Last Updated on 12 months by Francis
UV light therapy is a treatment that involves exposing the skin or affected area to ultraviolet light in order to treat a range of conditions, from psoriasis to seasonal depression. However, as with any medical treatment, there are concerns about the safety of UV light therapy. In this discussion, we will explore the potential risks and benefits of this treatment and answer the question: is UV light therapy dangerous?
Contents
Understanding UV Light Therapy
UV light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a medical treatment that involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light. This treatment is commonly used to treat skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo. UV light therapy is also used to treat seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and some types of cancer.
The Different Types of UV Light
There are three different types of UV light: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA and UVB are the types of UV light used in phototherapy. UVA penetrates deep into the skin and is used to treat conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. UVB is used to treat vitiligo and other skin conditions. UVC is not used in phototherapy because it is dangerous to humans.
How UV Light Therapy Works
UV light therapy works by slowing down the growth of skin cells. It also reduces inflammation and can help with the production of vitamin D in the skin. The treatment is usually administered in a doctor’s office or treatment center, but some people may use UV light therapy at home with a prescription from their doctor.
The Risks of UV Light Therapy
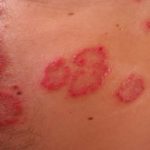
While UV light therapy can be an effective treatment for certain conditions, it does come with some risks. The most significant risk associated with UV light therapy is an increased risk of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer
Exposure to UV radiation is a known risk factor for skin cancer. When undergoing UV light therapy, patients are exposed to high levels of UV radiation, which can increase their risk of developing skin cancer. The risk of skin cancer is higher in people who have fair skin, a history of skin cancer, or a family history of skin cancer.
Other Risks
In addition to an increased risk of skin cancer, UV light therapy can also cause other side effects such as:
- Sunburn
- Itching
- Dry skin
- Nausea
- Dizziness
Precautions
To minimize the risks of UV light therapy, it’s essential to take certain precautions. Patients who undergo UV light therapy should:
- Wear protective eyewear during treatment
- Protect their skin from the sun after treatment
- Avoid tanning beds and other sources of UV radiation
Alternatives to UV Light Therapy
If you’re concerned about the risks associated with UV light therapy, there are several alternatives available.
Blue Light Therapy
Blue light therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses blue light to kill bacteria on the skin. It’s commonly used to treat acne but may also be effective for other skin conditions.
Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses red light to promote healing and reduce inflammation. It’s commonly used to treat skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a medical treatment that uses a laser to target specific areas of the skin. It’s commonly used to treat skin conditions such as acne, rosacea, and scars.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments such as creams and ointments can also be effective for treating skin conditions. These treatments are applied directly to the skin and work by reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
FAQs – Is UV Light Therapy Dangerous?
What is UV light therapy?
UV light therapy is a treatment method used to treat certain skin conditions, such as psoriasis, vitiligo, and eczema. This therapy involves the use of ultraviolet light, which is a type of radiation that is produced by the sun. It is administered either through a special light box or by exposure to natural sunlight.
What are the potential risks of UV light therapy?
While UV light therapy is generally considered safe and effective, it does come with certain risks. Exposure to UV radiation can increase the risk of skin cancer, premature aging, cataracts, and other skin-related problems. Overexposure to UV radiation can also cause burns, rashes, and other skin irritations.
Who is at risk of experiencing negative side effects from UV light therapy?
Individuals with fair skin, those who have a history of skin cancer, and those who are taking certain medications that increase sensitivity to light may be at a higher risk of experiencing negative side effects from UV light therapy. Pregnant women and individuals with certain medical conditions should also consult with a doctor before undergoing UV light therapy.
Can UV light therapy be done safely?
Yes, UV light therapy can be done safely when administered by a qualified healthcare professional. The risks associated with this therapy can be minimized with proper pre-treatment evaluation and monitoring, as well as appropriate protective measures, such as wearing sunscreen and protective eyewear during treatment.
How can I ensure the safety of UV light therapy?
To ensure the safety of UV light therapy, it is important to follow the instructions of the healthcare professional administering the treatment. This may include taking certain precautions, such as avoiding exposure to sunlight for a specified period of time before and after treatment, wearing protective gear during treatment, and following post-treatment care instructions. It is also important to communicate any concerns or questions with the healthcare professional before undergoing treatment.