Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Have you ever wondered why sodium is so important for the human body? Sodium is an essential mineral and an important electrolyte, meaning it carries an electrical charge. But what is the charge of sodium? Is sodium negatively charged? In this article, we will explore the answer to this question, and the role sodium plays in the human body.
Sodium is a chemical element with symbol Na (from Latin “natrium”) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists naturally in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite and rock salt.
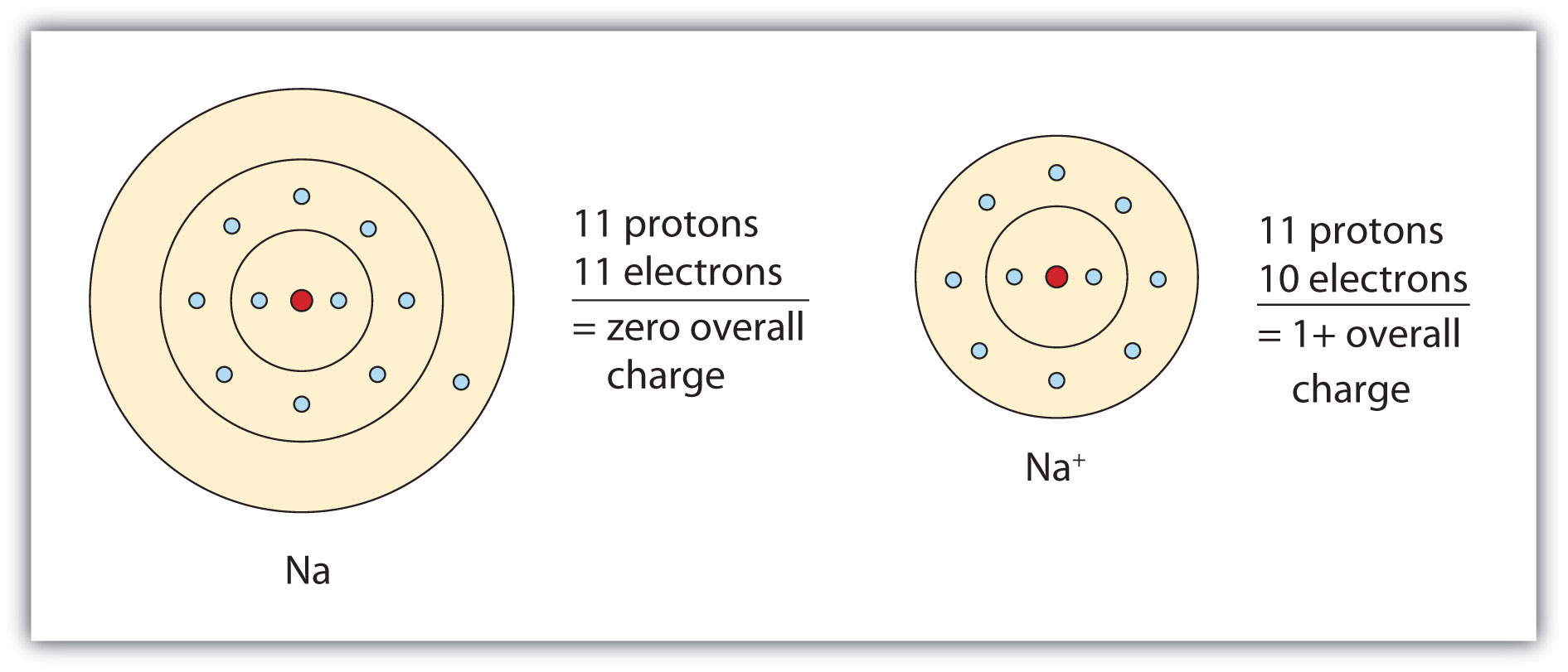
Sodium is a positively charged ion, Na+, while chloride is a negatively charged ion, Cl−. When they combine, they form a neutral compound, sodium chloride, which is salt. So, sodium is not negatively charged.
Contents
Exploring the Charge of Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element found in nature and is essential to life. It is used in many different industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and even industrial processes. Sodium has a number of properties, one of the most important of which is its charge. So, is sodium negatively charged?
To better understand the charge of sodium, it is important to understand what a charge is and how it works. A charge is an electrical property that describes the ability of an atom or molecule to attract or repel other atoms or molecules. Positively charged particles, like protons, are attracted to negatively charged particles, like electrons. Negatively charged particles, like electrons, are attracted to positively charged particles, like protons.
