effectively. In this article, we’ll explain how to use a CGM, from preparation to ongoing glucose monitoring. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to make better decisions about your diabetes management and live a healthier life.
Using a Continuous Glucose Monitor is a great way to keep track of your blood sugar levels. Here are the steps to get started:
- Consult your doctor and get a prescription for a Continuous Glucose Monitor.
- Follow the instructions that come with the Continuous Glucose Monitor.
- Place the sensor on your arm and wear it continuously.
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly and record them.
- Check the data on the Continuous Glucose Monitor and make any necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle.

Contents
What is a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
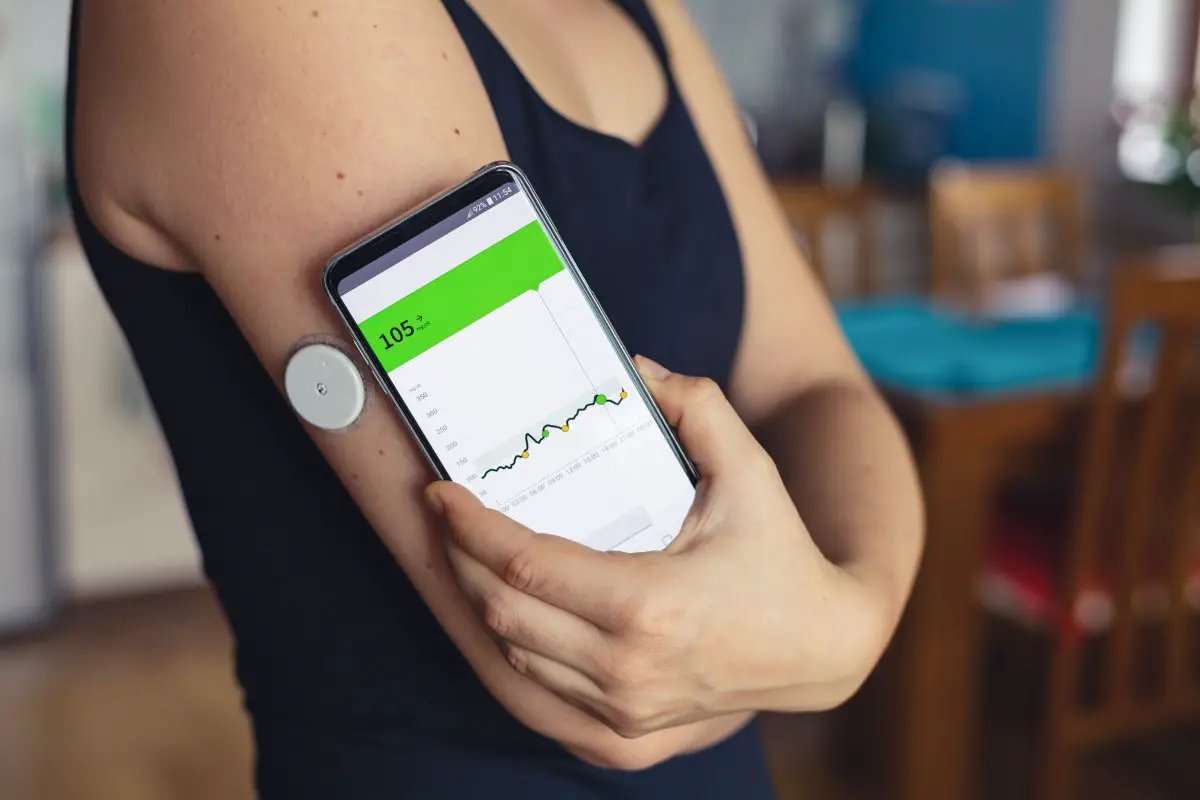
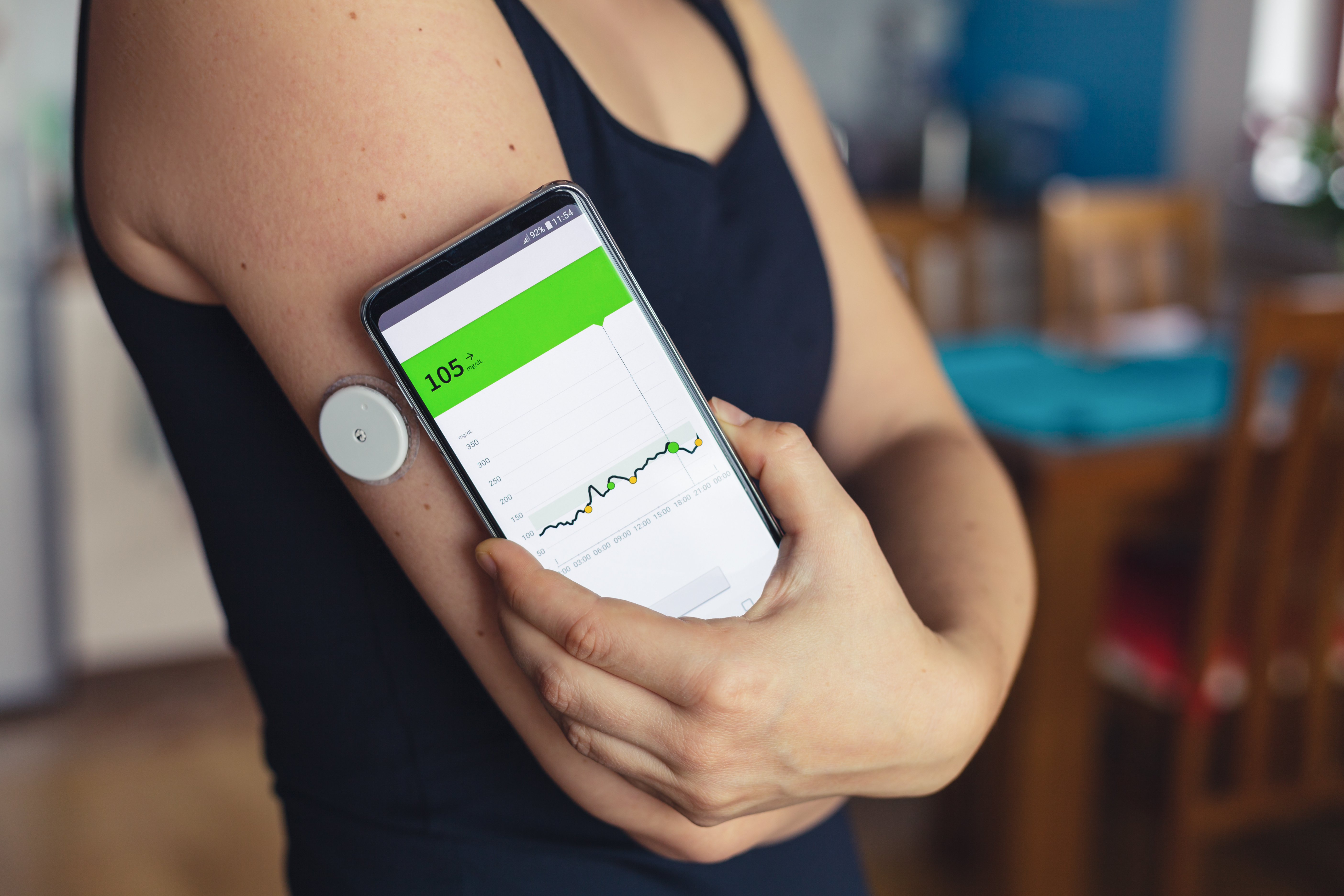
A Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) is a device that helps track a person’s blood glucose levels. It is worn on the body and is typically used by people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The device measures the amount of glucose in the bloodstream and sends real-time data to an app or device. This allows the user to monitor their glucose levels throughout the day and make adjustments to their diet or lifestyle accordingly.
CGM devices come in a variety of shapes and sizes and are designed to be as unobtrusive as possible. The devices can be customised to suit the user’s needs and lifestyle. They are also designed to be water-resistant and durable, so they can be worn in all types of weather.
What Are the Benefits of Using a CGM?
