Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Oil is an essential part of our daily lives, but do you know if it is polar or non-polar? It is a question that has long puzzled scientists and laypeople alike, and the answer might surprise you. In this article, we will explore the concept of polarity and discuss whether oil is a polar or non-polar substance. We will also look at the various properties of oil and how they relate to its polarity, as well as its uses and applications. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the properties and uses of oil, and you will know the answer to the question: is oil a polar or non-polar substance?

Contents
What Is Oil?
Oil is a type of hydrocarbon, which is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid that is composed of a mix of different hydrocarbons. Oil is made up of a complex mixture of hydrogen and carbon atoms, and it is found in many different forms, such as crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products. Oil is a non-renewable resource and is used for a variety of purposes, including energy production, transportation fuel, and lubricants.
Oil is one of the most important commodities in the world and is responsible for powering our modern economy. It is used in a wide range of products, from gasoline, jet fuel, and heating oil, to plastic, rubber, and lubricants. Oil is also used as a raw material for the production of many synthetic materials, such as plastics and fabrics, and it is used in the manufacturing of many everyday products, from pharmaceuticals to cosmetics.
What Is the Difference Between Polar and Non-Polar Molecules?
Polar molecules are molecules that have an uneven distribution of electrons, which gives them a slightly positive and negative charge, while non-polar molecules have an even distribution of electrons, which makes them neutral. Polar molecules are attracted to each other, while non-polar molecules are not.
A good example of a polar molecule is water, which has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The water molecule has two regions of positive and negative charges, which makes it a polar molecule. When two water molecules come close together, they form hydrogen bonds, which are the basis of the attraction between them.
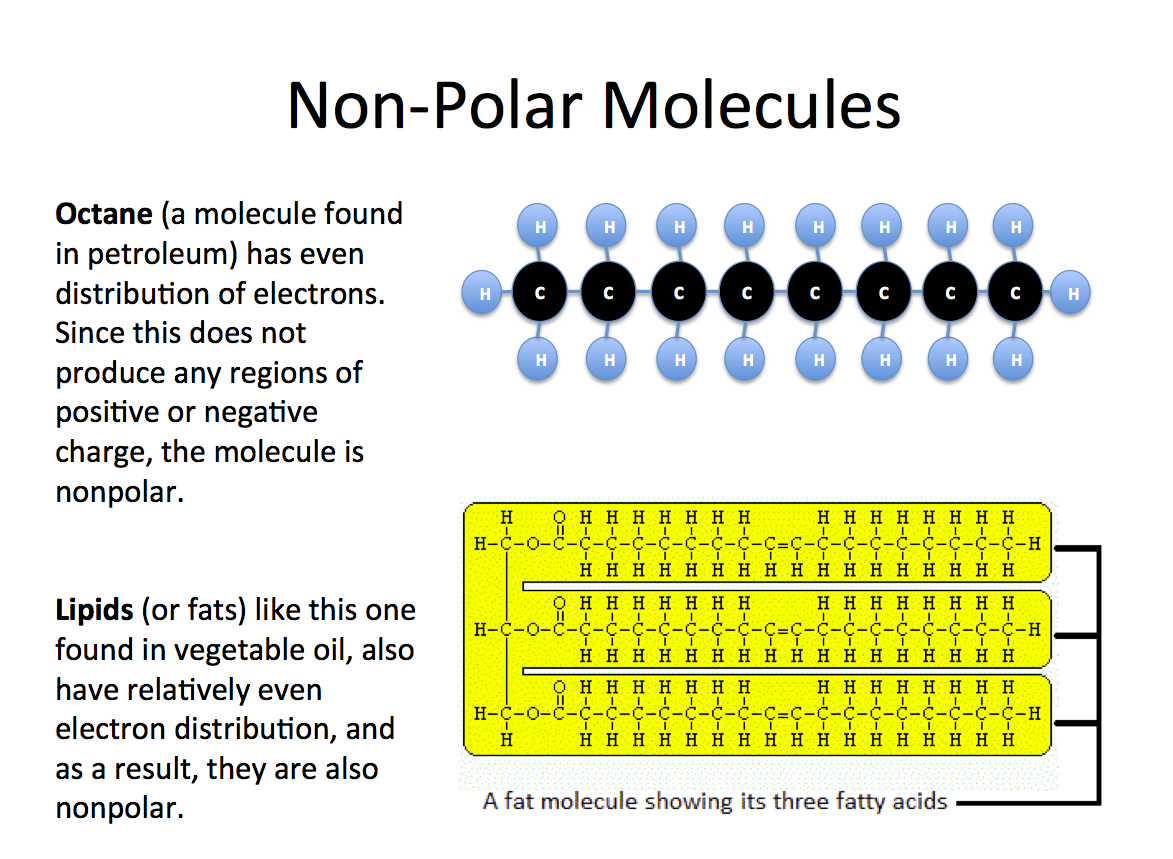
Non-polar molecules, on the other hand, have an even distribution of electrons, which means that they are not attracted to each other. A good example of a non-polar molecule is oil, which is made up of a mixture of different hydrocarbons. Oil does not have any regions of positive and negative charges, which makes it a non-polar molecule.
