Last Updated on 1 year by Francis
Have you ever wondered how ions are formed? Ions are atoms or molecules that have either gained or lost an electron, therefore giving them an electric charge. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of ions and explore the different ways in which they are formed, as well as their various properties and uses. So, if you’re curious about the mysterious world of ions and want to learn more, keep reading!
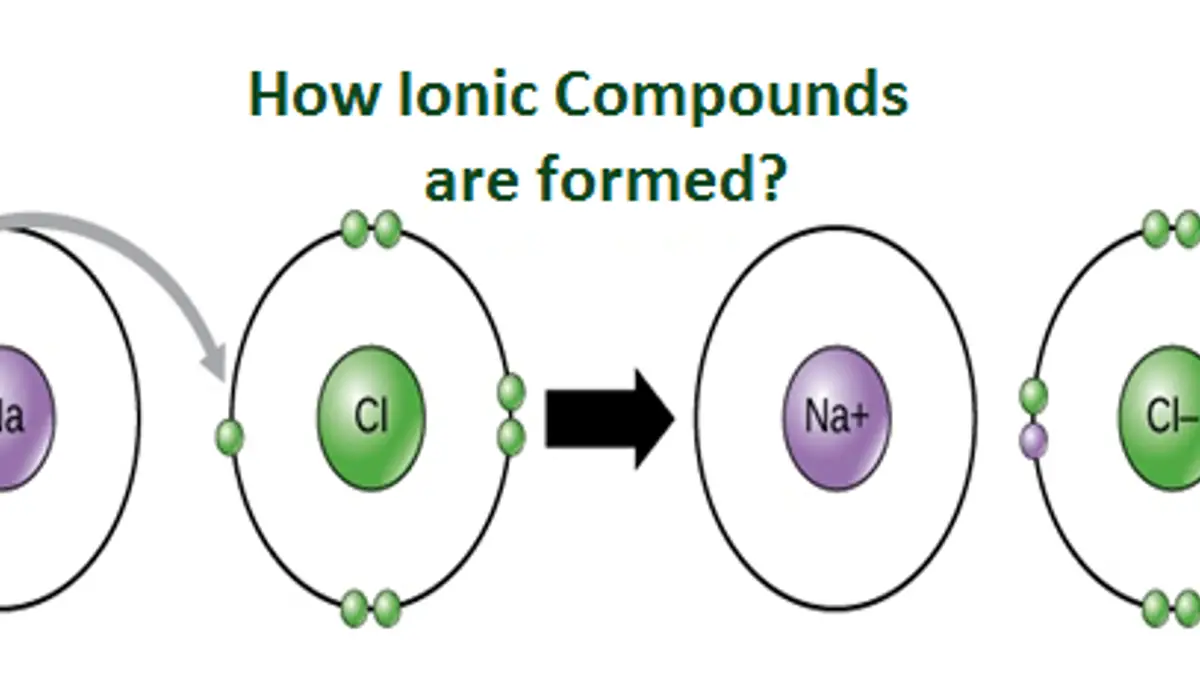
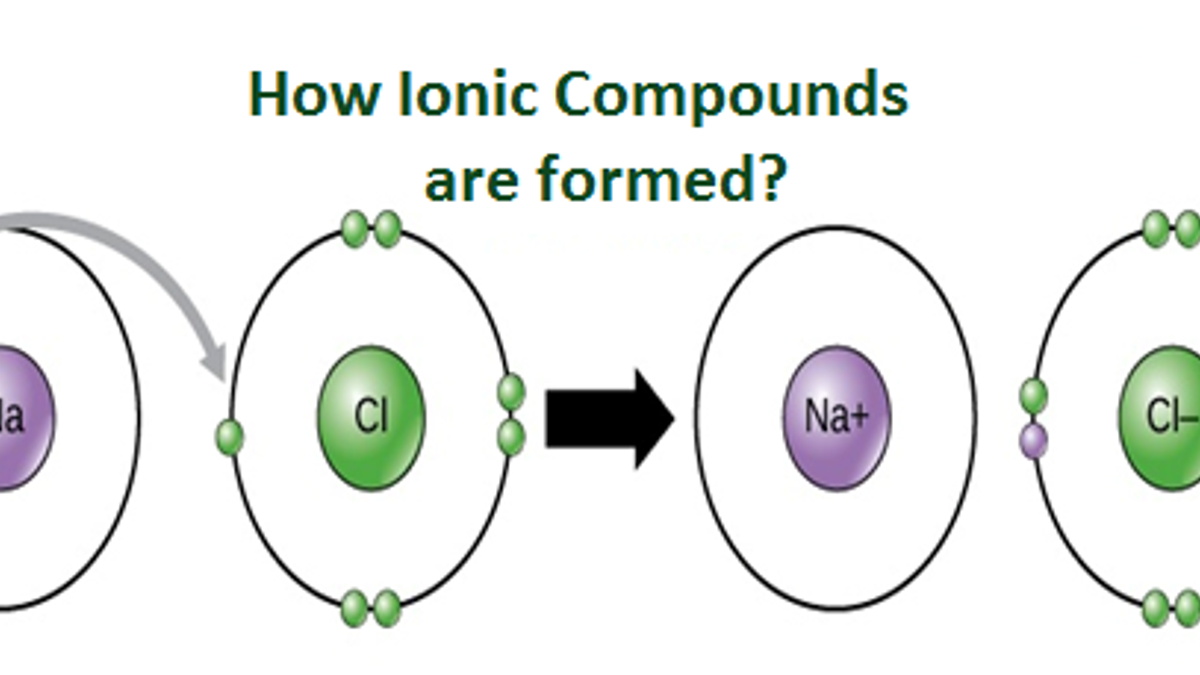
Ions are formed when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons. This process is known as ionization. Positively charged ions are formed when electrons are lost, and negatively charged ions are formed when electrons are gained. Ions can be formed from a variety of sources, including radiation, chemical reactions, and electric currents.
