The sun has been a key source of light and heat for human life since the dawn of time. But, with the rise in skin cancer rates, the question of how to safely tan has become even more important. While there are a variety of options out there, one of the most popular is UV tanning. But what is the best UV to tan? In this article, we’ll explore the pros and cons of UV tanning and how to choose the best UV to tan. With the right information and precautions, you can enjoy a safe and healthy summer tan.
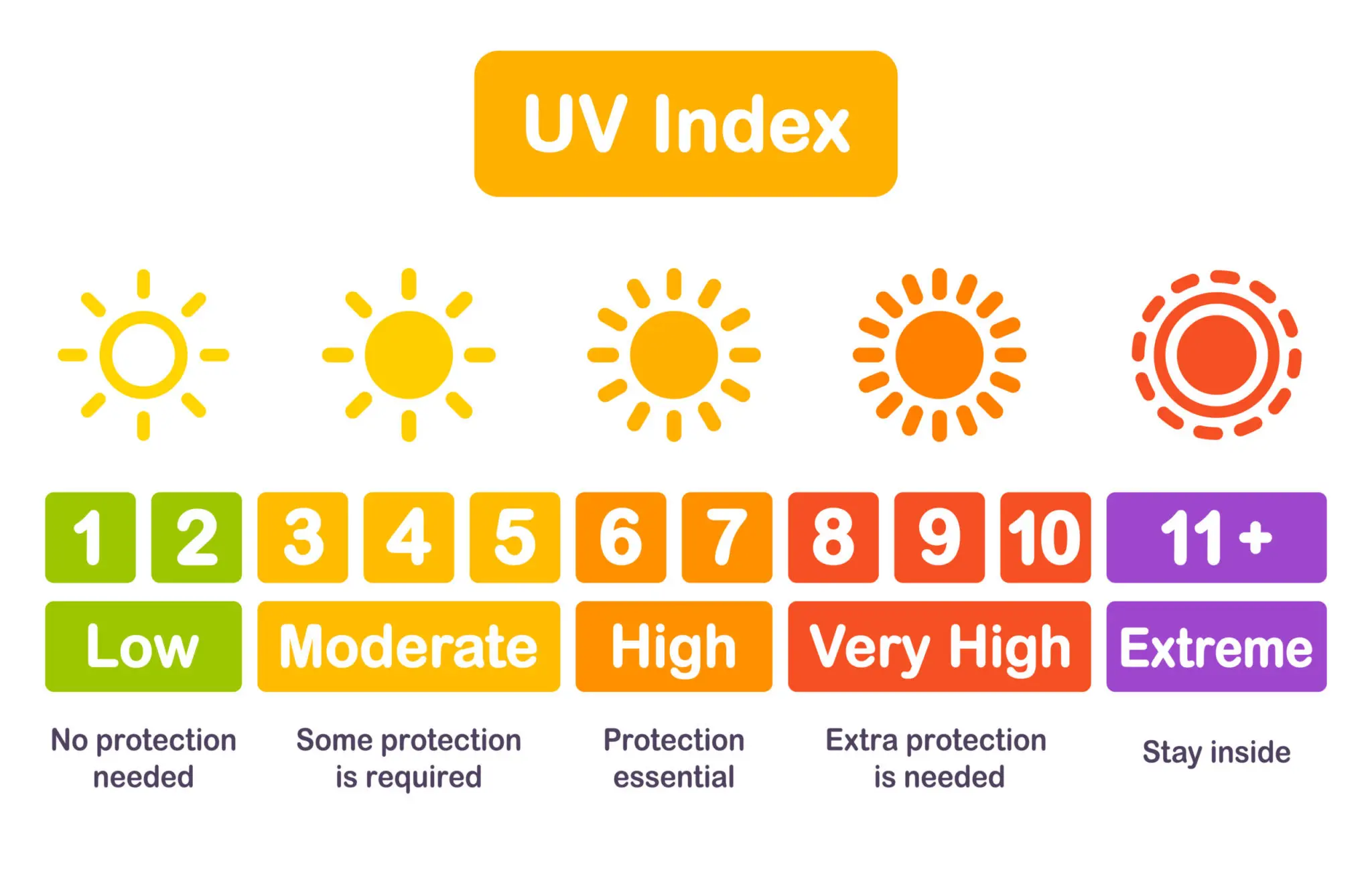
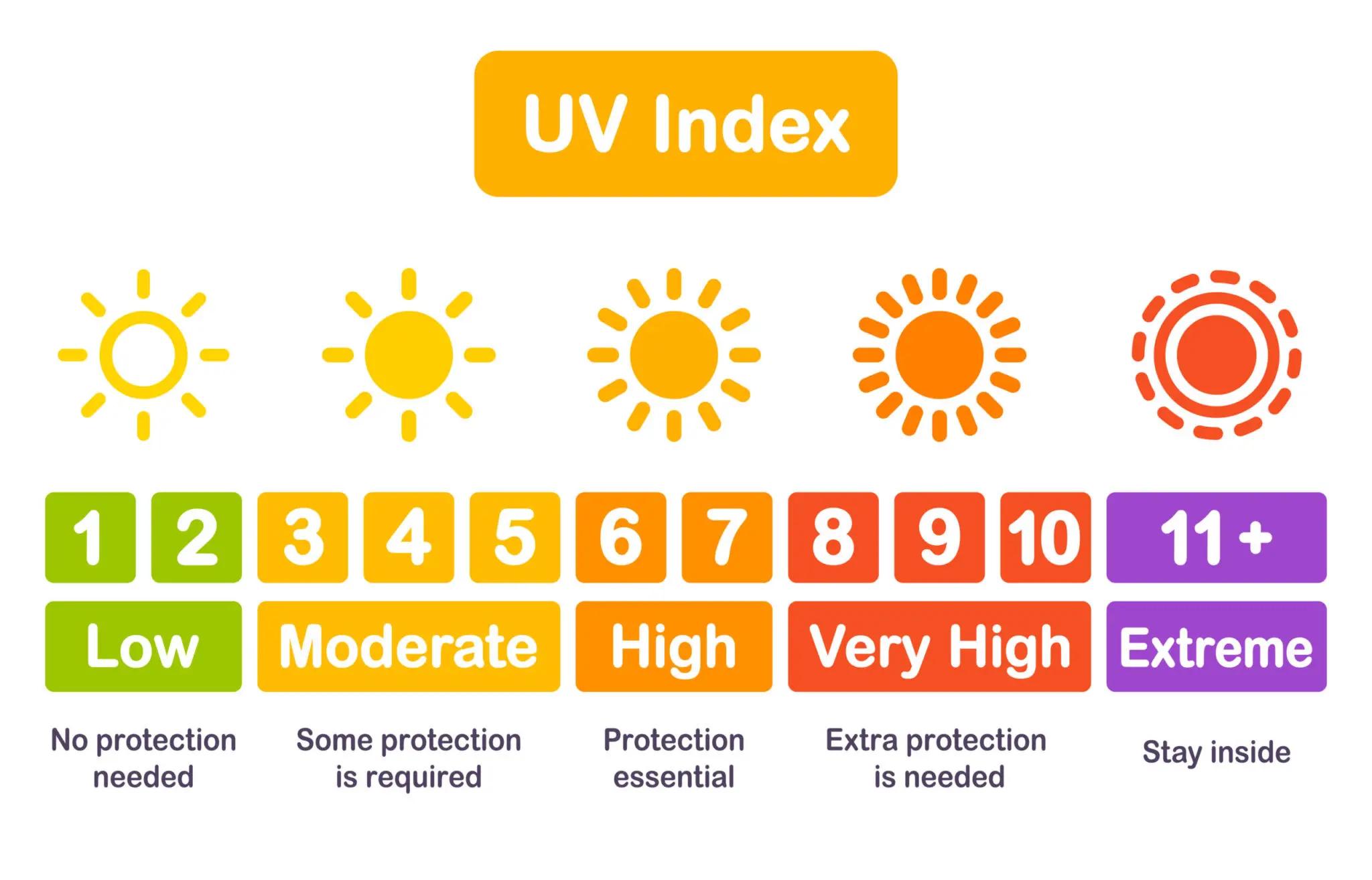
The best time to tan is during the mid-morning and mid-afternoon hours, when the sun is less intense. However, this is also the time when the UV index is the highest, so you should use sun protection measures such as sunscreen and protective clothing. The UV index is a measure of the intensity of ultraviolet radiation from the sun and is given on a scale of 0–11. It is important to use a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and to reapply it every two hours. Sunscreen should also be applied even on cloudy days, as UV radiation can still reach the skin.
Contents
What is the Best UV Level for Tanning?