Using a CGM can help people with diabetes to better manage their condition. The device can provide near-real-time data on blood glucose levels and alert the user when their glucose levels are too high or too low. This allows the user to take preventative steps to avoid dangerous levels of glucose in their bloodstream.
Another benefit of using a CGM is that it can help to improve a person’s quality of life. By being able to track their glucose levels, the user can make changes to their diet or lifestyle to help improve their overall health. This can reduce the risk of serious medical complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Finally, using a CGM can help to reduce the amount of time and effort required to manage diabetes. The device allows the user to monitor their glucose levels without having to manually check their blood sugar levels. This can save time and energy, allowing the user to focus on other aspects of their health.
How to Use a Continuous Glucose Monitor
Step 1: Gather the Necessary Materials
Before using a CGM, it is important to make sure that you have all of the necessary materials. This includes the CGM device, the transmitter, and the receiver. You will also need an adhesive patch to attach the device to your body. The patch should be placed on the back of the arm or abdomen, depending on the type of CGM device you are using.
Step 2: Prepare the Device
Once you have all of the necessary materials, you will need to prepare the device. This includes charging the transmitter and receiver, as well as setting up the CGM device. Different CGM devices have different setup processes, so it is important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Step 3: Attach the Device
Once the device is charged and set up, it is time to attach the device to your body. Start by cleaning the area of skin where you plan to attach the device. Then, remove the adhesive patch and attach the device to your skin. Make sure that the device is securely attached and that the adhesive patch is properly sealed.
Step 4: Monitor Glucose Levels
Once the device is attached to your body, it is time to start monitoring your glucose levels. The device will transmit data to the receiver, which can then be viewed on the app or device. The device will also alert you if your glucose levels are too high or too low.
Step 5: Adjust Diet and Lifestyle
Once you have been monitoring your glucose levels for a while, you can start to make changes to your diet and lifestyle. This may include making changes to your meals, increasing your physical activity, or taking medications. It is important to consult with your doctor before making any major changes to your diet or lifestyle.
Related Faq
What is a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)?
A Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) is a device used to monitor a person’s blood glucose levels over a period of time. It uses a tiny sensor that is inserted just below the skin and a transmitter that sends the data to a receiver. The receiver displays the glucose level readings and can be used to set up alarms for when the levels are too high or too low.
What are the benefits of using a CGM?
Using a CGM can help people with diabetes better manage their health by providing more detailed and accurate readings than traditional methods. It can also alert them to potential problems before they become severe and help them adjust their diet and lifestyle accordingly. Additionally, CGMs can be used to track trends over time, allowing for better long-term management of diabetes.
How do you use a CGM?
Using a CGM is fairly straightforward. First, the sensor is inserted just below the skin, typically on the abdomen. The sensor is then calibrated to the user’s glucose levels with a finger prick. Once the sensor is in place, it will send readings to the receiver every few minutes. The receiver will display the glucose levels, alerting the user if the levels are too high or too low.
Are there any risks associated with using a CGM?
As with any medical device, there are potential risks associated with the use of a CGM. Most of these risks are related to the insertion and removal of the sensor, including infection, bleeding, and bruising. Additionally, some people experience skin irritation from the adhesive used to keep the sensor in place. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use and to contact a doctor if any issues arise.
Who should use a CGM?
CGMs are typically used by people with Type 1 diabetes, although people with Type 2 diabetes may also benefit from its use. People who have difficulty managing their blood glucose levels, those who have experienced hypoglycemic episodes, and those who are pregnant may also benefit from using a CGM.
How often do you need to change the CGM sensor?
Most CGM sensors need to be changed every 7-10 days, although this can vary depending on the type of sensor and the manufacturer. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use and to replace the sensor as soon as it begins to show signs of wear or malfunction.
By using a continuous glucose monitor, you can easily keep track of your blood sugar levels and ensure that you are keeping your blood sugar within the desired range. Not only does it provide you with a reliable and precise reading, but it can also help you better manage your diabetes, allowing you to make better lifestyle choices and lead a healthier life. So, if you’re looking for an accurate and effortless way to keep an eye on your blood sugar levels, a continuous glucose monitor is an ideal solution.