Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Water is one of the most essential elements of life. But have you ever noticed that it can feel a bit strange when you touch it? Why is water sticky? In this article, we’ll explore the science behind why water has a sticky feeling and how it affects us. We’ll also look at some interesting facts about water that you may not know. Read on to find out more about why water is sticky and why it plays such an important role in our lives.

Contents
What Makes Water Sticky?
Water has a unique property that makes it sticky and it is called surface tension. This is the property of a liquid to resist the force of an object applied to it, and it is caused by the molecule of the liquid being attracted to each other. When an object is placed in the water, the molecules of the liquid are attracted to the surface of the object, causing it to stick to the water. This phenomenon is seen in many everyday situations, such as when a paper clip is dropped into a glass of water or when a soap bubble is made.
Surface tension is also responsible for the “beading” effect that is seen when water droplets are placed on a surface. This is because the water molecules are attracted to each other at the point of contact with the surface, resulting in a small “bead” of water. This effect can be seen when water is placed on a waxed surface, such as a car window.
Surface tension can also be used to explain why water is sticky in certain situations. For example, when a sponge is placed in a bucket of water, the water molecules are attracted to the surface of the sponge, causing the water to stick to it. This same principle is also at work when a wet cloth is used to wipe a surface, as the water molecules are drawn to the surface of the cloth, creating a sticky surface.
The Role of Adhesion and Cohesion in Making Water Sticky
Adhesion and cohesion are two additional forces that are responsible for making water sticky. Adhesion is the force that causes two different substances to stick together, while cohesion is the force that causes like substances to stick together. In the case of water, adhesion is the force that causes the water molecules to stick to the surface of an object, while cohesion is the force that causes the water molecules to stick to each other.
Adhesion and cohesion work together to form surface tension. When two different substances come into contact, such as a paper clip and water, the molecules of the two substances are attracted to each other. This results in the paper clip sticking to the water, and is due to the adhesion between the paper clip and the water molecules. Meanwhile, the cohesion between the water molecules causes them to stick to each other, resulting in the water being sticky.
Adhesion Between Water and a Surface
Adhesion is also responsible for the stickiness of water when it comes into contact with a surface. When a wet cloth is wiped on a surface, the water molecules are attracted to the surface of the cloth, resulting in the water sticking to it. Similarly, when water is poured onto a surface, the water molecules are attracted to the surface, resulting in the water sticking to it.
The adhesion between water and a surface is also responsible for the beading effect that can be seen when water droplets are placed on a surface. As the water molecules are attracted to the surface, they form small beads of water, which can be seen on a waxed surface.
Cohesion Between Water Molecules
Cohesion is also responsible for the stickiness of water, as it is the force that causes the water molecules to stick to each other. This is the same force that is responsible for the beading effect that is seen when water droplets are placed on a surface, as the water molecules are attracted to each other at the point of contact with the surface.
Cohesion is also responsible for the “wetting” effect that is seen when water is poured onto a surface. As the water molecules are attracted to each other, they form a thin film on the surface, which is referred to as the “wetting” effect. This is the same effect that is seen when a wet cloth is used to wipe a surface, as the water molecules are attracted to each other, resulting in a thin film of water on the surface.
Conclusion
Water has a unique property called surface tension, which is responsible for its stickiness. Surface tension is caused by the adhesion and cohesion of water molecules, which are attracted to each other and to the surfaces they come into contact with. Adhesion is responsible for the stickiness of water when it comes into contact with a surface, while cohesion is responsible for the beading and wetting effects that can be seen when water is placed on a surface.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Water Made Of?
Water is made up of two elements: oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen is the larger of the two molecules and gives water its liquid form. Hydrogen is a much smaller molecule and is responsible for the chemical properties of water, like its ability to dissolve other molecules.
What Is Water’s Molecular Structure?
