Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Have you ever wondered why protons are always positively charged? It’s one of the most fundamental principles of physics and chemistry, but understanding the details behind this phenomenon can be difficult. In this article, we’ll explore the scientific principles behind the positive charge of protons and what makes them so important to all forms of matter. By the end, you’ll understand why a proton is always positive and its implications in the larger universe.

Contents
What is a Proton?
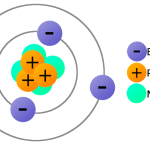
A proton is a subatomic particle found in all atoms. It is the positively charged nucleus of an atom and is composed of three quarks. Protons are stable, meaning they do not decay or change over time. Proton is the most abundant of the three subatomic particles, making up nearly all of an atom’s mass.
The proton is the most important particle in the nucleus of an atom. It is important in nuclear stability and in the formation of chemical bonds. It is also the source of energy in nuclear reactions, and is used in a variety of medical applications.
What is the Charge of a Proton?
The charge of a proton is always positive. It is equal to the charge of an electron but of opposite sign. The charge of a proton is 1.602 x 10^-19 Coulombs. This means that it attracts electrons and other negatively charged particles and repels other positively charged particles.
The charge of a proton is exactly the same as the charge of a hydrogen ion. This is why a proton is sometimes referred to as a hydrogen ion. Protons are also the basis of the periodic table of elements because each element is defined by the number of protons it contains.
What is the Mass of a Proton?
The mass of a proton is equal to 1.6726 x 10^-27 kilograms. This is much less than the mass of an electron. This difference in mass is what allows protons and electrons to form chemical bonds.
The mass of a proton is not affected by its charge. This is why a proton is always positive, even when it is part of a molecule or atom.
How is a Proton Formed?
A proton is formed when two up quarks and one down quark come together. This combination is known as a baryon, and it is the basis for all matter. Baryons are held together by the strong nuclear force, which is much stronger than the electromagnetic force that holds electrons and protons together.
The quarks are held together by gluons, which are particles that carry the strong nuclear force. This is why a proton is stable and will not decay over time.
How Many Protons are in an Atom?
The number of protons in an atom is equal to its atomic number. This is because protons are the basis of the periodic table of elements and each element is defined by the number of protons it contains.
The number of protons in an atom also determines its identity. For example, hydrogen has one proton and oxygen has eight protons. This is why a proton is so important in the formation of molecules and chemical bonds.
What is the Difference Between a Proton and Neutron?
The main difference between a proton and neutron is their respective charges. A proton is positively charged, while a neutron is neutral. Protons and neutrons are both found in the nucleus of an atom, but they are held together by different forces.
The strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together, while the electromagnetic force holds electrons and protons together. This is why a proton is always positive, while a neutron can be either positive or negative.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is a proton?
A proton is a subatomic particle that forms part of an atom. It has a positive electric charge and is the heaviest particle in the atom. Protons are found in the nucleus of an atom, along with neutrons. They are made up of quarks, which are held together by the strong nuclear force.
Q2: Is a proton always positive?
Yes, a proton is always positively charged. The charge of a proton is +1, and it is the same no matter where it is located. This is because a proton’s charge is determined solely by its quark composition, which is always the same.
Q3: What causes the positive charge of a proton?
The positive charge of a proton is caused by its quark composition. A proton is composed of two up quarks and one down quark. Up quarks have a positive charge of +2/3, while down quarks have a negative charge of -1/3. When these quarks are combined, the net charge of the proton is +1.
Q4: How does the charge of a proton affect its behavior?
The charge of a proton affects its behavior in a number of ways. For example, it has an effect on the way it interacts with other particles. Protons will repel other particles with the same charge, while they will attract particles with the opposite charge. This is due to the fact that like charges repel and opposite charges attract.
Q5: What other particles have a positive charge?
Other particles that have a positive charge include positrons, antiprotons, and pions. Positrons have a charge of +1, antiprotons have a charge of -1, and pions have a charge of either +1 or -1. All of these particles are found in nature and are created in various physical processes.
Q6: Are there any particles with a charge other than positive or negative?
Yes, there are particles with a charge other than positive or negative. These particles are called neutral particles and they have no charge. Examples of neutral particles include neutrons, neutrinos, and photons. Neutrons, which are found in the nucleus of atoms, have no charge, while neutrinos, which are produced by radioactive decay, also have no charge. Photons, which are the particles that make up light, also have no charge.
Why Is An Electron Negative In Charge
In conclusion, it is clear that a proton is always positively charged. Through its basic properties, a proton always has a positive charge and this charge is what allows it to interact with other particles. This positive charge is essential to the stability of the universe, making protons one of the most important particles in physics.