Contents
How Ions are Formed?
Ions are atoms or molecules with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. The process of forming an ion is known as ionization. Ions can be formed through a variety of ways. In this article, we will discuss the different processes in which ions are created.
Ionization by Gaining Electrons
Atoms or molecules can gain electrons to form anions, which have a net negative charge. This process occurs when an atom or molecule comes into contact with a negatively charged particle. This can happen naturally through a process called electron capture. Electron capture occurs when a negatively charged electron is attracted to a positively charged nucleus. The nucleus then absorbs the electron and undergoes ionization.
Another way in which anions can form is through a process known as electron affinity. Electron affinity occurs when a positively charged atom or molecule gains an electron from a nearby source. This forms a negatively charged anion.
Ionization by Losing Electrons
Atoms or molecules can also lose electrons to form cations, which have a net positive charge. This process occurs when an atom or molecule comes into contact with a positively charged particle. This can happen naturally through a process called photoionization. Photoionization occurs when a photon, or light particle, is absorbed by an atom or molecule and causes it to lose an electron.
Another way in which cations can form is through a process known as electron detachment. Electron detachment occurs when a negatively charged atom or molecule loses an electron to a nearby source. This forms a positively charged cation.
Ionization by Neutralization
Ionization can also occur through a process known as neutralization. Neutralization occurs when a positively charged particle comes into contact with a negatively charged particle. This causes the two particles to cancel each other out, thus forming a neutralized ion. This process is often seen in chemical reactions, such as the reaction between an acid and a base.
Ionization by Radiation
Ionization can also occur through a process known as radiation. Radiation occurs when an atom or molecule is exposed to high-energy particles, such as gamma rays or X-rays. These particles have enough energy to knock electrons from the atom or molecule, thus forming an ion.
Ionization by Heat
Ionization can also occur through a process known as thermal ionization. Thermal ionization occurs when an atom or molecule is exposed to high temperatures. The heat energy causes the electrons to move faster, thus increasing their chances of escaping the atom or molecule and forming an ion.
Ionization by Electrolysis
Ionization can also occur through a process known as electrolysis. Electrolysis occurs when an atom or molecule is placed in an electrolyte solution. An electric current is then passed through the solution, causing the molecules to break apart and form ions.
Ionization by Chemical Reactions
Ionization can also occur through a process known as chemical reactions. Chemical reactions occur when two or more molecules interact and form a new molecule. During this process, some of the atoms or molecules may lose or gain electrons, thus forming ions.
Ionization by Catalysis
Ionization can also occur through a process known as catalysis. Catalysis occurs when a catalyst molecule helps to speed up a chemical reaction. During this process, some of the atoms or molecules may lose or gain electrons, thus forming ions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What are Ions?
Answer: Ions are atoms or molecules that have an electrical charge due to having an unequal number of protons and electrons. Ions can be either positively charged (having more protons than electrons) or negatively charged (having more electrons than protons).
Question 2: How are Ions Formed?
Answer: Ions are usually formed when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons. This can happen when an atom or molecule comes into contact with another atom or molecule and the electrostatic attraction causes an electron to be transferred from one atom to the other. This process is called ionization and results in the formation of ions.
Question 3: What is an Example of an Ion?
Answer: A common example of an ion is sodium chloride (NaCl). In this compound, the sodium atom has one more proton than it has electrons, giving it a positive charge, while the chlorine atom has one more electron than it has protons, giving it a negative charge. The two ions are attracted to each other due to their opposite charges, forming an ionic bond.
Question 4: What is the Difference Between Ions and Electrons?
Answer: The primary difference between ions and electrons is that ions have an electrical charge due to having an unequal number of protons and electrons, while electrons do not have an electrical charge. Additionally, ions are usually formed when atoms or molecules transfer electrons to each other, while electrons are usually formed when atoms or molecules lose or gain energy.
Question 5: What is the Significance of Ions?
Answer: Ions are important for a variety of different processes, including chemical reactions, electrical conductivity, and even life. In chemical reactions, ions can help stabilize molecules and allow them to interact with each other. In electrical conductivity, ions are used to transmit electrical signals. Finally, ions are essential for life as they are used in the production of proteins, hormones, and other molecules necessary for life.
Question 6: What is the Difference Between Cations and Anions?
Answer: Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. Cations are formed when atoms or molecules lose electrons, while anions are formed when atoms or molecules gain electrons. Additionally, cations are attracted to anions due to their opposite charges, while cations are repelled by other cations and anions are repelled by other anions.
What Are Ions | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Ions are a fascinating and essential part of the natural world. By understanding how they are formed, we can better appreciate the chemical and physical properties that make them so important. From understanding the nature of ionic bonds to how certain elements can become ionized, we now have a better understanding of how ions are formed. We can use this knowledge to help us better understand the wide range of materials and processes that rely on ions.