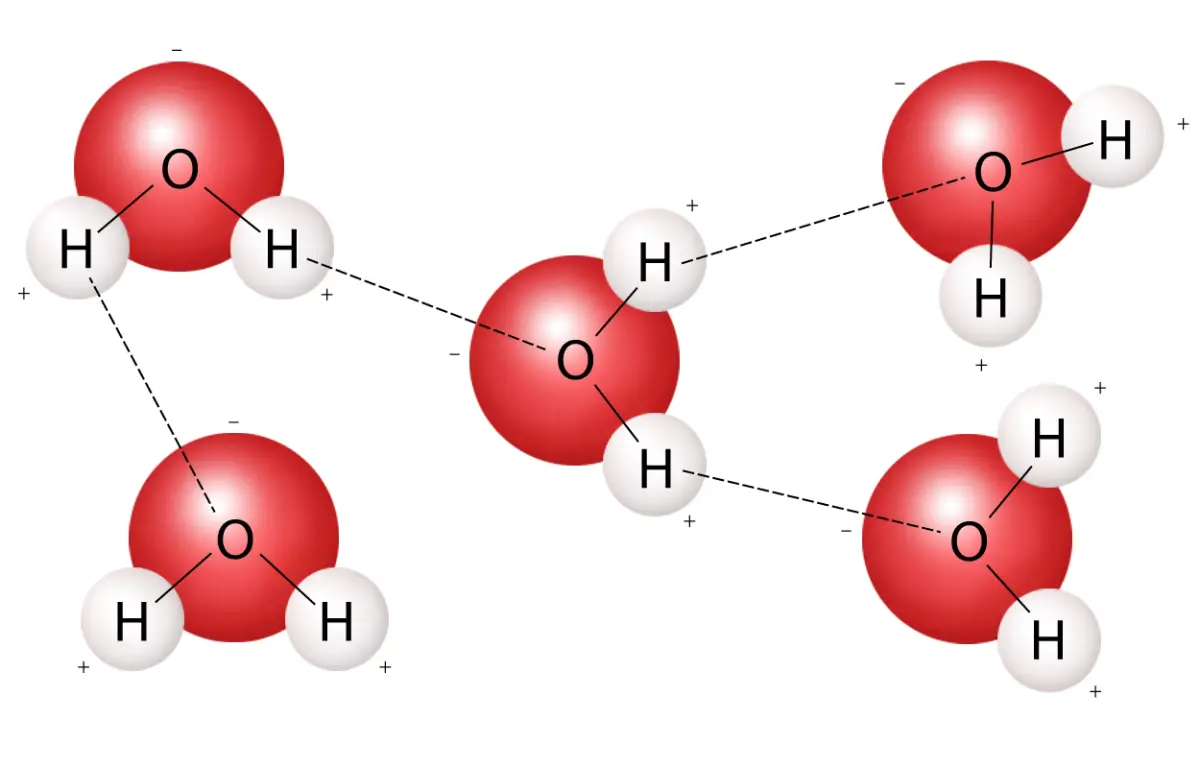
Water has a very unique molecular structure. Its molecules are arranged in what is known as a “bent” shape. This shape allows water to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules, which is what gives it its “stickiness”. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons which are highly attracted to hydrogen atoms from other molecules. This creates a strong bond between the molecules, allowing them to stick together.
Why Is Water Sticky?
Water is sticky because of its molecular structure. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons which are highly attracted to hydrogen atoms from other molecules. This creates a strong bond between the molecules, allowing them to stick together. Water has a very low surface tension due to its bent molecular structure and this allows it to easily spread and cling to other surfaces.
What Is Surface Tension?
Surface tension is the force that occurs between the molecules of a liquid when they come together at the surface. This force is caused by the attractive forces of the molecules trying to maintain the liquid’s shape. Water has a very low surface tension due to its bent molecular structure, allowing it to easily spread and cling to other surfaces.
What Other Factors Contribute To Water’s Stickiness?
Apart from its molecular structure, other factors contribute to water’s stickiness. Water has the ability to dissolve other molecules, which makes it cling to many different surfaces. It is also able to absorb and retain heat, which can cause it to become more viscous and sticky. Additionally, chemicals, salts, and other materials can also affect the stickiness of water.
How Does Water’s Stickiness Affect Us?
Water’s stickiness can have both positive and negative effects on us. On the one hand, it can help us clean surfaces and objects by clinging to dirt and grime. On the other hand, it can also cause problems by making surfaces slippery, or by causing mold or mildew to form. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the stickiness of water and how it can affect us.
Is Water Sticky?
Water is an essential substance in our everyday lives. Not only is it the source of life, but it also plays an important role in sustaining our environment. What we may not have known is that water is also sticky – its viscosity means that it can cling to surfaces and objects. This property is useful in a variety of applications, from controlling dust particles in the air to helping with adhesives. In conclusion, water is not only a vital part of our existence, but it is also an incredibly useful tool that we often take for granted.