Acute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency that can cause significant damage to the muscles, nerves and other tissues in the body if not addressed quickly and appropriately. Fortunately, there are a number of steps that can be taken to help prevent acute compartment syndrome before it develops. In this article, we’ll explore the vital importance of preventing acute compartment syndrome, and provide insight into the most effective ways to do so.
Acute compartment syndrome (ACS) is a condition in which increased pressure within a muscle compartment of the body causes decreased blood flow to the affected area. To prevent ACS, it is important to speak with a doctor if you experience swelling, pain, or numbness in a limb. Other preventive measures include avoiding activities that increase muscle compartment pressure, such as prolonged immobilization, intravenous drug use, and wearing tight clothing. It is also important to watch for signs of ACS, such as swelling and increasing pain that does not respond to pain medications.
- Step 1: Speak with your doctor if you experience swelling, pain, or numbness in a limb.
- Step 2: Avoid activities that increase muscle compartment pressure.
- Step 3: Take pain medications if you experience any pain.
- Step 4: Watch for signs of ACS, such as swelling and increasing pain.
Contents
Understanding What is Acute Compartment Syndrome
Acute Compartment Syndrome (ACS) is a condition that can lead to permanent tissue damage. It occurs when pressure in a specific compartment of the body rises to a level that is higher than the normal pressure that is found in the area. This can lead to decreased blood flow and oxygen to the affected area, resulting in tissue death. The most common cause of ACS is a traumatic injury, such as a broken bone or a severe muscle strain. Other causes can include a ruptured aortic aneurysm, burns, and severe muscle or nerve injury.