Tanning is a popular activity that involves exposing skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. Tanning is often done to achieve a bronzed glow or to improve the appearance of skin that has been damaged by sunburns. However, too much UV exposure can be dangerous. Therefore, it is important to determine the best UV level for tanning to get the desired results without compromising your health.
The UV index measures the intensity of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. This index is used to determine the best UV level for tanning. It ranges from 0 to 11, with 0 being the lowest level of UV radiation and 11 being the highest. The higher the UV index, the stronger the intensity of ultraviolet radiation and the greater the risk of sunburn and skin damage.
Best UV Level For Tanning
The best UV level for tanning depends on an individual’s skin type and tanning goals. Generally, a UV index of 3 or lower is considered safe for most skin types. This is the ideal UV level for tanning as it allows for a gradual tan without causing sunburn or skin damage.
For those with darker skin tones, a UV index of 6 or higher may be necessary to achieve a tan. This level of UV radiation can be dangerous, however, and is not recommended for those with fair skin.
UVA and UVB Rays
UVA and UVB rays are two types of ultraviolet radiation that are found in sunlight. UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, causing it to tan more quickly, while UVB rays primarily cause sunburns.
The best UV level for tanning should include a balance of both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays are best for tanning, while UVB rays help to protect the skin from sunburn. A UV index of 3 or lower is ideal for most skin types as it provides a healthy balance of both UVA and UVB rays.
Safety Tips For Tanning
It is important to take safety precautions when tanning in order to reduce the risk of sunburn, skin damage, and other health issues. The following tips can help you stay safe when tanning:
Wear Sunscreen
Always wear sunscreen when tanning, even if the UV index is low. Sunscreen helps to protect your skin from UV damage and can help prevent sunburns.
Limit Exposure
Limit your exposure to the sun and tanning beds. Start with a few minutes at a time and increase your exposure as your skin gets used to the UV rays.
Wear Protective Clothing
Wear protective clothing such as a hat and sunglasses to protect your eyes and face from the sun. Lightweight, long-sleeved shirts and pants can also help to protect your skin from UV rays.
Monitor Skin Condition
Monitor your skin for any changes in color or texture. If you notice any signs of sunburn or skin damage, stop tanning and seek medical attention.
Related Faq
Q1: What is Tanning?
A1: Tanning is the process of exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) radiation to produce a cosmetic tan. This is typically done in a tanning salon, but can also be done outdoors, where UV rays from the sun are used. Tanning is not recommended, as it increases the risk of skin cancer and other health issues.
Q2: What are the Different Types of UV Rays?
A2: There are three main types of UV rays – UVA, UVB and UVC. UVA rays are the longest wavelength, and penetrate the deepest into the skin. They can cause skin aging and wrinkling, and are the main cause of skin cancer. UVB rays are shorter in wavelength, and are the main cause of sunburns. UVC rays are the shortest wavelength, and are almost completely blocked by the ozone layer, so they are not a concern when it comes to tanning.
Q3: What is the Best UV for Tanning?
A3: UVA rays are the best UV for tanning, as they penetrate the deepest into the skin. While they are the main cause of skin cancer, they are also responsible for the production of the cosmetic tan. Therefore, when tanning in a salon, it is important to ensure that the tanning bed is producing UVA rays.
Q4: What are the Risks of Tanning?
A4: Tanning is not recommended, as it increases the risk of skin cancer and other health issues. UVA and UVB radiation can both cause skin damage, including sunburns, premature skin aging, and other skin conditions. Long-term exposure to UV radiation can also increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
Q5: What are the Alternatives to Tanning?
A5: There are many alternatives to tanning, such as self-tanning products, spray tans, and bronzing powders. These options can help you achieve a sun-kissed look without the risk of skin damage. Additionally, wearing sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors is highly recommended.
Q6: What are the Benefits of Tanning?
A6: While there are many risks associated with tanning, some people still choose to do it. Some of the possible benefits of tanning include improved mood, increased Vitamin D levels, and a more even skin tone. However, it is important to understand the risks and take precautions when tanning, such as using a sunscreen with a high SPF rating.
What is the best UV index for tanning?
After considering all the available options, it is clear that the best UV to tan is the one that offers a balanced approach between safety and efficacy. This means choosing a UV tanning option that provides the right intensity and duration of exposure, as well as proper safety precautions. With the right UV tanning option, you can enjoy a safe and beautiful tan without risking your health.