Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
positive and negative ions are formed through a process called ionization. This occurs when atoms gain or lose electrons, resulting in an imbalance of positive or negative charges. In this way, atoms can become charged ions and play important roles in various chemical reactions and electrical phenomena. In this article, we will explore how ionization occurs and why it is significant in understanding many basic scientific concepts.
Contents
The Basics of Ions
Before we delve into how positive and negative ions form, let’s first define what ions are. An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons, giving it a net positive or negative charge.
The Formation of Positive Ions
Positive ions, also known as cations, form when an atom loses one or more electrons. This leaves the atom with more protons than electrons, resulting in a net positive charge.
One common way that positive ions form is through the process of ionization, which occurs when an atom or molecule gains or loses an electron due to an external force. This can happen through exposure to radiation, heat, or chemical reactions.
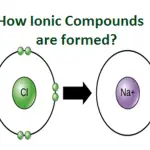
Another way that positive ions can form is through the dissociation of ionic compounds, such as salts. In these compounds, the positively charged ions (cations) are attracted to the negatively charged ions (anions), creating a stable structure. However, when the compound is dissolved in water, the attractions between the ions weaken, allowing the cations to separate and become free in solution.
The Formation of Negative Ions
Negative ions, also known as anions, form when an atom gains one or more electrons. This leaves the atom with more electrons than protons, resulting in a net negative charge.
One common way that negative ions form is through the process of electron affinity, which occurs when an atom or molecule gains an electron due to its attraction to another atom or molecule that has lost an electron.
Another way that negative ions can form is through the dissociation of covalent compounds, such as acids. In these compounds, the hydrogen ions (H+) are attracted to the negatively charged ions (anions), creating a stable structure. However, when the compound is dissolved in water, the attractions between the ions weaken, allowing the anions to separate and become free in solution.
A key takeaway from this text is that ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Positive ions form when atoms lose electrons, while negative ions form when atoms gain electrons. Ions play an important role in our environment and our bodies, with negative ions having potential health benefits such as improving mood and energy levels. Ion therapy, which involves exposure to high concentrations of negative ions, has become popular as a form of alternative medicine, although the scientific evidence supporting its benefits is mixed. It is important to be cautious of overexposure to negative ions and to consider the potential risks before undergoing ion therapy.