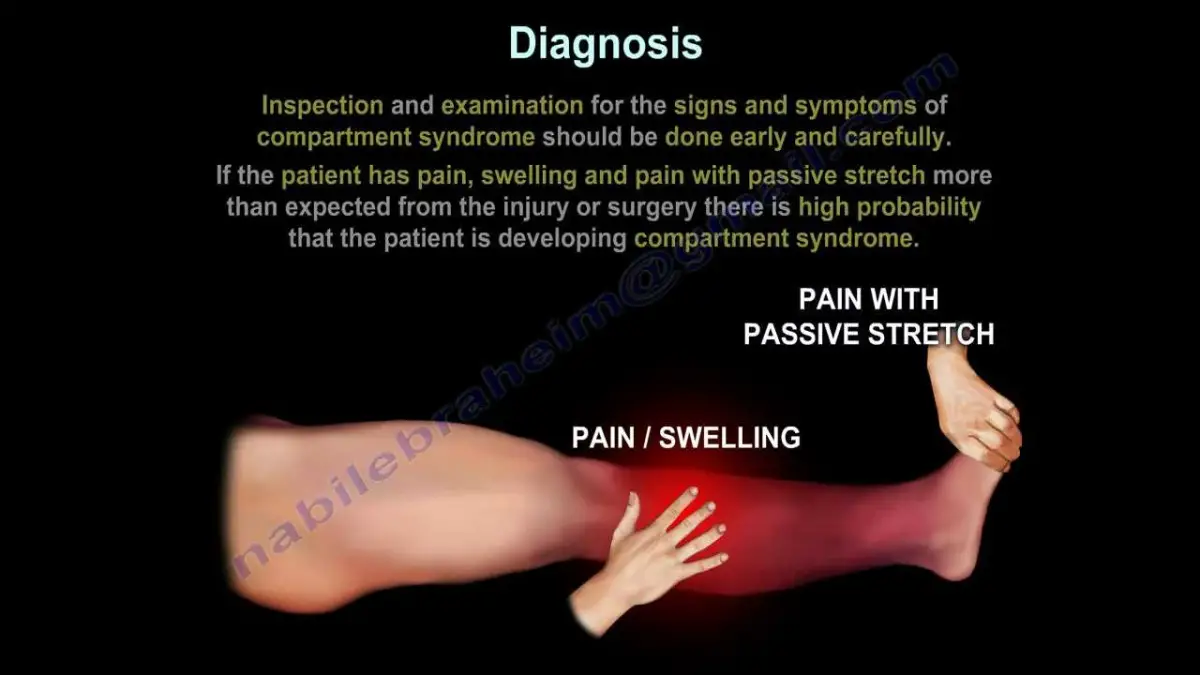
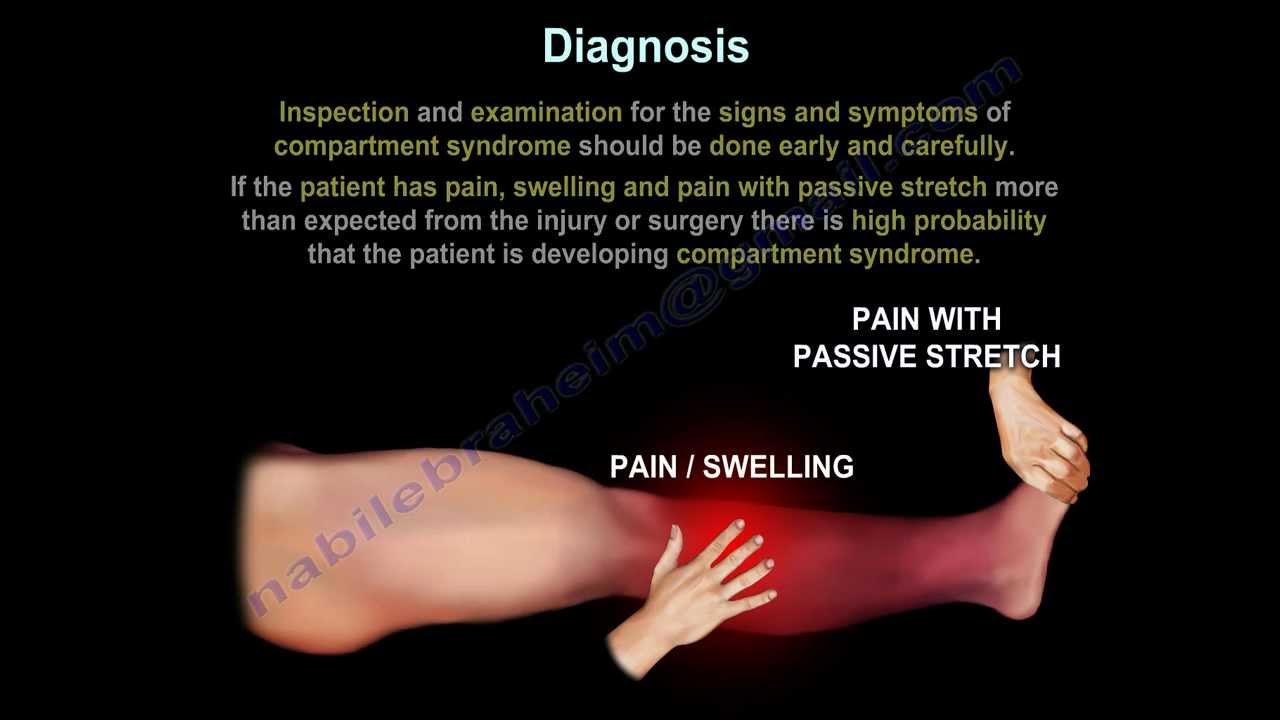
The most common symptom of ACS is severe pain in the affected area. Other symptoms may include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected area. Without proper treatment, ACS can lead to tissue death and permanent nerve damage. Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of ACS and seek medical attention if they occur.
Risk Factors for Acute Compartment Syndrome
There are several factors that can increase a person’s risk of developing ACS. These include fractures and crush injuries, burns, and bleeding. Other risk factors include an increase in pressure in the affected area, prolonged immobilization of the limb, and the use of certain medications, such as anticoagulants and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
People who have had previous surgery in the affected area are also at an increased risk of developing ACS. It is important to speak to your doctor about any previous medical conditions or treatments that may put you at an increased risk for ACS.
Steps for Preventing Acute Compartment Syndrome
The best way to prevent ACS is to recognize the signs and symptoms early on and seek medical attention as soon as possible. It is also important to take steps to reduce your risk of developing ACS.
One of the most important steps to take is to avoid activities that could lead to a traumatic injury, such as contact sports. If you have had previous surgery in the affected area, it is important to speak to your doctor about any activities that may put you at an increased risk of developing ACS.