Why Is Oil Considered a Non-Polar Molecule?
Oil is composed of a mixture of different hydrocarbons, which are molecules that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. These molecules are not attracted to each other, and they do not have any regions of positive and negative charges. This makes oil a non-polar molecule.
The lack of polarity in oil is one of the main reasons why it is so useful. Non-polar molecules do not dissolve in water, which means that oil and water do not mix. This makes it possible to separate oil from water, which is important in many industries, such as the petroleum industry.
Non-polar molecules also have a low surface tension, which makes them less likely to adhere to other molecules. This makes them ideal for lubrication, as they can easily slide past each other without sticking.
How Does Oil Behave in an Electric Field?
Oil is considered to be a non-polar molecule, which means that it is not affected by electric fields. Non-polar molecules have an even distribution of electrons, which makes them neutral and unable to be attracted or repelled by electric fields.
This lack of polarity makes it possible for oil to be used as an insulator, as it will not conduct electricity. It is also useful as a lubricant, as it is not affected by electric fields and can easily slide past each other without sticking.
The Properties of Oil
Oil is a non-polar molecule, which means that it has a low surface tension and is not affected by electric fields. It also has a low viscosity, which makes it easier to move through pipelines and other vessels.
Oil is also a valuable resource, as it is a non-renewable resource that is used in a variety of industries, from energy production to transportation fuel. It is also used as a raw material for the production of many synthetic materials, such as plastics and fabrics.
Oil has many useful properties, which makes it an important resource for the modern economy. Its non-polar nature makes it easy to separate from water, which is important in many industries, and its low viscosity and surface tension make it an ideal lubricant and insulator.
Related Faq
What is a Non-Polar Substance?
A non-polar substance is one where the electrons in the molecules are evenly distributed, rather than being attracted to one side. This means that the molecules are not attracted to each other, and therefore do not form strong bonds. This type of molecule is often referred to as “hydrophobic,” as it does not mix well with water.
Is Oil a Non-Polar Substance?
Yes, oil is a non-polar substance. Oil molecules are composed of hydrocarbons, which are carbon and hydrogen atoms. Since the electrons are evenly distributed throughout the molecule, oil does not form strong bonds with other molecules, making it a non-polar substance.
What Are the Properties of a Non-Polar Substance?
Non-polar substances are not soluble in water and are generally hydrophobic. They also tend to be less dense than water, meaning they will float on the surface. Non-polar substances are also non-conductive, meaning they do not conduct electricity.
What Are the Uses of Non-Polar Substances?
Non-polar substances are often used in industry and in everyday life. They are used as lubricants, as insulation, and as solvents. They are also used in the manufacture of plastics and pharmaceuticals.
Why is Oil a Non-Polar Substance?
Oil is a non-polar substance because it is composed of hydrocarbons. The electrons in the molecules of oil are evenly distributed, meaning that the molecules do not form strong bonds with each other. This makes oil a non-polar substance, which is why it does not mix well with water.
What Other Substances are Non-Polar?
In addition to oil, other non-polar substances include waxes, fats, and many other organic molecules. Some inorganic substances, such as carbon dioxide, are also non-polar. All of these substances have molecules with evenly distributed electrons, which result in a lack of strong bonds between molecules.
Polar & Non-Polar Molecules: Crash Course Chemistry #23
In conclusion, it is clear that oil is a non-polar molecule. This is due to its molecular structure, which consists of hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains that are bound together with strong covalent bonds. As a result, oil does not mix with water, and instead forms a separate layer on the surface. This property makes oil a useful material for many industrial processes, and it is also a major source of energy.