Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Ions are incredibly important when it comes to understanding how elements and molecules interact with each other. Ions are atoms or molecules that have either gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. In this article, we’ll discuss the two most common types of ions and how they work.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, giving them a net electric charge. There are two types of ions: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions and are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. Anions are negatively charged ions created when an atom gains one or more electrons.
Cations are positively charged ions and are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. Anions are negatively charged ions created when an atom gains one or more electrons.

Contents
An Overview of Two Types of Ions
Ions are atoms or molecules with a net electrical charge. These charges can be either positive or negative and can be found in a variety of environments, including the atmosphere and water. Ions can be divided into two main categories: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
What Are Cations?
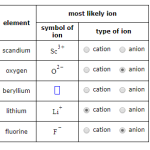
Cations are atoms or molecules that have lost one or more electrons, making them positively charged. Common examples of cations include sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca2+). Cations are often found in rock and soil, and can be found in the ocean.
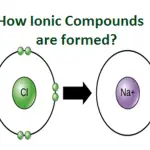
Cations are also found in a variety of chemical reactions. In these reactions, cations can act as Lewis bases, or electron donors. For example, when sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves in water, the sodium cation forms a bond with the water molecule, allowing the chloride anion to dissolve.
What Are Anions?
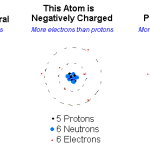
Anions are atoms or molecules that have gained one or more electrons, making them negatively charged. Common examples of anions include chloride (Cl-), sulfate (SO42-), and nitrate (NO3-). Anions are commonly found in soil, water, and air.
Anions are also found in a variety of chemical reactions. In these reactions, anions can act as Lewis acids, or electron acceptors. For example, when carbon dioxide (CO2) reacts with water, the carbon dioxide molecule forms a bond with the water molecule, allowing the oxygen anion to be released.
Uses of Ions
Ions play an important role in a variety of processes, including biological, chemical, and physical processes. In biology, ions are important for maintaining the balance of electrolytes in the body, while in chemistry they are used in a variety of reactions to form new compounds.
In Biology
In biology, ions play an important role in the maintenance of electrolyte balance. Electrolytes are substances that are able to conduct electricity when dissolved in water, and they are essential for the proper functioning of cells. Sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium are some of the most important electrolytes in the body, and they are all present in the form of ions.
In Chemistry
In chemistry, ions are used to form new compounds. Ions can form ionic bonds, which are bonds formed between two oppositely charged ions. These bonds are strong and stable, and are responsible for the stability of many compounds. For example, when sodium chloride (NaCl) is dissolved in water, the sodium cation forms an ionic bond with the chloride anion, resulting in the formation of a stable compound.
Ionization Energy
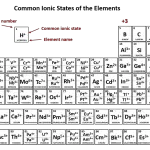
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. Ionization energy increases as the atomic number of an element increases, meaning that it takes more energy to remove an electron from more massive atoms.
Atomic Number and Ionization Energy
Atomic number is a measure of the number of protons an atom has, and it is directly related to the ionization energy of an atom. As the atomic number increases, so does the ionization energy, meaning that it takes more energy to remove electrons from more massive atoms. This phenomenon is known as the “atomic number effect”.
Factors That Affect Ionization Energy
In addition to the atomic number, there are other factors that can affect the ionization energy of an atom. These include the number of electrons present in the atom, the nuclear charge, and the electron configuration of the atom. For example, when an atom has more electrons, it takes more energy to remove an electron from the atom.
Conclusion
Ions are atoms or molecules with a net electrical charge and can be divided into two main categories: cations and anions. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. Ions are important for a variety of processes, including biological, chemical, and physical processes. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or molecule, and it is affected by the atomic number and other factors such as the number of electrons present in the atom, the nuclear charge, and the electron configuration of the atom.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Two Types of Ions?
Answer: An ion is an atom or molecule that has an electrical charge due to a difference in the number of protons and electrons. There are two types of ions: cations and anions.
What is a Cation?
Answer: A cation is a positively charged ion that occurs when an atom or molecule has lost one or more electrons. Cations are formed when an atom or molecule has more protons than electrons, resulting in a net positive charge. Cations are attracted to anions, which have a net negative charge. Examples of cations include sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), and copper (Cu2+).
What is an Anion?
Answer: An anion is a negatively charged ion that occurs when an atom or molecule has gained one or more electrons. Anions are formed when an atom or molecule has more electrons than protons, resulting in a net negative charge. Anions are attracted to cations, which have a net positive charge. Examples of anions include chloride (Cl-), sulfate (SO4 2-), and nitrate (NO3-).
What is the Difference Between Cations and Anions?
Answer: The difference between cations and anions is that cations are positively charged ions and anions are negatively charged ions. Cations are formed when an atom or molecule has lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive charge. Anions are formed when an atom or molecule has gained one or more electrons, resulting in a net negative charge.
What Particles Make up Ions?
Answer: Ions are made up of atoms or molecules that have an electrical charge due to a difference in the number of protons and electrons. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge. When an atom or molecule has an unequal number of protons and electrons, it forms an ion with either a positive or negative charge.
Where Do Ions Occur in Nature?
Answer: Ions occur in nature in many different forms. They are found naturally in the environment, and they are also present in the human body, plants, and animals. Ions form when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons, resulting in a difference in the number of protons and electrons. Ions can occur in chemical reactions, such as in the formation of salts, acids, and bases. Ions are also present in the atmosphere and in water.
IONS – CATION & ANION [ AboodyTV ] Chemistry
In conclusion, Ions are atoms or molecules that have an electrical charge. They can be either positively charged, where there are more protons than electrons, or negatively charged, where there are more electrons than protons. Understanding the two types of ions is important for understanding the behavior of many chemical reactions.