It is also important to wear protective gear when engaging in activities that could lead to trauma, such as skiing and bicycling. Additionally, if you are taking any medications that could increase your risk of ACS, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Acute Compartment Syndrome
The most common symptom of ACS is severe pain in the affected area. Other symptoms may include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected area. If left untreated, ACS can lead to permanent nerve damage and tissue death.
It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the signs and symptoms of ACS. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the better the chances of preventing permanent damage to the affected area.
Diagnosis of Acute Compartment Syndrome
The diagnosis of ACS is based on a physical exam and a review of the patient’s medical history. The doctor may order imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis. The doctor may also order blood tests to check for inflammation or infection.
Treatment of Acute Compartment Syndrome
The goal of treatment for ACS is to reduce the pressure in the affected area and restore blood flow to the area. Treatment may include elevation of the affected area, pain medications, and immobilization of the affected area.
In severe cases, the doctor may order a procedure known as a fasciotomy, which involves cutting the affected area to relieve the pressure. Following the procedure, the doctor may recommend physical therapy to help restore strength and mobility to the affected area.
Conclusion
Acute Compartment Syndrome is a serious condition that can lead to permanent nerve damage and tissue death. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of ACS and seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, it is important to take steps to reduce your risk of developing ACS, such as avoiding activities that could lead to trauma, wearing protective gear, and speaking to your doctor about any medications that could increase your risk.
Related Faq
What is Acute Compartment Syndrome?
Acute Compartment Syndrome (ACS) is a medical condition caused by excessive pressure within a compartment or space of the body. It is a medical emergency that can cause permanent nerve damage, muscle damage, and even death if not treated promptly. The most common cause of ACS is a fracture or injury that causes bleeding or swelling of the affected tissue. Other causes include burns, trauma, surgery, and prolonged immobilization.
What are the Symptoms of Acute Compartment Syndrome?
The symptoms of Acute Compartment Syndrome can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include pain that increases with any movement of the affected area, numbness or tingling, and decreased sensation or motor function. Other symptoms may include difficulty straightening the affected limb, pale or mottled skin, and decreased pulse.
How Can Acute Compartment Syndrome be Prevented?
There are a few steps that can be taken to prevent Acute Compartment Syndrome. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of ACS early and seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, following the recommended guidelines for using splints, casts, and other forms of immobilization can help reduce the risk of ACS. Finally, avoiding activities that are known to increase pressure within a compartment, such as weightlifting or running, can help reduce the risk of ACS.
What are the Treatment Options for Acute Compartment Syndrome?
The main treatment for Acute Compartment Syndrome is to reduce the pressure within the compartment. This is typically done by performing a fasciotomy, which is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the fascia, or sheath of tissue, around the affected compartment. This procedure allows the pressure to be released, reducing the risk of permanent nerve and muscle damage. Other treatments, such as medication and physical therapy, may be recommended to help reduce pain and improve mobility.
How Can Acute Compartment Syndrome be Managed?
Once a patient has been diagnosed with Acute Compartment Syndrome, there are several steps that can be taken to manage the condition. It is important to follow the recommendations of the healthcare provider, including using any prescribed medications, taking part in physical therapy, and avoiding activities that could increase the pressure within the compartment. Additionally, it is important to monitor for any signs or symptoms of ACS, such as increased pain or decreased sensation, and seek medical attention if any of these occur.
What are the Long Term Effects of Acute Compartment Syndrome?
The long term effects of Acute Compartment Syndrome can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the amount of time it took to receive treatment. In some cases, the damage from ACS can be permanent, leading to decreased sensation or motor function, or even muscle and nerve damage. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if any signs or symptoms of ACS occur in order to minimize the long term effects.
Compartment Syndrome: Nursing Process
In conclusion, preventing acute compartment syndrome requires following a few simple steps. It is important to monitor the affected area regularly for swelling, pain, and discoloration. If these symptoms occur, medical attention should be sought immediately. It is also important to avoid activities that could cause additional swelling or trauma. By following these steps, you can help reduce the risk of developing acute compartment syndrome.