The Structure of Sodium
Sodium is made up of 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons. The protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of the atom, while the electrons form shells around the nucleus. The number of protons determines the chemical element, and the number of electrons determines its charge. In the case of sodium, it has 11 protons and 11 electrons, which means it has a neutral charge.
However, when sodium is exposed to other elements, such as oxygen or chlorine, it can gain or lose electrons. If it gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged. If it loses an electron, it becomes positively charged. This process is called ionization, and it is the key to understanding the charge of sodium.
The Effects of Ionization on Sodium
When sodium is ionized, it can gain or lose electrons. If it gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged. If it loses an electron, it becomes positively charged. This process is known as “charge transfer”, and it is what determines the charge of sodium.
When sodium is ionized, it can form bonds with other elements. For example, when sodium combines with chlorine, it creates the compound sodium chloride, which is also known as table salt. In this process, the sodium atom gains an electron from the chlorine atom, and the chlorine atom loses an electron. This gives the sodium atom a negative charge, and the chlorine atom a positive charge.
Sodium in Solutions
When sodium is dissolved in water, it forms a solution. In this solution, the sodium atom is surrounded by water molecules. The water molecules can donate or remove electrons from the sodium atom, changing its charge. If the water molecules donate electrons to the sodium atom, it will become negatively charged. If the water molecules remove electrons from the sodium atom, it will become positively charged.
The charge of sodium in a solution will depend on the pH of the solution. If the solution is acidic, the sodium will be positively charged. If the solution is basic, the sodium will be negatively charged.
The Role of Sodium in the Human Body
Sodium plays an important role in the human body. It helps maintain the balance of fluids in the body, as well as the acid-base balance. It also helps to regulate nerve and muscle function, and it is essential for the absorption of nutrients.
In the human body, sodium is typically found in the form of sodium chloride, or table salt. It is important to maintain the proper balance of sodium in the body, as too much or too little can lead to health problems. For this reason, it is important to pay attention to your sodium intake and ensure that you are eating a healthy, balanced diet.
Conclusion
To answer the question, “Is sodium negatively charged?” it is important to understand the structure of sodium and how it is affected by ionization and solutions. In its natural state, sodium is neutral, but it can become either positively or negatively charged when it is ionized. In addition, the charge of sodium in a solution will depend on the pH of the solution. Lastly, sodium plays an important role in the human body, and it is important to maintain a healthy balance of sodium in the body.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is Sodium?
A1: Sodium is a chemical element that is found in many foods and used in a variety of industrial and medical processes. It has the symbol Na and its atomic number is 11. Sodium is a soft, silvery-white metal that is highly reactive and does not occur naturally in its elemental form. It is most commonly found in the form of compounds such as sodium chloride (table salt), sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), and sodium hydroxide (lye).
Q2: What is the charge of Sodium?
A2: Sodium is a highly reactive metal and has a single positive charge. The outermost electron of sodium is in the 3s orbital, which is relatively far away from the nucleus and is easily lost. This makes sodium a cation, meaning it has a positive charge. Sodium ions have a +1 charge.
Q3: Is Sodium Negatively Charged?
A3: No, sodium is not negatively charged. As stated above, sodium is a cation and has a single positive charge. Additionally, it is important to note that the charge of an atom or ion cannot be changed. Therefore, sodium will always remain positively charged.
Q4: How does Sodium React with other Molecules?
A4: Sodium is a highly reactive metal and reacts readily with other molecules. Due to its positive charge, it is attracted to negatively charged ions and molecules. When sodium reacts with other molecules, it often forms a salt, such as sodium chloride (table salt). In these reactions, the positive charge of the sodium ion is balanced by the negative charge of the ion or molecule it is reacting with.
Q5: What is the Electron Configuration of Sodium?
A5: The electron configuration of sodium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1. This means that the outermost electron of sodium is in the 3s orbital, which is relatively far away from the nucleus and is easily lost. This makes sodium a cation, meaning it has a positive charge.
Q6: What are the Uses of Sodium?
A6: Sodium has a variety of uses, both domestically and industrially. Common domestic uses include baking, seasoning, and preserving food. Industrially, sodium is used in a variety of processes, including the production of glass, paper, and soap, as well as in the manufacture of detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, sodium is used in many medical processes, such as in the treatment of hypertension and in MRI scans.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Membrane Potential
To conclude, it is clear that sodium is indeed negatively charged. It is a type of ion that has a single negative charge, due to the loss of an electron. This charge affects the way in which sodium interacts with other molecules and is an integral part of many biochemical processes. As such, it is important to understand the nature of sodium and its negative charge in order to better understand the chemistry of many important systems.


.jpg)




